- GA4 replaces Universal Analytics with an event-based tracking model for better cross-platform insights.
- Setup includes creating a property, adding data streams, and installing tags via gtag.js or GTM.
- All interactions are tracked as events—custom, recommended, or automatically collected—making data more flexible.
- GA4 integrates with tools like Google Ads, Search Console, and BigQuery for deeper marketing and performance analysis.
- Features like engagement rate, predictive metrics, and funnel explorations help optimize SEO, ecommerce, and user experience.
Google Analytics 4, commonly known as GA4, is the latest generation of Google’s web and app analytics platform.
Launched to eventually replace Universal Analytics (UA), GA4 is designed to provide a more holistic view of user behavior across websites and mobile applications.
Unlike its predecessor, GA4 uses an event-based data model, enabling businesses to track every interaction as a standalone event rather than grouping them into sessions.
This shift provides greater flexibility and a more detailed understanding of user journeys.
GA4 marks a significant evolution in how digital analytics works. It incorporates machine learning to fill data gaps caused by stricter privacy regulations and the diminishing use of third-party cookies.
With its built-in predictive capabilities, GA4 not only reports on past activity but also forecasts future actions, such as the likelihood of a user making a purchase or churning.
The transition from Universal Analytics to GA4 became essential as of July 1, 2023, when UA stopped processing new data.
As a result, businesses and marketers have had to adopt GA4 to continue measuring website and app performance accurately.
This guide walks through everything you need to understand and effectively use GA4, whether you’re setting it up for the first time, looking to improve your analytics strategy, or wanting to uncover deeper insights into user behavior.
Google Analytics 4 is not just a new version of an old tool—it’s a completely reimagined approach to digital analytics.
Understanding how it works and how to use it properly is now critical for data-driven decision-making.
Make Smarter Decisions With GA4
Nexa Growth helps you unlock powerful insights from Google Analytics 4 to fuel real growth.
Contact UsBenefits of GA4 Over Universal Analytics
The shift from Universal Analytics to Google Analytics 4 is more than a software update—it’s a fundamental change in how digital data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
Understanding the benefits of GA4 can help businesses make the most of their analytics setup and future-proof their measurement strategy.
-
Event-Based Data Model
GA4 uses an event-driven model, which tracks individual interactions like clicks, scrolls, downloads, or video plays as distinct events.
In contrast, Universal Analytics relied heavily on sessions and pageviews. This change allows for more granular tracking and a better understanding of how users engage with digital properties.
-
Cross-Platform Tracking
GA4 enables seamless tracking across websites and mobile apps through a unified property.
This is especially important for businesses with multi-platform user journeys, such as users who browse on mobile but convert on desktop.
By consolidating data streams, GA4 provides a single view of the customer journey.
-
Predictive Metrics Powered by Machine Learning
GA4 includes predictive capabilities, such as purchase probability, churn probability, and revenue prediction.
These metrics allow marketers to identify valuable audience segments and act on them before users convert or disengage. This can help improve targeting, personalization, and ROI.
-
Enhanced Privacy and Compliance
With privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA becoming stricter, GA4 is designed with privacy at its core.
It minimizes the need for cookies, allows users to delete data more easily, and supports consent mode. This ensures compliance while still providing valuable insights.
-
Deeper Customer Insights
GA4’s enhanced reporting tools and customizable dashboards allow businesses to explore data more flexibly.
Features like user lifetime reports, engagement rate, and funnel exploration offer a clearer view of how users interact with content over time.
By embracing these advantages, GA4 gives businesses a more modern, flexible, and privacy-conscious approach to analytics—one that aligns better with the evolving digital landscape.
Your Data Has Evolved—Has Your Strategy?
We help you harness GA4 to understand user behavior and improve performance across the board.
Contact UsSetting Up Google Analytics 4: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
Whether you’re transitioning from Universal Analytics or starting fresh, setting up Google Analytics 4 properly is critical to capturing accurate data.
The process is straightforward, but attention to detail is important to ensure data flows correctly and aligns with your business goals.
Step 1: Create a Google Analytics Account
If you don’t already have a Google Analytics account, visit analytics.google.com and sign up using your Google credentials.
Once logged in, click on “Start Measuring” to begin the setup process. You’ll be prompted to enter your account name and select data-sharing preferences.
Step 2: Create a GA4 Property
Next, you’ll need to create a property. Enter a name for your GA4 property, choose your reporting time zone, and select your currency.
This information helps structure your analytics environment and ensures reports reflect your local business context.
Step 3: Add a Data Stream (Web or App)
Google Analytics 4 allows you to collect data from multiple sources through data streams.
You’ll need to create a stream for each platform (Web, iOS, or Android). For a website, click on “Web,” enter your website URL, and give your stream a name.
By default, GA4 enables Enhanced Measurement for web streams, which automatically tracks basic interactions like scrolls, file downloads, outbound clicks, and site search queries. You can toggle these settings based on your needs.
Step 4: Install the GA4 Tag on Your Website
After creating your data stream, you’ll receive a Measurement ID (looks like G-XXXXXXXXXX). This ID is required to activate tracking. You can install it in one of two ways:
- Using the global site tag (gtag.js): Copy and paste the provided code into the <head> section of your website’s HTML.
- Using Google Tag Manager (GTM): Create a new GA4 Configuration tag and enter your Measurement ID. Set the tag to fire on all pages.
For most websites, GTM offers greater flexibility and is easier to maintain over time.
Step 5: Verify Tracking Installation
After installation, visit your website and check the Real-Time report in GA4 to confirm data is being received.
Alternatively, use Google’s Tag Assistant Chrome extension or the DebugView feature in GA4 to test and troubleshoot the setup.
Correct setup ensures that you capture data accurately from the beginning, laying the groundwork for effective analysis and reporting.
Once your property is live and tracking, you can begin configuring events, conversions, and integrations to suit your goals.
Featured Article: How to Optimize Your Google Business Profile – A Complete Guide
Core GA4 Features and Interface Walkthrough
Google Analytics 4 introduces a redesigned interface and new reporting structure, which may look unfamiliar to users coming from Universal Analytics.
However, the layout is designed to provide faster access to key insights and make exploration more intuitive. Understanding the GA4 interface is essential for navigating your data effectively.
-
Navigation and Home Dashboard
The left-hand navigation menu is where you’ll find all primary reporting sections.
The Home dashboard provides a snapshot of user activity, real-time data, and personalized insights powered by machine learning.
It’s ideal for quickly checking top-performing content, traffic sources, and audience behavior.
-
Reports Section
This section includes predefined reports grouped under categories such as Life Cycle and User.
These are automatically generated based on your data and are the primary way to monitor performance over time.
-
Real-Time Report
The Real-Time section shows data from users who are currently active on your site or app.
It allows you to monitor live behavior, check campaign performance immediately after launch, and verify that your tracking setup is working.
-
Life Cycle Reports
Life Cycle reports are divided into four key stages:
- Acquisition: View where users are coming from (channels, campaigns, or referral sources).
- Engagement: Track how users interact with your site, including events, conversions, and content viewed.
- Monetization: For ecommerce or app-based businesses, this section displays revenue data, in-app purchases, and average purchase value.
- Retention: Understand how well you’re keeping users over time, including frequency of return visits.
-
User Reports
These provide insight into your audience demographics and technology, such as devices, locations, languages, operating systems, and interests.
This data helps refine marketing strategies and personalize user experiences.
-
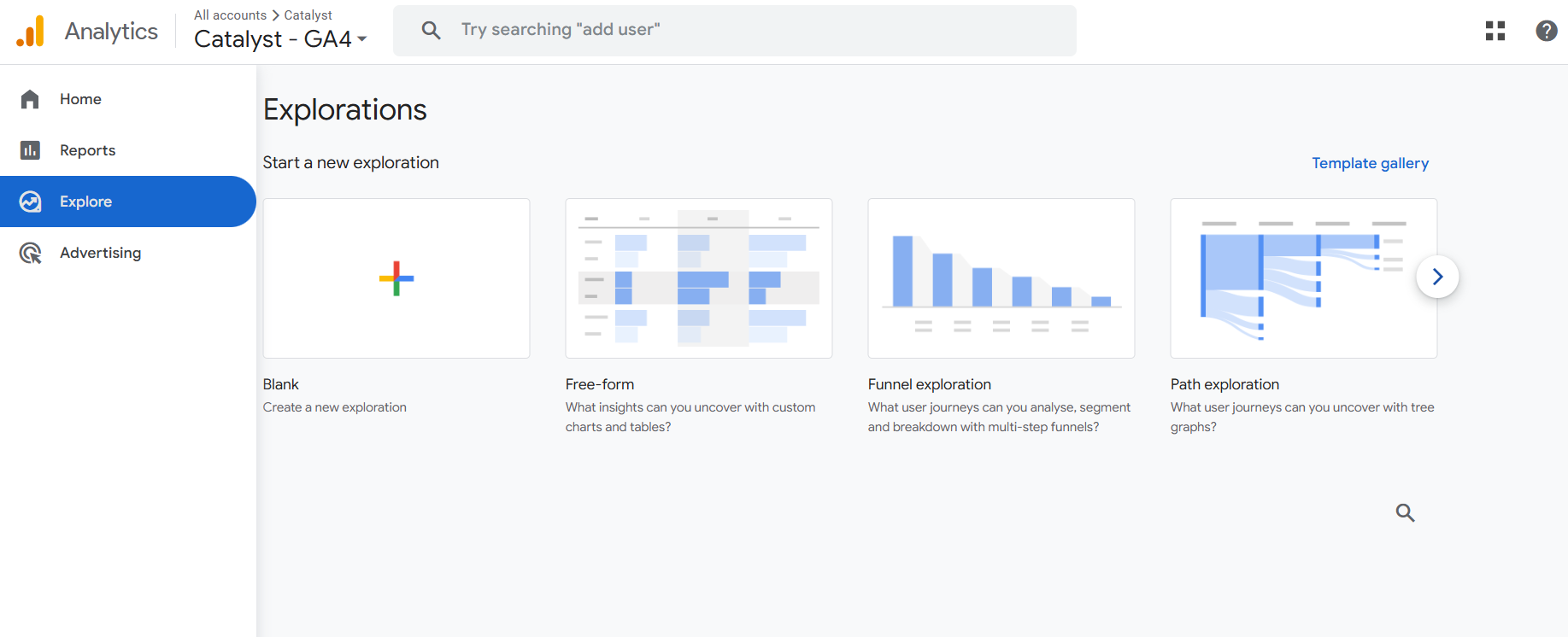
Explore (Advanced Analysis)
Explore offers custom reporting tools and templates like Funnel Exploration, Path Analysis, and Segment Overlap.
These features are useful for deeper analysis beyond standard reports and are especially valuable for analysts and marketers needing tailored insights.
Advertising Workspace
This area allows you to evaluate performance across different advertising platforms. You can link your GA4 property to Google Ads and other platforms to view cross-channel attribution, conversion paths, and ROI in one place.
By familiarizing yourself with these key areas, you’ll be able to access, understand, and act on your analytics data more efficiently. GA4’s interface is built to accommodate both high-level overviews and detailed, exploratory analysis—all within a single platform.
Turn GA4 into Your Competitive Advantage
We configure and customize GA4 to reveal what drives traffic, conversions, and revenue.
Contact UsEvents in GA4: What They Are and How to Use Them
Events are the foundation of data collection in Google Analytics 4.
Unlike Universal Analytics, which categorized user interactions under different hit types like pageviews, events, and transactions, GA4 treats all user interactions as events.
This simplifies tracking and offers more flexibility in how data is collected and reported.
-
Automatically Collected Events
GA4 automatically tracks a set of basic events without any additional configuration. These include events such as:
- first_visit: When a user visits your site or app for the first time
- session_start: When a new session begins
- user_engagement: When a user stays on a page for more than 10 seconds or triggers an event
These provide a baseline of user activity and are essential for understanding traffic volume and engagement.
-
Enhanced Measurement Events
Enhanced Measurement is a feature in GA4 that, when enabled, automatically tracks additional on-site interactions such as:
- Pageviews
- Scrolls
- Outbound clicks
- Site search
- Video engagement
- File downloads
These events can be toggled on or off in your data stream settings and help you understand how users are interacting with your content without the need for custom code or tag manager setup.
-
Recommended Events
Google provides a list of recommended events you can implement based on your industry or business model.
These are not automatically tracked but are recognized by GA4 for enhanced reporting. Examples include:
- login, sign_up, purchase, add_to_cart, view_item, and generate_lead
Implementing recommended events allows GA4 to organize and display data more effectively in reports.
-
Custom Events Setup
For interactions that are unique to your website or business, you can create custom events.
These can be set up using Google Tag Manager or directly through gtag.js. Custom events include a name and optional parameters to define the specific action, category, or context.
For example, you could track a button click that leads to a downloadable guide by creating an event called download_guide with a parameter like file_name: ‘analytics_guide.pdf’.
-
Conversion Events
In GA4, goals have been replaced by conversion events. Any event can be marked as a conversion with a single toggle in the admin panel.
This simplifies the process of tracking meaningful actions, such as form submissions, purchases, or lead captures.
Understanding and leveraging the different types of events in GA4 allows you to create a detailed picture of user behavior and measure the actions that align with your business objectives.
Featured Article: JavaScript SEO: How Google Crawls, Renders, and Indexes Your Site
GA4 Goals and Conversions: How to Track What Matters
Tracking conversions is one of the most critical functions of any analytics setup.
In Google Analytics 4, conversions are handled differently than in Universal Analytics. Instead of defining “goals” with set conditions, GA4 allows you to designate any event as a conversion, offering more flexibility and precision.
How to Define a Conversion
To define a conversion in GA4, you must first ensure the action you want to track—such as a form submission, button click, or transaction—is being recorded as an event.
Once that event is being tracked, you can mark it as a conversion by navigating to:
Admin > Events > Mark as Conversion
There’s no need to create separate goals with destination URLs or duration-based criteria. GA4’s event-based model allows you to track exactly what users do, with no assumptions or approximations.
Setting Up Goals via Events
If an action isn’t tracked automatically or through Enhanced Measurement, you can create a custom event using Google Tag Manager or directly within GA4.
For example, if you want to track clicks on a specific contact button, you can configure a custom event with a name like contact_click and set it as a conversion.
This approach is especially useful for micro-conversions, such as newsletter signups, video plays, or PDF downloads, which can help measure engagement earlier in the funnel.
Analyzing Conversion Funnels
Once you’ve defined your conversion events, GA4 enables you to visualize how users move through key steps using the Funnel Exploration tool in the Explore section.
You can create custom funnels based on any combination of events to see where users drop off and how efficiently they move toward conversion.
This helps answer questions such as:
- Where are users abandoning the checkout process?
- How many users watch a video before signing up?
- What percentage of visitors who view a product page end up purchasing?
Using events for conversions provides a more adaptable framework for tracking user actions and business outcomes.
It allows for clearer attribution and more actionable insights, especially when combined with audience segments and predictive metrics.
Featured Article: How to Fix Duplicate Content Issues: Canonical Tags and Strategies
Reporting in GA4: How to Extract Meaningful Insights
Google Analytics 4 offers a redesigned reporting experience that emphasizes user journeys and customizable analysis.
While the default reports cover many common use cases, the platform’s strength lies in its flexibility—allowing users to build tailored reports based on specific business questions.
-
Built-in Reports Overview
GA4 includes several standard reports accessible under the “Reports” tab. These are organized into collections like Life Cycle and User:
- Life Cycle includes acquisition, engagement, monetization, and retention.
- User reports focus on demographics, devices, locations, and other user-specific attributes.
These reports offer quick access to key metrics like sessions, users, engagement rate, conversions, and revenue.
-
Custom Report Creation
For more control over what you see, GA4 allows you to create custom reports through the Library section. Here, you can build and publish collections tailored to your needs.
For example, you might create a report that highlights conversion rates by traffic source or engagement metrics by page title.
Custom dimensions and metrics can also be added to enhance your reports, letting you segment data in ways that aren’t possible in the default views.
-
Funnel Exploration Reports
The Funnel Exploration tool, found in the Explore section, lets you visualize multi-step user journeys.
You can define the steps of a funnel—like product view, add to cart, checkout, and purchase—and measure how users move through each stage.
This is especially useful for identifying where drop-offs occur and optimizing conversion paths.
-
Pathing and Segment Overlap
GA4’s Path Exploration helps you understand what users do before or after a specific event, such as a conversion or page visit. It visually maps user behavior, uncovering common navigation patterns.
Segment Overlap is another valuable tool for comparing user groups. For instance, you can see how much overlap exists between users who watch a video, download a guide, and convert—all within a single chart.
These advanced exploration tools turn GA4 into a powerful platform for uncovering trends, diagnosing issues, and identifying opportunities.
By leveraging both standard and custom reports, you can translate raw data into actionable insights that align with your business goals.
Data-Driven Growth Starts Here
Nexa Growth handles your migration, event setup, and reporting with ease.
Contact UsGA4 and SEO: 5 Tactical Use Cases
Google Analytics 4 can be a valuable resource for improving your SEO strategy.
While GA4 doesn’t provide keyword-level data by default, it offers detailed insights into user behavior, landing page performance, and engagement—critical metrics for measuring the effectiveness of your organic search efforts.
-
Analyze User Engagement by Landing Page
In GA4, you can use the “Pages and Screens” report to see how users interact with your landing pages.
By focusing on metrics like engagement rate, average engagement time, and conversions, you can assess which pages are performing well in search and which need optimization.
This data helps you prioritize SEO updates for high-traffic but low-performing pages.
-
Track SEO Campaign Performance
By connecting Google Analytics 4 with Google Search Console, you can view organic traffic data alongside user behavior.
This allows you to see which queries are driving traffic, how those users engage with your site, and whether they convert.
This integrated view helps bridge the gap between keyword visibility and on-site performance.
-
Keyword Performance With Search Console Integration
Although GA4 doesn’t show keyword-level data natively, linking it with Search Console brings in organic keyword insights.
These appear in the “Acquisition” section and can be combined with GA4’s behavioral metrics for a more complete picture.
For example, you can analyze how traffic from a specific keyword performs in terms of bounce rate, scroll depth, or conversions.
-
Engagement Rate vs. Bounce Rate
GA4 replaces bounce rate with engagement rate, a more insightful metric that tells you how many users stayed for at least 10 seconds, viewed two or more pages, or triggered an event.
This makes it easier to identify which pages truly hold user attention—something bounce rate couldn’t accurately convey.
Tracking engagement rate for organic landing pages provides a clearer signal of SEO success.
-
Custom SEO Dashboards
Using the Explore tool or Looker Studio integration, you can create SEO-focused dashboards that track metrics like:
- Organic traffic by landing page
- New vs. returning users from organic search
- Conversion rate by keyword or query
- Scroll depth and event engagement on content pages
Custom dashboards simplify reporting and make it easier to share insights with SEO teams, content creators, and stakeholders.
When used strategically, GA4 becomes more than a data tool—it supports smarter SEO decision-making by showing how users from search behave once they land on your site.
Featured Article: What is Google E-E-A-T and How to Optimize for it?
GA4 Integration With Other Google Tools
One of the strengths of Google Analytics 4 is its ability to integrate seamlessly with other Google products.
These integrations enhance data visibility, streamline workflows, and allow for more effective marketing and performance analysis across platforms.
-
Google Search Console
Connecting GA4 to Google Search Console allows you to view organic search data—such as impressions, clicks, average position, and CTR—alongside user behavior metrics like engagement, conversions, and page performance.
This gives you a complete picture of how search visibility translates into on-site actions.
You can set up this integration in the GA4 Admin panel by linking the relevant Search Console property. The data appears in the Acquisition section and can be used in custom explorations and dashboards.
-
Google Ads
Linking GA4 with Google Ads lets you analyze how paid traffic interacts with your website or app.
You can import GA4 conversions into your Google Ads account, enabling smarter bidding strategies based on real user actions rather than simple clicks.
This integration also provides a clearer view of campaign effectiveness by combining ad spend data with user engagement and conversion performance.
-
Looker Studio (Formerly Google Data Studio)
Looker Studio allows you to build fully customized dashboards and reports using GA4 data. You can blend multiple data sources—such as GA4, Search Console, and Google Ads—into a single report.
This is especially useful for agencies, marketing teams, and business owners who need clear, shareable insights tailored to specific KPIs or clients.
-
Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager simplifies the deployment and management of GA4 tracking.
It enables you to set up events, configure triggers, and manage multiple tags from a single interface—without touching the website’s codebase.
You can use GTM to implement both GA4 Configuration and Event tags, helping you track custom interactions like video plays, button clicks, and form submissions.
-
Google Optimize
Although Google Optimize was sunset in 2023, users can still leverage past integrations to analyze the impact of A/B tests within GA4. For those using alternative experimentation tools, GA4 continues to support custom event tracking for testing and personalization efforts.
These integrations not only expand GA4’s capabilities but also unify your marketing ecosystem—making it easier to track, optimize, and report across all digital touchpoints.
GA4 for Ecommerce: Tracking and Optimization
Google Analytics 4 provides robust features for ecommerce businesses to monitor product performance, customer behavior, and revenue trends.
With proper setup, GA4 can deliver actionable insights into every stage of the online buying journey—from product views to purchases.
-
Set Up GA4 for Shopify or WooCommerce
To enable ecommerce tracking in GA4, you’ll need to implement enhanced ecommerce events through your platform or tag manager.
For Shopify, this typically requires editing the checkout.liquid file or using an app that sends ecommerce data to GA4. WooCommerce users can use plugins or custom GTM setups to pass ecommerce events.
The essential ecommerce events to implement include:
- view_item
- add_to_cart
- begin_checkout
- purchase
These events allow GA4 to build a complete funnel of user interactions.
-
Enhanced Ecommerce Events
GA4 uses event parameters to track ecommerce activity in detail. For example, the purchase event includes data such as transaction ID, value, items purchased, quantity, and coupon codes.
This granular data enables you to analyze revenue trends, product performance, and user flow through the checkout process.
Unlike Universal Analytics, GA4 doesn’t require separate Enhanced Ecommerce settings—once the events are implemented, the reports automatically populate.
-
Monetization Reports
Under the Life Cycle section, GA4 offers dedicated Monetization reports. These include:
- Overview: A snapshot of total revenue, purchases, and average order value
- Ecommerce Purchases: Performance of individual products or categories
- In-app Purchases: Revenue generated from apps (if applicable)
You can segment these reports by traffic source, device type, user location, or other dimensions to see what’s driving revenue.
GA4’s ecommerce capabilities provide a deeper understanding of user purchasing behavior and help identify opportunities for optimization—such as improving checkout flow, refining product pages, or personalizing offers for high-value segments.
GA4 for Mobile Apps
Google Analytics 4 was built with cross-platform tracking in mind, making it a powerful solution for mobile app analytics.
By integrating GA4 with Firebase, Google’s app development and analytics platform, you can track user behavior, engagement, and revenue across iOS and Android applications.
Firebase Integration
To use GA4 with mobile apps, you’ll need to integrate Firebase SDK into your app. Firebase acts as the data source for mobile app streams in GA4.
Once connected, events from the app are automatically sent to GA4 in real time.
This integration enables tracking of core app metrics such as:
- App installs
- Screen views
- In-app purchases
- User engagement
- Crashes and errors (via Firebase Crashlytics)
With Firebase and GA4 working together, businesses get a unified view of how users interact with their app and website.
App Event Tracking
Firebase automatically collects key events like first_open, in_app_purchase, and screen_view. You can also define custom events relevant to your app experience, such as:
- level_complete for games
- share_content for social features
- submit_form for lead generation
Each event can include parameters like screen name, item ID, or user role to provide deeper context.
GA4 also supports predictive metrics in mobile apps, such as purchase probability and churn likelihood, which help you segment and retarget users more effectively.
Using GA4 with mobile apps offers a streamlined way to monitor performance, optimize user experience, and support marketing efforts across platforms—all from a single analytics property.
Featured Article: Mobile-First Indexing: How to Optimize Your Site in 2026
GA4 Best Practices and Common Mistakes to Avoid
Optimizing your GA4 setup is essential for collecting accurate data and deriving actionable insights.
While GA4 offers advanced features and flexibility, there are several best practices you should follow and common mistakes to avoid.
-
Use Consistent Naming Conventions
Establish a standardized naming convention for events, parameters, and custom dimensions.
Consistency ensures that your data remains organized and facilitates easier reporting and analysis across different teams.
-
Test Your Setup Regularly
Employ DebugView and Google’s Tag Assistant to test your tagging and tracking setup frequently.
Regular testing helps detect configuration errors early, preventing long-term data discrepancies and ensuring that all events are recorded accurately.
-
Avoid Duplicated Conversions
Be cautious when marking events as conversions. Duplicated conversion events can inflate conversion counts and skew performance metrics.
Review your event settings periodically to ensure that only the intended actions are marked as conversions.
-
Leverage Custom Dimensions and Metrics
Custom dimensions and metrics add depth to your analysis by capturing unique business data that standard GA4 metrics might miss.
Plan which additional dimensions provide the most value and integrate them carefully into your reporting framework.
-
Utilize Data Filters and Segments
Make use of GA4’s filtering and segmentation tools to isolate specific user behaviors or campaigns.
Proper segmentation enables you to understand different user groups and tailor strategies to improve overall engagement and conversion rates.
-
Document Your Implementation
Keep thorough documentation of your GA4 configuration, including event names, custom definitions, integration setups, and tag management processes.
Documentation serves as a crucial reference for team members and simplifies troubleshooting when issues arise.
-
Stay Updated With Google’s Guidelines
GA4 is continually evolving. Regularly review Google’s documentation and update your setup to leverage new features and improvements.
Staying current ensures that you are making the most out of the platform’s capabilities while maintaining data accuracy.
Troubleshooting GA4: Is It Working Correctly?
Once GA4 is installed, it’s essential to verify that it’s collecting accurate data. Tracking errors, missing events, or duplicated conversions can result in misleading reports and poor decision-making.
A solid troubleshooting routine ensures your setup is working as intended.
Real-Time Data Check
The quickest way to confirm GA4 is receiving data is to use the Real-Time report. Visit your website or app and trigger key interactions—such as page views, clicks, or form submissions—and see if those events appear in the report within seconds.
If no data appears, double-check your tag implementation, data stream configuration, and filters that might be excluding traffic.
Tag Assistant and DebugView
Google Tag Assistant, a browser extension, can help you validate whether your GA4 tags are firing correctly. It will highlight issues with tag installation, such as missing IDs or improperly placed code.
Additionally, DebugView in GA4 offers a real-time stream of events from your browser.
By enabling debug mode (via Tag Manager or a URL parameter), you can observe all events, parameters, and user properties as they are triggered.
This tool is especially useful during initial setup or when configuring new events.
Fixing Common Setup Errors
Here are some of the most common GA4 issues and how to resolve them:
- Incorrect Measurement ID: Verify that the Measurement ID in your tag matches the one in your GA4 property.
- Event name typos: Custom events are case-sensitive and must match exactly. Check for misspellings or naming inconsistencies.
- Missing data in reports: Ensure the correct data stream is selected and that no filters are removing your traffic.
- Duplicate tags: Using both gtag.js and GTM on the same site can result in redundant events. Choose one method for implementation and stick with it.
By using these diagnostic tools and following a checklist, you can confidently confirm your GA4 property is functioning properly. Troubleshooting early and often protects your data integrity and ensures that your analytics foundation remains solid.
Advanced GA4 Tips for Analysts
For those with more experience in analytics or more complex business needs, Google Analytics 4 offers a range of advanced features that go beyond basic reporting.
These tools enable deeper analysis, more accurate tracking, and more effective targeting.
-
Custom Dimensions and Metrics
GA4 allows you to define your own dimensions and metrics to collect information that isn’t included by default. For example, you can capture user roles, content types, campaign stages, or form field selections.
Once configured in the Admin panel and properly implemented via your event tags, these custom definitions can be used in reports, explorations, and audience segmentation to support more specific analysis.
-
Attribution Modeling
GA4 includes built-in attribution models that help you understand which channels contribute most to conversions. You can compare models such as:
- Cross-channel data-driven
- First click
- Last click
- Linear
- Position-based
These models are found in the Advertising section and are crucial for assessing the true impact of your marketing efforts across multiple touchpoints.
-
Predictive Audiences and Metrics
GA4 offers predictive capabilities powered by machine learning. Predictive metrics like purchase probability, churn probability, and predicted revenue can be used to build predictive audiences.
For instance, you can create an audience of users with a high likelihood of purchasing and then export it to Google Ads for targeted remarketing.
These features require a minimum level of data (usually several thousand events and conversions) but can significantly improve campaign precision and performance once enabled.
-
Using BigQuery for Raw Data Analysis
One of the most powerful features in GA4 is the native BigQuery export. With just a few clicks, you can stream your GA4 data into BigQuery, allowing for advanced SQL-based analysis and data blending with other sources.
This is ideal for organizations that require:
- Custom attribution analysis
- Retention cohort breakdowns
- Cross-platform data blending
- Long-term data storage beyond the GA4 retention window
By combining these advanced features, analysts can unlock a much deeper understanding of user behavior and campaign performance. These tools also provide the flexibility needed for more complex data environments and enterprise-level reporting requirements.
Featured Article: What Is Schema Markup & How to Implement It in 2026
Glossary of GA4 Terms (Quick Reference)
Google Analytics 4 introduces several new concepts and redefines familiar ones.
This glossary helps clarify key terms you’ll encounter while working with GA4, whether you’re new to the platform or transitioning from Universal Analytics.
-
Event
Any user interaction on your site or app—such as a page view, button click, form submission, or video play. Unlike Universal Analytics, all interactions are tracked as events.
-
Parameter
Additional information attached to an event that provides context. For example, a download event might include parameters like file_name or file_type.
-
Session
A group of user interactions that take place within a given time frame. In GA4, sessions are triggered by a session_start event and measured differently than in Universal Analytics.
-
Engagement Rate
The percentage of sessions that lasted longer than 10 seconds, had at least one conversion event, or included two or more page views or screen views. This replaces the traditional bounce rate metric.
-
Conversion
Any event you designate as valuable to your business, such as a purchase or form submission. Conversions are set by marking specific events in the admin panel.
-
User
Represents a unique individual visiting your site or app. GA4 distinguishes between total users, active users, and new users, with a primary focus on active users.
-
DebugView
A real-time diagnostic tool in GA4 that allows you to view incoming events, parameters, and user properties for testing and troubleshooting.
-
Explore
A section in GA4 that offers customizable, advanced reports such as funnel analysis, path exploration, and segment comparisons.
-
Audience
A group of users defined by a set of conditions (e.g., visited a product page but didn’t purchase). Audiences can be used for analysis or exported to Google Ads for remarketing.
-
Data Stream
The source from which GA4 collects data—either a website or mobile app. Each GA4 property can have multiple data streams for cross-platform tracking.
Understanding these terms will help you navigate GA4 more effectively and communicate more clearly with teams, stakeholders, or clients. As the platform evolves, familiarity with its core language becomes essential for accurate reporting and strategic insights.
Featured Article: A-Z SEO Glossary: Key Terms Every Marketer Should Know
Final Thoughts: Why GA4 Is Essential in 2026
Google Analytics 4 represents a major shift in how digital analytics works, and adapting to it is no longer optional—it’s necessary. With Universal Analytics officially sunset, GA4 has become the standard for tracking and understanding user behavior across websites and mobile apps.
Its event-based model offers more flexibility than the session-based structure of its predecessor. From tracking every touchpoint of a user journey to integrating advanced tools like predictive audiences and machine learning insights, GA4 delivers the capabilities modern businesses need.
Whether you run an ecommerce store, publish content, or manage lead generation campaigns, GA4 gives you the ability to measure what matters most—across platforms, with greater privacy, and with tools that can scale as your business grows.
If you haven’t fully adopted GA4 yet, now is the time to implement it correctly, explore its features, and start using it as your primary source of truth for digital performance. The sooner you become fluent with the platform, the better positioned you’ll be to make data-informed decisions in an increasingly competitive and privacy-focused digital landscape.
GA4 Is Powerful—If You Know How to Use It
We make your analytics work harder for your SEO, ads, and content strategy.
Contact Us