- Product page SEO is the process of optimizing individual product listings to achieve higher search rankings and increase sales.
- According to a Semrush study, 38% of all e-commerce traffic comes from organic search, highlighting the importance of optimizing these pages.
- Key strategies include performing keyword research to find long-tail, intent-driven keywords.
- You must write unique and persuasive product descriptions, not generic manufacturer text.
- Structured data (schema markup) can provide search engines with detailed information, leading to rich results and better visibility.
When it comes to driving traffic and conversions on an ecommerce site, your product pages are the real workhorses.
They’re where decisions happen—where shoppers become buyers. But without solid SEO, even the best-designed product page can get buried in search results, never reaching the audience it’s meant for.
Product page SEO is the process of optimizing individual product listings so they can rank higher in search engines like Google.
And it’s more important now than ever. According to a 2024 study by Semrush, 38% of all ecommerce traffic still comes from organic search.
That means if your product pages aren’t optimized, you’re likely leaving a big chunk of revenue on the table.
But ranking in search results isn’t just about plugging in keywords. Google’s algorithm is more sophisticated now.
It’s looking at how helpful your content is, how fast your page loads, whether your layout is mobile-friendly, and how well your product information aligns with what users are actually searching for.
In this guide, we’ll walk through the key strategies to improve your product page SEO—from keyword research and on-page content, to structured data and user-generated content.
Whether you’re managing 10 products or 10,000, these best practices will help you improve visibility, attract more qualified traffic, and ultimately increase sales.
Let’s get started!
Turn Product Pages Into Sales Machines
We optimize every detail—from meta tags to mobile speed—so your product pages work harder and sell faster.
Contact Us-
Build a Solid Foundation With Keyword Research
Before you make any changes to your product pages, you need to understand what your customers are actually searching for.
Keyword research isn’t just a box to check—it’s the foundation for everything else that follows in your SEO strategy.
At the product page level, this means identifying the terms and phrases people use when they’re close to making a purchase.
These are often long-tail, intent-driven keywords like “best noise-canceling headphones under $200” or “organic cotton baby onesie 0-3 months.”
These types of queries show a clear buying intent and often face less competition than broader terms.
Understand Buyer Intent
Start by identifying the types of searches that happen in your niche. Are people looking for comparisons, product reviews, or detailed specs?
Tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, or Semrush can show you which keywords already bring users to your site—and what your competitors are ranking for that you’re not.
You can also look at autocomplete suggestions in Google or browse marketplaces like Amazon to see how products are titled and described.
These real-world search patterns offer clues about how your pages should be structured and optimized.
Use Keyword Tools Strategically
Keyword tools can surface thousands of ideas, but the trick is knowing how to filter them. Focus on:
- Search volume: Aim for keywords with a balance of decent volume and manageable competition.
- Keyword difficulty: Don’t chase head terms if your domain isn’t strong enough to compete. Go after lower-competition long-tails first.
- Click potential: Some keywords trigger SERP features (like featured snippets or Google Shopping) that may limit clicks to organic results. Prioritize terms with a clearer path to traffic.
Let’s say you sell wireless earbuds.
Instead of targeting the broad and competitive “wireless earbuds,” you might go after more specific phrases like “best wireless earbuds for small ears” or “Bluetooth earbuds with long battery life.”
These can bring in more qualified traffic and help your page stand out.
Don’t Skip Category-Level Research
Even though we’re focusing on product pages, your category pages influence internal linking and authority flow. Keywords used at the category level should complement, not compete with, your product pages.
This also helps create a more organized site architecture that search engines can crawl and understand more easily.
Scale It for Large Sites
If you manage a large ecommerce catalog, manual keyword research isn’t scalable. Consider scraping product data, titles, and queries from tools like Ahrefs’ Site Explorer or using a custom crawler to analyze what’s already ranking.
Map keywords to product types programmatically, and prioritize optimization efforts by traffic potential or revenue impact.
When you match the right product page with the right keyword, everything else—titles, descriptions, internal links—starts falling into place. It’s the most critical step, and it’s worth doing well.
Featured Article: How to Write Meta Descriptions: Tips and Examples 2026
-
Craft SEO-Optimized Product Titles and URLs
Once you’ve nailed your keyword research, the next step is applying those insights to your product titles and URLs.
These are two of the first elements search engines and users see, and they play a huge role in determining whether your page gets clicked—or skipped.
Product Titles That Work for SEO and Users
Your product title (often wrapped in an H1 tag) should do two things well: describe the product clearly and include the primary keyword naturally.
This isn’t the place to get overly creative or vague. Clarity matters more than cleverness.
For example, instead of “SoundBlaster X1000,” a more SEO-friendly product title might be “SoundBlaster X1000 Wireless Noise-Canceling Headphones.”
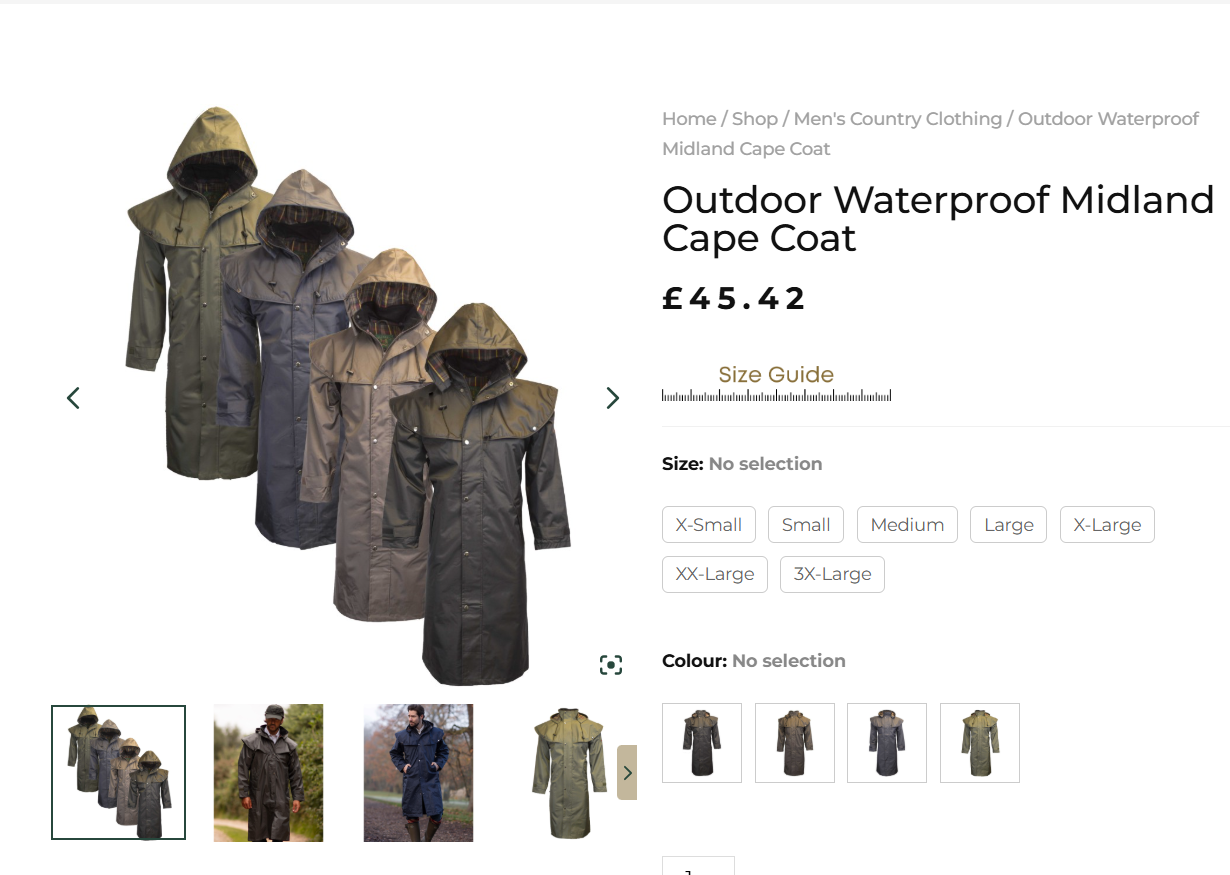
SEO-Optimized Product Title You’re still using the product name, but you’re also describing what it is and what people might be searching for.
Here’s what to keep in mind:
- Place important keywords toward the front of the title
- Avoid keyword stuffing—focus on natural readability
- Include attributes that matter to buyers (e.g., size, color, material, use case)
If your platform allows it, consider customizing H1 titles separately from page titles to better align with search intent and SERP appearance.
Page Titles (Title Tags) for Better Click-Through Rates
The page title (seen in search results) should be compelling enough to encourage clicks while still including your primary keyword. Aim for under 60 characters to avoid truncation in the SERPs.
A good structure to follow:
[Product Name] – [Key Feature or Benefit] | [Brand]
For instance:
“SoundBlaster X1000 Headphones – Wireless, 40-Hour Battery | TechZone”Adding a unique benefit or differentiator can increase your click-through rate, especially when you’re up against dozens of similar listings.
Clean, Keyword-Friendly URLs
URL structure might not feel like a big deal, but it affects both SEO and user trust. Short, descriptive URLs tend to perform better and are easier to share.
Avoid URLs with unnecessary parameters, session IDs, or vague terms. A clean structure looks like this:
/wireless-noise-canceling-headphones/soundblaster-x1000Best practices for product page URLs:
- Use hyphens, not underscores
- Keep it short but descriptive
- Include your primary keyword
- Avoid changing URLs after indexing unless absolutely necessary
If you do need to change a URL, always use a proper 301 redirect to preserve SEO equity.
Use Canonical Tags for Variants
If your product comes in multiple variants (like colors or sizes), be careful about duplicate content.
Either consolidate them into one main product page or use canonical tags to point search engines to the primary version.
This avoids splitting ranking signals across multiple nearly-identical pages.
Optimized titles and URLs help search engines understand what your page is about and help users feel confident they’ve found what they’re looking for.
Now that your page is easier to find and click, let’s focus on what keeps users engaged: the product description.
Featured Article: The Importance of Title Tags and How to Optimize Them
-
Write Unique, Persuasive Product Descriptions
Once a visitor lands on your product page, the description is one of the first elements they’ll engage with.
It’s your chance to answer questions, highlight key features, and persuade the shopper to buy—all while satisfying search engine requirements for quality, original content.
Unfortunately, this is where many ecommerce sites fall short. They rely on generic manufacturer descriptions that are often duplicated across dozens of other websites.
This not only hurts your SEO but also does little to convince shoppers that your store is the right place to buy.
Why Unique Content Matters
Google prioritizes helpful, original content. If your product description is the same as hundreds of other sites, it’s unlikely to rank well.
Worse, if the manufacturer description is thin or vague, your page might not rank at all.
Creating a unique product description doesn’t mean writing a novel for every product, but it should:
- Highlight what makes the product different or better
- Address common questions or concerns
- Incorporate keywords naturally
- Align with your brand’s voice and tone
According to a report by Salsify, 87% of online shoppers say detailed product content is extremely or very important when deciding to buy. That’s a huge opportunity to stand out.
Structure for Clarity and Conversion
People don’t read product descriptions word-for-word—they scan. Use formatting that supports skimming while delivering key information quickly:
- Start with a brief summary paragraph
- Use bullet points for features and specs
- Add headings or labels for sections like “Materials,” “Care Instructions,” or “Sizing.”
- If relevant, include a short use case or scenario
For example, instead of saying:
“This is a durable and stylish backpack.”
Try something more specific and benefit-driven:
“Built for daily commutes and weekend trips, this water-resistant backpack features padded straps, a 15-inch laptop sleeve, and a minimalist design that suits any outfit.”
The Role of Keywords in Descriptions
Your target keywords should appear naturally in the product description, especially in the opening sentence and near key features. However, avoid stuffing them in just for SEO—it can sound robotic and reduce trust.
If you’re optimizing for “leather travel wallet,” for instance, include variations like:
- “Slim leather wallet for travel”
- “passport holder with RFID protection”
- “Leather wallet for international travel”
This supports semantic SEO and increases the chances of ranking for multiple relevant queries.
Leveraging AI (With a Human Touch)
AI writing tools can help you generate product descriptions at scale, especially for large catalogs. But they shouldn’t replace human oversight.
Use them to draft a base, then refine for tone, clarity, and accuracy. AI can help ensure consistency, but human editors make the content compelling.
Bonus: Add Personality When Appropriate
Depending on your brand, you may be able to add humor, lifestyle references, or subtle storytelling. A skincare brand might describe how a serum feels or smells.
An outdoor gear company might tie a product to a trail or trip experience. These little touches make your descriptions more memorable—and more trustworthy.
A well-written, keyword-optimized product description not only improves your rankings—it can be the final nudge a shopper needs to hit “add to cart.”
Next, let’s look at how structured data can help boost visibility even further by enhancing how your product appears in search results.
-
Use Structured Data to Win Rich Results
Structured data is one of the most overlooked—but most powerful—ways to improve how your product pages appear in search results.
By adding the right markup, you can give Google and other search engines detailed context about your product, which can lead to enhanced listings called “rich results.”
These are more visually appealing, contain more information, and typically have higher click-through rates.
What Is Structured Data?
Structured data is a standardized format (usually in JSON-LD) that helps search engines understand the content of your page beyond just the text on it.
For product pages, this includes data like:
- Product name
- Price
- Availability (in stock, out of stock)
- Brand
- SKU
- Review ratings
- Images
When this data is properly implemented, Google can display these details directly in the search results, making your product stand out.
Why It Matters
Rich results help your listings catch the eye in search results. A study from Milestone Inc. found that websites with rich results get 20–30% higher click-through rates than those without.
When shoppers can see star ratings, pricing, and availability before they even visit your site, it builds trust and drives more traffic.
For ecommerce, the most relevant schema types include:
- Product
- Offer
- Review
- AggregateRating
These should be added to every product page you want to rank and convert.
Integrating With Google Merchant Center
If you’re running Google Shopping campaigns or submitting your product feed to Google Merchant Center, structured data can also help ensure consistency between your site and your listings.
Google Merchant Center It gives Google more confidence in your product info and helps avoid mismatches that could trigger disapprovals.
Merchant Center can even pull structured data directly from your site if the markup is properly formatted. That means fewer manual updates and better alignment between your organic and paid listings.
How to Implement Product Schema
Most ecommerce platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, and Magento offer apps or built-in features that handle structured data. However, it’s always a good idea to double-check your markup using tools like:
- Google’s Rich Results Test
- Schema.org validator
- Google Search Console’s Enhancements report
Here’s a basic example of structured data in JSON-LD format:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "SoundBlaster X1000 Wireless Headphones",
"image": "https://example.com/product.jpg",
"description": "Wireless noise-canceling headphones with 40-hour battery life.",
"sku": "SBX1000",
"brand": {
"@type": "Brand",
"name": "SoundBlaster"
},
"offers": {
"@type": "Offer",
"priceCurrency": "USD",
"price": "149.99",
"availability": "https://schema.org/InStock"
},
"aggregateRating": {
"@type": "AggregateRating",
"ratingValue": "4.5",
"reviewCount": "284"
}
}
Even if you don’t have all the elements (like reviews), it’s still worth implementing what you do have.Keep It Updated
Structured data isn’t “set it and forget it.” Make sure pricing, availability, and other dynamic fields stay up to date—especially if your inventory changes frequently.
Google can remove rich results if your structured data is inaccurate or misleading.
Structured data is a behind-the-scenes tactic, but its impact is very visible.
It helps your product pages stand out in crowded search results, improves your click-through rate, and builds trust before users even land on your site.
Fix What’s Broken. Rank What Matters.
Product pages often go overlooked—we audit, optimize, and elevate them to drive real revenue.
Contact Us -
Optimize Product Images for SEO and UX
Product images aren’t just visual placeholders—they’re essential content for users and search engines.
In ecommerce, where customers can’t physically touch or try the product, images often serve as the deciding factor in whether someone buys or bounces.
But good visuals alone aren’t enough. To help your product pages rank and convert better, you need to make sure your images are optimized for both SEO performance and user experience.
High-Quality Product Images Why Image Optimization Matters
According to Google, 36% of shoppers say they use visual search when shopping online.
That means your images don’t just support text—they can actually drive organic traffic from Google Images and enhance how your page appears in the SERP.
At the same time, poorly optimized images can slow down your site. And speed matters: Google has confirmed that page load time is a ranking factor.
A study by Portent showed that ecommerce sites that load in one second convert 2.5x better than those that take five seconds.
Best Practices for SEO-Friendly Product Images
Let’s take a look at some best practices to create SEO-friendly product pages.
Use Descriptive File Names
Instead of something generic like IMG1234.jpg, use a filename that reflects what’s actually in the image. For example:
wireless-noise-canceling-headphones-black.jpg
This helps search engines better understand the image content and can improve rankings in image search.
Write Effective Alt Text
Alt text serves multiple purposes: it improves accessibility, provides context if the image can’t load, and gives search engines another clue about your page content.
Write concise, descriptive alt text that accurately reflects what’s shown.
Ineffective: headphones
Better: black wireless noise-canceling headphones with a foldable designAvoid keyword stuffing—alt text should be natural and beneficial.
Choose the Right Format
- Use JPEG for photos (small file size, good quality)
- Use PNG if you need transparency
- Consider WebP for better compression and performance, especially if your platform supports it
Compress Images Without Losing Quality
Use tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or built-in plugins to compress images before uploading. Aim for the smallest file size possible without making your product look bad.
Use Responsive Images
Responsive design ensures that images scale appropriately on different screen sizes. Use srcset and sizes attributes so the browser can load the best image for the user’s device.
Example:
<img
src=”product.jpg”
srcset=”product-400.jpg 400w, product-800.jpg 800w”
sizes=”(max-width: 600px) 400px, 800px”
alt=”Black wireless headphones with cushioned ear cups”>Host Images on Your Own Domain
When possible, host images on your domain rather than third-party CDNs or image hosts. This keeps authority consolidated and helps with crawlability and indexing.
Bonus: Add Structured Data for Images
If your images support key product details (like different views, labels, or packaging), make sure they’re included in your product schema as well. Google uses this to show richer product thumbnails in search results.
Support Multiple Angles and Use Cases
Beyond technical optimization, also think about what your users want to see. Include:
- Multiple angles of the product
- Zoom-in capabilities
- Close-ups of key features
- Lifestyle images (showing the product in context)
- Size comparison visuals, if relevant
Shoppers are more likely to convert when they feel confident about what they’re getting. And great images, when optimized correctly, can do a lot of heavy lifting in both SEO and sales.
Now that your visuals are working hard, it’s time to look at how your product page content is structured, because even great content needs the right framework to shine.
Featured Article: What Is Schema Markup & How to Implement It in 2026
-
Structure Your Content With Semantic HTML and Headings
Search engines don’t just look at what you write—they care how you organize it.
Semantic HTML and a logical heading structure help Google better understand your product pages and make it easier for users to scan and find what they’re looking for.
This isn’t just a technical detail—it’s directly tied to SEO performance.
Clean, well-structured HTML helps with crawling and indexing, reduces accessibility issues, and makes your pages easier to navigate for all types of users.
What Is Semantic HTML?
Semantic HTML refers to using HTML tags that clearly describe the content inside them.
Instead of relying on <div> and <span> for everything, semantic tags like <article>, <section>, <header>, <nav>, and <main> give structure and meaning to your code.
For ecommerce product pages, key semantic tags include:
- <main> for the core product content
- <article> to wrap the product itself
- <section> to separate content blocks (like features, reviews, or FAQs)
- <h1> to <h6> to create a hierarchy of headings
- <figure> and <figcaption> for product images
When search engines crawl your page, these tags help them understand the relationships between different elements, and that can boost relevance and rankings.
Use a Clear Heading Hierarchy
Your headings (H1–H6) should reflect the logical structure of your page content. Think of them as an outline:
- H1: Product name (only one per page)
- H2s: Major sections (e.g., Description, Specs, Reviews, FAQs)
- H3s and H4s: Sub-sections within those
Avoid skipping levels (like jumping from an H2 to an H5) and never use headings purely for styling. Use CSS for visuals, and stick to semantic structure for clarity.
Example of a solid heading structure for a product page:
<h1>SoundBlaster X1000 Wireless Headphones</h1>
<h2>Product Description</h2>
<h3>Designed for Comfort and Sound</h3>
<h3>Technical Specifications</h3>
<h2>Customer Reviews</h2>
<h3>Top-Rated Feedback</h3>
<h3>Write a Review</h3>
<h2>FAQs</h2>
This helps both users and bots navigate the content more easily.
Improve Accessibility (and SEO) at the Same Time
Using semantic HTML and headings improves accessibility for screen readers and other assistive technologies.
That’s not just good for users—it’s good for business. Accessibility is increasingly a ranking consideration, especially with Google’s focus on inclusive design and usability.
Support Featured Snippets and Sitelinks
A clear heading structure also increases your chances of winning featured snippets (like FAQ boxes) or generating sitelinks in Google. These can significantly boost your visibility and click-through rate.
To give yourself the best shot at this, pair clear headings with concise, relevant content directly underneath.
For example, an FAQ section formatted with <h3> headings and straightforward answers can be eligible for rich results if paired with structured data.
Great content that isn’t well-structured won’t perform as well as it could.
Semantic HTML and thoughtful heading use give your product pages a solid technical foundation and help elevate your content in the eyes of both users and search engines.
-
Write Unique, Compelling Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions might seem like small details, but they play a big role in your product pages’ SEO performance and user engagement.
These brief snippets of text appear in the search results beneath the page title and URL.
Although meta descriptions themselves aren’t a direct ranking factor for Google, they influence click-through rates (CTR)—and a higher CTR can indirectly improve your rankings.
What Makes a Good Meta Description?
A well-crafted meta description serves as a “sales pitch” for your product page in search results. It should be engaging, relevant, and give users a clear idea of what to expect when they click through.
In fact, research shows that over 60% of users have clicked on a search result because of a compelling meta description.
Here’s how to write meta descriptions that work for both SEO and users:
Be Concise and Relevant
Meta descriptions should be between 150–160 characters to avoid truncation in search results. Focus on the most relevant and compelling aspects of the product.
For example, instead of writing:
“SoundBlaster X1000 headphones are great, featuring wireless connectivity, noise cancellation, and more.”
Write:
“Shop the SoundBlaster X1000 Wireless Headphones. 40-hour battery life, noise-canceling tech, and comfortable fit for all-day use.”
Notice how this version:
- Uses important keywords (e.g., “wireless headphones,” “noise-canceling”)
- Highlights key product benefits (e.g., “40-hour battery life”)
- Uses action-oriented language (“Shop”)
Include Keywords, But Keep It Natural
Make sure to include your primary keyword in the meta description (e.g., “wireless headphones”).
But remember, this is written for humans, not bots, so avoid overstuffing keywords. Make it sound natural, as if you’re having a conversation with a potential buyer.
Appeal to User Intent
What are customers looking for when they search for your product? Address their needs directly in the meta description.
Use language that appeals to their pain points, desires, or interests. For example, if you’re selling a product that solves a common problem, like noise-canceling headphones for frequent flyers, say so:
“Block out noise on your next flight with SoundBlaster X1000 Wireless Headphones. Comfort, sound quality, and a 40-hour battery for long-haul trips.”
Include a Call to Action (CTA)
Encourage users to click through by adding a simple, clear call to action. Phrases like “Buy now,” “Shop today,” or “Discover more” can motivate people to visit your page and make a purchase.
“Buy the SoundBlaster X1000 Headphones today and enjoy 40-hour battery life, noise cancellation, and more.”
Highlight Unique Selling Points (USPs)
If your product has any special offers, discounts, or features that differentiate it from the competition, make sure to mention them in the meta description.
For example, if you’re offering a free shipping promotion, include that:
“Free shipping on all orders of SoundBlaster X1000 Headphones. Shop now for the best in wireless sound.”
Keep It Unique for Each Page
Every product page should have a unique meta description that reflects the specific product and its features.
Duplicate meta descriptions across multiple pages can hurt your SEO performance because search engines prefer original content.
How to Implement Meta Descriptions
Most ecommerce platforms allow you to edit the meta description directly from the product page’s settings. Here’s a quick checklist to ensure you’re implementing them properly:
- Character count: Ensure your meta description is between 150 and 160 characters to avoid truncation.
- Primary keyword: Include your main target keyword naturally within the description.
- Call to action: Add a CTA to encourage user clicks.
- Unique content: Each product page should have a unique meta description.
- Appeal to intent: Make sure your meta description reflects what the user is searching for and what your product offers.
Meta descriptions may seem small, but they can be the deciding factor for whether someone clicks on your page. Well-written descriptions increase CTR, which can lead to higher rankings in the long run.
Featured Article: Common On-Page SEO Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
-
Leverage User-Generated Content (UGC) for Social Proof and SEO
User-generated content (UGC) is a powerful way to improve your product pages’ SEO while also building trust with potential customers.
UGC includes customer reviews, ratings, and even user-submitted photos or videos that showcase your product in action.
Search engines value UGC because it’s original, fresh, and adds credibility to your product page.
From an SEO perspective, UGC can significantly improve your chances of ranking higher in search results while enhancing the user experience and driving conversions.
Why UGC Matters for SEO
Google values content that provides real, relevant, and helpful information to users. Reviews, ratings, and Q&A sections provide both fresh content and key signals about the popularity and quality of your products.
According to a BrightLocal study, 79% of people trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations, and 63% of consumers are more likely to purchase from a website that has reviews.
The Benefits of Reviews, Ratings, and Q&A
Some benefits include:
Fresh Content for SEO
One of the challenges of maintaining SEO performance is keeping your content fresh.
Since reviews and ratings are constantly updated, they provide an ongoing source of fresh content for your product pages.
Google favors pages that are frequently updated with new information, and UGC is a great way to meet that need.
Improve Trust and Conversions
Users trust reviews and ratings because they come from fellow shoppers, not from your marketing copy.
When potential buyers see that others have had a positive experience with your product, they’re more likely to make a purchase.
A study by Podium found that 93% of consumers read online reviews before making a purchase decision.
Answer Questions and Address Concerns
A Q&A section, where users can ask questions and receive answers either from the business or other customers, can provide valuable content for search engines and help potential buyers feel confident in their decision.
Additionally, it can reduce the number of bounce-backs due to unaddressed concerns.
For example, if a customer asks, “Does this backpack fit a 15-inch laptop?” and you or another customer answers, that could be the deciding factor for a shopper who had the same question.
Boost Long-Tail Keyword Rankings
UGC often includes long-tail keywords that you may not have anticipated targeting.
For example, if someone leaves a review that says, “I love these noise-canceling headphones for traveling,” you may start to rank for the long-tail query “noise-canceling headphones for traveling.”
This can help expand your visibility in search results.
How to Encourage More Reviews and UGC
Here’s how you can encourage your customers to leave reviews.
Make It Easy to Leave Reviews
The easier you make it for customers to leave reviews, the more likely they are to do so.
Send follow-up emails asking customers to leave feedback after they’ve received their product, or use pop-up reminders on your product pages.
Keep the review process simple and intuitive, and allow users to submit reviews directly on the product page.
Offer Incentives
While you shouldn’t buy reviews, offering incentives like a small discount on a future purchase or entry into a giveaway can encourage users to leave feedback.
Just be sure to ask for honest reviews and make it clear that you’re not incentivizing positive feedback, just genuine opinions.
Leverage Social Media
Encourage customers to share their experiences with your products on social media. You can even create a branded hashtag or run a campaign to encourage UGC.
For example, ask users to post photos of themselves using your product and tag your brand in exchange for a chance to be featured on your website.
Respond to Reviews and Q&A
Engage with your customers by responding to their reviews and questions. This not only shows that you value their input, but it also adds more content to your pages, which can help with SEO.
Positive responses can further build trust, while addressing negative reviews quickly and professionally can prevent potential damage to your reputation.
Add User-Generated Photos and Videos
Photos and videos submitted by customers showcasing your product in real-life scenarios can enhance your product pages and provide added value.
These types of content are also likely to increase conversions. If you sell clothing, for example, a user-uploaded photo of the product being worn can help others envision themselves using it.
Structured Data for Reviews
Just like product details, you can mark up reviews using structured data.
This allows Google to display review stars and ratings in the search results, which makes your product stand out more and encourages clicks.
Reviews and ratings are one of the key components of the Review schema markup.
Here’s an example of how to add review schema markup in JSON-LD format:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "SoundBlaster X1000 Wireless Headphones",
"image": "https://example.com/product.jpg",
"description": "Wireless noise-canceling headphones with 40-hour battery life.",
"sku": "SBX1000",
"brand": {
"@type": "Brand",
"name": "SoundBlaster"
},
"aggregateRating": {
"@type": "AggregateRating",
"ratingValue": "4.5",
"reviewCount": "150"
},
"review": [
{
"@type": "Review",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "John Doe"
},
"datePublished": "2026-04-20",
"reviewBody": "These headphones are fantastic for travel. The noise cancellation works great, and they’re incredibly comfortable for long flights.",
"name": "Great headphones for travel!",
"reviewRating": {
"@type": "Rating",
"bestRating": "5",
"worstRating": "1",
"ratingValue": "5"
}
}
]
}
By adding review markup, you’re making it easier for Google to show rich snippets in the search results, which can give your product pages a significant visibility boost.
User-generated content provides fresh content for SEO, builds trust with potential customers, answers their questions, and ultimately drives more conversions.
Reviews, ratings, and Q&A sections are invaluable resources that boost your page’s credibility and relevance in the eyes of both users and search engines.
Featured Article: Technical SEO Audit: The Complete Step-by-Step Guide (2026 Edition)
-
Implement Effective Internal Linking
Internal linking is one of the most underutilized SEO strategies, especially on ecommerce sites.
By strategically linking to relevant products, categories, and other key pages, you not only help your customers navigate your site more easily, but you also improve your SEO by passing link equity (ranking power) between pages.
When done right, internal linking can help search engines discover new pages, understand the context and relationship between content, and distribute ranking power across your site.
On top of that, it improves user experience by making it easier for visitors to find related products or relevant information.
Why Internal Linking Is Important
Internal links help search engines crawl your website more effectively, ensuring that all important pages are indexed and rank well. Additionally, they allow you to pass link equity (SEO value) to pages you want to rank higher.
An effective internal linking strategy can also help spread out link equity across your entire website.
This means that even product pages that are deeper in the site hierarchy can still benefit from the authority of your home page or top-level category pages.
From a user perspective, internal links improve the overall experience by guiding users to discover products they might not have found otherwise.
For example, if someone is looking at a specific pair of headphones, showing them complementary accessories like carrying cases or charging stands can help boost sales across different product lines.
Best Practices for Internal Linking
Some best practices for internal linking include:
Link to Relevant Categories and Subcategories
Linking to relevant categories is one of the most effective ways to improve your internal linking structure.
If someone is viewing a particular product, offer them links to broader category pages (e.g., “Headphones,” “Wireless Headphones,” or “Noise-Canceling Headphones”).
This helps users easily explore your product offerings while boosting category page SEO.
For example:
- Product page: “Wireless Noise-Canceling Headphones”
- Internal link: “View more in our Noise-Canceling Headphones collection”
Use Descriptive Anchor Text
Anchor text is the clickable part of a link, and it plays a big role in SEO.
Instead of generic phrases like “click here” or “learn more,” use descriptive and keyword-rich anchor text that gives both search engines and users a clear idea of where the link leads.
For example, instead of:
“Click here to explore other products in this category.”
Use:
“Browse our full range of wireless headphones.”
This improves keyword relevance and enhances user experience.
Link to Complementary Products
Internally linking to complementary products can help boost cross-selling opportunities. If a customer is viewing a laptop, link to relevant accessories, such as laptop sleeves, chargers, or mousepads.
This not only enhances the user experience but also helps to distribute SEO value across different product pages.
For example:
On the product page for a camera: “You may also be interested in a camera bag, memory card, and tripod for the perfect setup.”
Create “Frequently Bought Together” or “Related Products” Sections
Many ecommerce sites add a section for related products, or “Frequently Bought Together,” right on the product page.
This is another powerful way to implement internal links, encouraging users to discover products that complement what they’re already viewing.
These sections can also help drive SEO value to related products and category pages.
Example of anchor text:
“You may also like our portable speaker,” linking to the speaker product page.
Link to Parent Categories and Sibling Products
For deeper product pages, make sure they link back to parent categories or sibling products (similar items).
This helps search engines understand the relationships between products and categories and can boost the ranking of these pages.
For example:
On a product page for a “wireless gaming mouse,” you might link to the broader category of “Gaming Accessories,” as well as to other types of mice, like “wired gaming mouse” or “ergonomic gaming mouse.”
Use Breadcrumb Navigation
Breadcrumbs are a great way to provide both internal links and a clear structure for users.
Breadcrumb navigation allows users to easily jump to parent categories or other relevant pages, which can improve user experience and reduce bounce rates.
It also helps Google understand the structure of your website, which is crucial for SEO.
For example, if you’re viewing a product page for a specific pair of shoes, the breadcrumb might look like this:
Home > Men’s Shoes > Sneakers > [Product Name]
Link to Important Pages Globally
Some key pages, such as a “Contact Us” or “Shipping Information” page, should be accessible from every product page.
Ensure that these important pages are linked in a global navigation menu or footer, so users can easily find them.
This not only improves user experience but also helps search engines crawl and index these essential pages more efficiently.
How Internal Linking Helps SEO
- Crawlability: Proper internal linking helps search engines crawl your site more effectively, ensuring that important pages are discovered and indexed.
- Page Authority Distribution: Internal links pass SEO value from high-authority pages (e.g., homepage, category pages) to deeper product pages, boosting their chances of ranking higher.
- User Experience: By guiding users to relevant content, you reduce bounce rates and increase the likelihood of conversions.
- Keyword Relevance: Linking with descriptive anchor text allows you to target long-tail and relevant keywords, which can boost the rankings of related pages.
How to Monitor and Improve Internal Linking
- Use SEO Tools: Tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Screaming Frog can help you identify pages with weak internal linking. They can also show you which pages have too many internal links, potentially spreading SEO value too thinly.
- Prioritize Important Pages: Ensure your most important pages (such as best-sellers, high-margin products, or strategic category pages) are well-linked throughout the site.
- Optimize Deep Pages: For products buried deeper within your site’s architecture, ensure that you’re linking to them from higher-authority pages to pass SEO value down.
Internal linking is a key tactic in helping search engines and users navigate your site. By linking to relevant categories, complementary products, and related content, you can boost your product pages’ SEO, improve your user experience, and increase your chances of ranking higher in the search results.
- Product page: “Wireless Noise-Canceling Headphones”
-
Set Up and Optimize XML Sitemaps
An XML sitemap is like a roadmap for search engines. It’s a file that lists all the important pages on your website, ensuring that search engines can easily find, crawl, and index them.
While Google and other search engines are capable of discovering pages on their own through links, an XML sitemap helps search engines prioritize which pages to crawl first and ensures no important page gets overlooked.
For ecommerce sites, having an optimized XML sitemap is crucial for ensuring all your product pages, category pages, and other important content are indexed correctly, allowing them to rank in search results.
Why XML Sitemaps Are Important for SEO
An XML sitemap makes it easier for search engines to discover your product pages, even if they aren’t linked to frequently from other pages.
Without an XML sitemap, search engines might miss deeper product pages or have trouble crawling large ecommerce sites with a complex structure.
For example, if a user is searching for a niche product, such as a “reusable travel water bottle,” and you have a deep product page buried within your site’s structure, an XML sitemap helps search engines locate it and potentially rank it for relevant queries.
Additionally, an XML sitemap ensures that your pages get indexed quickly after updates or additions.
Key Components of an Ecommerce XML Sitemap
A well-structured XML sitemap for ecommerce sites should include the following key components:
Product Pages
Make sure all individual product pages are listed in your sitemap. These pages are the heart of your ecommerce business, and ensuring that they are indexed properly is crucial for driving traffic and sales.
Category Pages
Category pages group products into logical categories, making them easier for users to browse.
Include these in your sitemap to make sure that search engines understand how your products are organized and can index the relevant pages effectively.
Static Pages
Your static pages, such as “About Us,” “Contact Us,” and “Shipping Information,” should also be included in the XML sitemap.
These pages are important for both users and search engines, and ensuring that they are indexed helps provide a complete picture of your site.
Pagination and Filters
If your site uses pagination (e.g., multiple pages of product listings) or filtering systems (e.g., products by size, color, or price), include these pages in your sitemap as well.
This ensures that search engines can crawl all the variations of your product listings, leading to better visibility and ranking.
Updated Content
A sitemap should include updated pages, especially when you add new products, launch seasonal collections, or change content on existing pages.
This helps search engines prioritize the most up-to-date content and index it quickly.
How to Create and Submit an XML Sitemap
There are multiple ways to create and submit an XML sitemap for your ecommerce website:
Use a Sitemap Generator Tool
There are several online tools and plugins that can generate an XML sitemap for your site. If you’re using a platform like WordPress, there are plugins (such as Yoast SEO or RankMath) that can automatically generate and update your sitemap as you add or modify pages.
For custom-built websites, tools like Screaming Frog or XML-Sitemaps.com can help you generate a sitemap manually.
Ensure Proper Structure
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”UTF-8″?>
<urlset xmlns=”http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9″><url>
<loc>https://www.yourstore.com/product-page-1</loc>
<lastmod>2026-04-01</lastmod>
<changefreq>weekly</changefreq>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url><url>
<loc>https://www.yourstore.com/product-page-2</loc>
<lastmod>2026-04-01</lastmod>
<changefreq>weekly</changefreq>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url></urlset>
<loc>: Specifies the URL of the page.<lastmod>: Indicates the last date the content was modified (in YYYY-MM-DD format).<changefreq>: Suggests how frequently the content is likely to change (e.g., daily, weekly, monthly).<priority>: Assigns a priority value (from 0.0 to 1.0) to indicate the page’s relative importance compared to other pages on your site.
Submit the Sitemap to Search Engines
Once your XML sitemap is generated, submit it to search engines like Google and Bing. For Google, you can do this through Google Search Console.
Once you’ve logged into your account:
- Go to the “Sitemaps” section under “Index.”
- Enter the URL of your sitemap (e.g., https://www.yourstore.com/sitemap.xml).
- Click “Submit.”
Bing has a similar process through Bing Webmaster Tools.
Regularly Update Your Sitemap
An important thing to keep in mind is that your sitemap should be updated regularly.
Whenever you add new products, categories, or blog posts, you should regenerate and resubmit your sitemap to ensure the changes are reflected in search engines.
Best Practices for XML Sitemaps
Some best practices include:
Limit Sitemap File Size
Google allows up to 50,000 URLs per sitemap, but if your sitemap grows too large, break it up into smaller, more manageable files.
You can use a sitemap index file to link to multiple sitemaps, which is especially useful for larger ecommerce sites.
Prioritize Important Pages
If you have thousands of products and pages, prioritize the most important pages in your sitemap. This could include your best-selling products, key category pages, or pages with the highest SEO potential.
Avoid Overloading With Low-Value Pages
Avoid including low-value pages, like thank-you pages after a purchase or login pages. These won’t help with SEO and could dilute the focus of your sitemap.
Track Sitemap Errors
Periodically check Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools for any errors related to your sitemap. This can help ensure that all pages are being indexed properly and that there are no crawl issues.
How XML Sitemaps Impact SEO
- Increased Crawl Efficiency: A well-structured XML sitemap makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index all your important pages, including those that might not be linked to from other pages.
- Faster Indexing: New or updated product pages will be indexed faster, helping them show up in search results more quickly.
- Priority Setting: By prioritizing key pages and updating the last-modified dates, you can signal to search engines which pages are the most important.
An XML sitemap is an essential tool for ecommerce SEO. It ensures that all important pages—product pages, category pages, static pages, and more—are discovered, crawled, and indexed by search engines.
By submitting an updated sitemap and following best practices, you can ensure that your product pages have the best chance of ranking in search results.
Featured Article: The Role of XML Sitemaps in SEO – Complete Guide in 2026
-
Mobile Optimization: Ensuring a Seamless Experience Across Devices
Optimizing your ecommerce product pages for mobile devices is no longer optional—it’s essential.
Mobile traffic now accounts for more than 60% of global internet traffic, and Google uses mobile-first indexing, which means it prioritizes the mobile version of your site for ranking purposes.
If your product pages aren’t mobile-friendly, you risk losing potential customers and damaging your search engine rankings.
Ensuring a smooth, responsive mobile experience will not only improve your SEO but also increase your conversion rates.
Why Mobile Optimization Is Critical for SEO
- Mobile-First Indexing: Since 2018, Google has adopted mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily crawls and indexes the mobile version of a website. If your mobile site is difficult to navigate or lacks essential information, it can negatively impact your rankings.
- User Experience (UX): If your site isn’t optimized for mobile users, it can lead to poor UX, longer load times, and frustrating navigation. This can increase bounce rates and decrease conversions.
- Site Speed: Mobile optimization often involves improving your site’s speed, which is a crucial ranking factor. Fast loading times on mobile devices are essential for user satisfaction and SEO.
- Local SEO: A significant portion of mobile searches is related to local intent. Optimizing your mobile product pages can improve your visibility in local search results, especially for customers searching on the go.
Key Strategies for Mobile Optimization
Here’s what you need to do to optimize your product pages.
Responsive Web Design
A responsive website design automatically adjusts to fit the screen size of any device, whether it’s a smartphone, tablet, or desktop.
Google favors responsive designs because they offer a seamless experience across all devices, ensuring that your content is presented well on any screen.
- Fluid Layouts: Use flexible grid-based layouts that scale depending on the screen size. This allows images, text, and other elements to resize automatically.
- Viewport Settings: Ensure your website uses the proper viewport settings to ensure content fits the screen. This prevents the need for horizontal scrolling and keeps elements from appearing too small or too large on mobile.
Optimize for Touchscreen Navigation
Mobile users rely on touchscreens to navigate, so ensuring your product pages are touch-friendly is crucial.
Buttons, links, and other interactive elements should be large enough to tap easily without zooming in.
- Larger Buttons: Make sure buttons (such as “Add to Cart” or “Buy Now”) are easy to tap with a finger. A good rule of thumb is to make buttons at least 48px by 48px.
- Easy Scrolling: Ensure that users can scroll effortlessly through product images and descriptions. Avoid elements that require excessive zooming or pinching.
Speed Up Your Mobile Site
Mobile users expect fast load times, and search engines like Google consider site speed as a ranking factor.
According to Google, 53% of mobile users will abandon a website if it takes more than three seconds to load. Here are some tips for improving mobile site speed:
- Optimize Images: Use smaller image sizes and compress them to reduce load times. Consider using formats like WebP, which provides high-quality images at smaller file sizes.
- Minimize HTTP Requests: Reduce the number of elements that need to be loaded on a page, such as scripts, images, and stylesheets.
- Use Lazy Loading: Lazy loading delays the loading of images and videos until they are needed (i.e., when they’re about to appear on the screen). This can significantly speed up your mobile page load times.
- Enable AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages): AMP is a framework developed by Google that enables faster loading of mobile pages by stripping down unnecessary elements and optimizing code.
Simplify Navigation for Mobile
Mobile users need to find information quickly, so streamlining your navigation is essential for a good mobile experience.
Use collapsible menus, clear categories, and search functions to make browsing easier on smaller screens.
- Sticky Navigation: Implement sticky navigation bars (where the menu stays visible as users scroll) to make it easier for users to find what they’re looking for, even as they move down the page.
- Hamburger Menus: A hamburger menu (three horizontal lines) can make it easier to access different sections of your site without cluttering the screen.
Simplify Forms and Checkout
When it comes to conversions, a complicated mobile checkout process is a major deterrent. Ensure your checkout process is as simple as possible, with minimal steps and easy-to-fill forms.
- Auto-Fill: Implement auto-fill for address fields and payment details to make it easier for users to complete their orders.
- Guest Checkout: Allow users to check out as guests without requiring them to create an account. This reduces friction in the purchasing process and improves conversion rates.
Test Mobile Usability Regularly
Mobile optimization is an ongoing process. Test your mobile site regularly using tools like the Mobile-Friendly Test to identify potential issues and improve the user experience.
Additionally, perform manual testing by browsing your site on multiple mobile devices to ensure everything works smoothly.
Mobile Optimization Best Practices for Product Pages
Here are some best practices:
- Product Image Zoom: Ensure that mobile users can zoom in on product images for a closer look. This is especially important for clothing, accessories, and other products where detail matters.
- Clear and Concise Product Descriptions: Keep product descriptions concise but informative on mobile. Use bullet points to highlight key features and benefits, making it easier for users to scan information quickly.
- Optimized Product Reviews: Reviews are crucial for ecommerce sites, so make sure they’re mobile-friendly. Display star ratings and reviews in a collapsible format to save space but still allow easy access.
- Optimized CTAs (Calls to Action): Your CTA buttons (e.g., “Add to Cart” or “Buy Now”) should be easily visible and accessible, with clear text and a contrasting color to stand out on mobile.
Mobile-Friendly Schema Markup
To further optimize your product pages for mobile users and search engines, implement structured data (schema markup) for products.
Adding structured data helps search engines display rich snippets, including product ratings, price, availability, and other important details directly in the search results.
This can improve visibility and increase click-through rates.
Here’s an example of structured data for a product page:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "Noise-Canceling Headphones",
"image": "https://example.com/images/headphones.jpg",
"description": "High-quality noise-canceling headphones for superior sound.",
"sku": "12345",
"brand": {
"@type": "Brand",
"name": "SoundTech"
},
"offers": {
"@type": "Offer",
"url": "https://example.com/noise-canceling-headphones",
"priceCurrency": "USD",
"price": "199.99",
"availability": "https://schema.org/InStock"
}
}By including product-related structured data, you can make it easier for search engines to display critical information about your products directly in search results, which can improve both SEO and user experience.
Optimizing your ecommerce product pages for mobile devices is crucial for both SEO and user experience.
A responsive design, fast load times, touch-friendly navigation, and simplified forms are essential components of a successful mobile strategy.
By prioritizing mobile optimization, you not only improve your search rankings but also boost conversion rates and enhance customer satisfaction.
Featured Article: Core Web Vitals: How to Optimize for Better Performance in 2026
-
Leverage Structured Data for Enhanced SEO
Structured data, also known as schema markup, is a powerful tool for improving the visibility and quality of your product pages in search engine results.
By providing additional context about your content, structured data helps search engines understand and display your pages more effectively.
This can lead to rich snippets, enhanced search results, and ultimately better rankings.
Structured data allows you to provide search engines with detailed information about your products, such as price, availability, reviews, and product details.
When done correctly, this can make your product pages stand out and improve user engagement.
What Is Structured Data and Why Is It Important?
Structured data is a standardized format for providing information about a page and classifying its content.
It uses a vocabulary defined by Schema.org, and it helps search engines like Google interpret the content of your pages more accurately.
For ecommerce websites, structured data is essential because it allows search engines to display detailed, relevant information in the search results without needing users to click on your page.
This can include:
- Price: Display the product’s price directly in the search result.
- Availability: Indicate whether the product is in stock, out of stock, or on backorder.
- Ratings and Reviews: Show star ratings and user reviews, which can increase credibility and click-through rates.
- Product Details: Include key information such as the product’s brand, model number, and SKU.
The more detailed the structured data, the more likely your product pages will appear in rich snippets, which take up more space on the search results page and often have higher click-through rates.
Types of Structured Data for Ecommerce Product Pages
The most common types of structured data used on product pages are:
Product Schema
Product schema markup is specifically designed to provide search engines with information about your products. It can include details like product name, price, brand, reviews, availability, and more.
Here’s an example of product schema markup in JSON-LD format:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "Wireless Bluetooth Headphones",
"image": "https://example.com/images/headphones.jpg",
"description": "Noise-canceling wireless headphones with long battery life.",
"sku": "12345",
"brand": {
"@type": "Brand",
"name": "SoundTech"
},
"offers": {
"@type": "Offer",
"url": "https://example.com/wireless-headphones",
"priceCurrency": "USD",
"price": "99.99",
"availability": "https://schema.org/InStock"
},
"aggregateRating": {
"@type": "AggregateRating",
"ratingValue": "4.5",
"reviewCount": "320"
}
}
- name: The name of the product.
- image: A URL to the product image.
- description: A brief description of the product.
- brand: The brand of the product.
- sku: The unique identifier for the product.
- offers: The price and availability of the product.
- aggregateRating: The product’s average rating and number of reviews.
Review Schema
In addition to product schema, implementing review schema helps search engines understand your product’s reviews and ratings.
This is crucial because reviews are often displayed directly in search results, which can improve your visibility and user trust.
Example of review schema markup:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Review",
"reviewRating": {
"@type": "Rating",
"ratingValue": "5",
"bestRating": "5"
},
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "John Doe"
},
"reviewBody": "These headphones are fantastic! The sound quality is excellent, and they are very comfortable to wear for long periods."
}
This schema markup allows you to show both the average rating and individual reviews directly in the search results, enhancing your product’s attractiveness.
Breadcrumb Schema
Breadcrumbs help users navigate through your site more easily, and they also enhance your SEO by providing context to search engines about the structure of your website.
Including breadcrumb schema markup on your product pages makes your breadcrumbs more visible to search engines and improves your chances of appearing in rich snippets.
Example of breadcrumb schema:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "BreadcrumbList",
"itemListElement": [
{
"@type": "ListItem",
"position": 1,
"name": "Home",
"item": "https://example.com/"
},
{
"@type": "ListItem",
"position": 2,
"name": "Electronics",
"item": "https://example.com/electronics"
},
{
"@type": "ListItem",
"position": 3,
"name": "Headphones",
"item": "https://example.com/headphones"
}
]
}
Breadcrumbs allow users to understand their location within your site, and implementing breadcrumb schema ensures that these breadcrumbs are visible in search results.
How to Implement Structured Data on Product Pages
There are three common formats for implementing structured data:
JSON-LD (Recommended)
JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is Google’s preferred method for adding structured data to web pages.
It’s easy to implement, doesn’t require modifying the HTML structure, and can be added directly in the <head> or the <body> of your product pages.
Microdata
Microdata is embedded directly within the HTML of your page using specific attributes. While it works similarly to JSON-LD, it’s more integrated into the content of your page and requires editing your HTML tags.
RDFa
RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes) is another method of adding structured data, though it’s less commonly used compared to JSON-LD and microdata.
It works by embedding data within the HTML attributes, but JSON-LD is generally the preferred format for SEO.
Testing and Validating Structured Data
Once you’ve added structured data to your product pages, it’s crucial to test and validate it to ensure it’s implemented correctly.
- Google’s Rich Results Test: This tool allows you to test individual pages and see how your structured data appears in search results. Simply enter your page URL, and the tool will show you which rich results are available for your product pages.
- Google Search Console: After you’ve implemented structured data, use Google Search Console to monitor any errors or issues related to your markup. It will help you identify and fix problems that could prevent your structured data from being displayed correctly in search results.
The Benefits of Structured Data for Ecommerce SEO
Some best practices include:
- Enhanced Rich Snippets: Structured data helps your product pages appear in rich snippets, which display additional information such as price, availability, and star ratings. This can increase click-through rates.
- Improved Visibility: Products with rich snippets tend to stand out more in search results, especially when they include reviews and pricing.
- Better User Engagement: When users see useful information directly in search results, they’re more likely to click on your product page, improving engagement and conversion rates.
- Voice Search Optimization: Structured data helps optimize your pages for voice search, as it allows voice assistants to retrieve detailed information about your products more easily.
Structured data is an invaluable tool for ecommerce sites looking to improve their visibility in search results.
By implementing product, review, and breadcrumb schema, you provide search engines with a clearer understanding of your product pages, which can lead to rich snippets, better rankings, and increased traffic.
-
Optimize Product Descriptions and Leverage User-Generated Content
Product descriptions and user-generated content (UGC) are critical elements for boosting SEO, improving user engagement, and driving conversions.
A well-crafted product description can help your page rank higher in search engine results, while user-generated content like reviews, ratings, and customer images can significantly enhance the credibility and trustworthiness of your product page.
Why Product Descriptions Matter for SEO
Your product descriptions serve two primary functions:
- Providing Search Engines with Relevant Content: The more descriptive and detailed your product pages are, the better search engines can understand what the product is and what keywords it should rank for. A well-optimized product description will help you target specific long-tail keywords, making it easier for potential customers to find your products.
- Informing and Persuading Customers: A compelling product description helps potential buyers understand the value of your product, leading to better engagement and increased conversion rates. If your description is vague or generic, customers may leave the page without making a purchase.
However, when optimizing product descriptions, it’s essential to strike a balance. Too much content may overwhelm the user, while too little can fail to convey key information. Your product descriptions should:
- Be Unique: Avoid copying product descriptions from manufacturers or other sites. Unique content helps search engines understand that your page is different from others and can lead to higher rankings.
- Include Relevant Keywords: Use keywords that align with how potential customers are searching for your product. These should be included naturally in the description, heading tags, and meta descriptions.
- Highlight Key Features and Benefits: Focus on the unique selling points of your product. Explain how it solves problems, improves the customer’s life, or offers value.
- Use a Conversational Tone: Write as if you’re talking directly to the customer. A friendly and approachable tone can make your product more relatable and persuasive.
How to Craft an Effective Product Description
Here are some tips for writing descriptions that both search engines and customers will love:
- Start with the Product Name: Ensure your product name includes relevant keywords that customers are likely to search for. For example, instead of just “Headphones,” use “Noise-Canceling Bluetooth Headphones.”
- Focus on Features and Benefits: Provide both the features (e.g., technical specifications) and benefits (e.g., why these features matter to the customer). For instance, instead of just stating “10-hour battery life,” you could say, “Enjoy long listening sessions with up to 10 hours of battery life, perfect for long flights or road trips.”
- Incorporate Use Cases and Scenarios: Help your customers visualize how the product will fit into their lives. This can be as simple as saying, “Ideal for fitness enthusiasts who need high-quality sound during their workouts.”
- Use Bullet Points: Break up key information into easy-to-scan bullet points, making it easier for users to quickly understand the most important features.
- Write for Mobile: With a growing number of users shopping on mobile devices, make sure your descriptions are concise and readable on smaller screens.
Here’s an example of an optimized product description:
Noise-Canceling Bluetooth HeadphonesExperience superior sound quality and comfort with our premium noise-canceling Bluetooth Headphones. Whether you’re traveling, working, or enjoying music at home, these headphones provide crystal-clear audio and block out background noise for an immersive listening experience.
Key Features:
-
- Active Noise-Canceling Technology: Enjoy a quieter environment by reducing up to 85% of ambient noise.
- Long Battery Life: Up to 10 hours of uninterrupted playtime on a single charge.
- Bluetooth Connectivity: Seamlessly connects to your smartphone, tablet, or laptop with Bluetooth 5.0 for a stable connection.
- Comfortable Fit: Adjustable headband and plush ear cups ensure a comfortable fit for extended use.
- Portable Design: Foldable design for easy storage and travel.
Perfect for: Commuters, travelers, and audiophiles looking for noise isolation and rich sound quality.
Optimizing your product descriptions with relevant keywords, detailed features, and engaging content will not only help search engines understand your products but also persuade customers to buy.
Pair this with user-generated content, such as reviews and ratings, to build trust, enhance SEO, and boost conversions.
Conclusion: Elevate Your Product Page SEO for Conversions
Optimizing your product pages for SEO is a critical step toward improving your visibility, driving more organic traffic, and increasing sales.
By implementing the strategies discussed in this guide, you’ll be well on your way to creating product pages that not only rank well in search engines but also provide a superior experience for your users.
Remember, SEO is not a one-time task but an ongoing process.
Regularly monitor your product page performance, update your content, and adjust your strategy as necessary to stay ahead of the competition.
Structured data, metadata optimization, and a thoughtful, user-focused approach will all contribute to stronger rankings and a better user experience, resulting in higher conversion rates and increased revenue.
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, but by prioritizing the key elements of ecommerce SEO, you ensure that your product pages are always optimized for success.
Implement these practices today and watch your ecommerce site reach new heights in search engine rankings, traffic, and sales.
Every Product Has a Buyer—We Help Them Find It
With Nexa Growth’s product page SEO, your listings stand out, rank better, and sell more.
Contact Us
