- Identify high-intent keywords that match your e-commerce products.
- Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, and SEMrush for in-depth research.
- Segment keywords by product category, buyer intent, and search volume.
- Continuously track keyword performance and refine your strategy.
If you’re running an online store, you already know that traffic is everything. But not just any traffic, you need qualified visitors who are actively searching for what you sell.
That’s where keyword research for e-commerce comes in. Done right, it can be the difference between a store that struggles to get clicks and one that ranks consistently, attracts buyers, and scales profitably.
Think about this: 68% of online experiences begin with a search engine. Yet, many e-commerce businesses are still guessing which terms their customers are typing into Google.
Without proper keyword targeting, your products could remain invisible—no matter how good they are.
Unlike general SEO, e-commerce keyword research requires a more strategic, conversion-focused approach.
You’re not just optimizing for clicks—you’re optimizing for sales.
That means finding terms with commercial intent, mapping them to the right pages (product, category, blog), and continually refining your strategy based on performance.
This guide is designed to walk you through the entire keyword research process—from fundamentals to advanced strategies.
Whether you’re starting a new Shopify store, managing a growing catalog on WooCommerce, or trying to beat out competitors on Amazon, you’ll find practical steps, tools, and insights to give you an edge.
By the end, you won’t just know how to find keywords—you’ll know how to use them to grow your business.
Let’s get started!
Discover the Search Terms Your Customers Are Using
Our E-commerce keyword strategies put your products in front of buyers, not just browsers.
Contact UsUnderstanding the Core Elements of Keyword Research
Before diving into tools and tactics, it’s important to understand the foundational concepts that drive effective keyword research for e-commerce.
These aren’t just SEO terms—they’re the pillars that help you identify the right keywords, attract the right audience, and ultimately convert visits into sales.
Search Intent
Every keyword represents a type of intent. In e-commerce, the most valuable keywords are typically those with transactional or commercial intent.
These are search queries from people who are actively looking to buy or compare products.
For example, someone searching for “buy noise cancelling headphones” is much closer to making a purchase than someone typing “how do noise cancelling headphones work.”
Understanding this difference allows you to prioritize keywords that align with your revenue goals.
Keyword Types
Not all keywords are created equal. Short-tail keywords (like “headphones”) have high search volumes but are extremely competitive and often vague.
Long-tail keywords (like “wireless noise cancelling headphones for travel”) may have lower volume, but they tend to convert better due to their specificity.
You’ll want a mix of both in your strategy, with a strong emphasis on long-tail terms for product and category pages.
Search Volume and Seasonality
Search volume indicates how often a keyword is searched each month. It’s a useful metric, but context matters.
A keyword with 500 monthly searches but strong buyer intent may be more valuable than a vague keyword with 5,000.
Seasonality is also key—search demand for some products can spike during holidays or certain times of year. Use tools like Google Trends to spot seasonal patterns.
Keyword Difficulty and Competition
Keyword difficulty measures how hard it will be to rank on the first page for a particular term.
While high-difficulty keywords can be tempting, they often require significant domain authority and backlink support.
A balanced approach means targeting lower-difficulty keywords that offer quick wins, while slowly building toward more competitive terms.
CPC and Buyer Intent
Cost-per-click (CPC) can offer a hint at how valuable a keyword is. Higher CPCs often indicate that advertisers are willing to pay for that traffic, which usually signals strong buyer intent.
It’s a helpful data point, especially when deciding between keywords with similar volume.
Featured Article: How Product Schema Markup Benefits E-commerce Websites
How to Do Keyword Research for E-commerce
Now that you understand the core elements, it’s time to apply them. Effective keyword research for e-commerce is both creative and analytical—it starts with brainstorming and ends with data-driven decisions.
Here’s a step-by-step process you can follow to build a keyword list that drives qualified traffic to your store.
Step 1: Brainstorm Seed Keywords Based on Your Products
Begin with what you know best—your product catalog. Your seed keywords are simple terms that describe your main product categories and offerings.
If you sell sustainable beauty products, some obvious seed keywords might include “organic face wash,” “vegan moisturizer,” or “cruelty-free sunscreen.”
You don’t need a huge list to start. Just focus on your primary product lines, bestsellers, and key categories.
Step 2: Expand Keyword Ideas Using Tools
Once you have your seed keywords, use keyword research tools to generate related terms. Here are a few effective methods:
Use Keyword Tool Suggestions
Plug your seed keywords into platforms like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, Semrush, or Ubersuggest. These tools will generate hundreds (or thousands) of keyword ideas related to your product terms.
Look for patterns and note keywords with strong commercial or transactional intent.
Leverage Competitor Analysis
Enter a competitor’s domain into a keyword research tool to uncover what they’re ranking for. This is a goldmine for discovering keywords you may have missed.
Look especially at their product pages, category pages, and blog content. You’ll often find low-hanging fruit—keywords that are ranking but not being fully optimized.
Analyze Auto-Suggest and People Also Ask
Don’t overlook Google itself. Type your seed keywords into the search bar and take note of the auto-suggested phrases. These are based on real searches and can reveal long-tail variations.
Also, check the “People Also Ask” and “Related Searches” sections at the bottom of search results.
Step 3: Filter and Qualify Your Keyword List
By this point, you might have hundreds of potential keywords. Now it’s time to filter them based on what matters most to your business.
By Search Intent
Prioritize keywords that show clear purchase intent. Phrases like “best,” “cheap,” “buy,” “discount,” or “reviews” often signal that the user is in buying mode.
By Difficulty and Relevance
If your site is newer or has lower domain authority, focus on lower-competition keywords to gain traction quickly. Relevance also matters—a keyword with high volume is useless if it doesn’t closely match what you’re selling.
By Commercial Value
Review the CPC data to get a sense of how valuable a keyword might be to advertisers. While not always precise, a higher CPC generally points to higher buyer intent and revenue potential.
Step 4: Map Keywords to the Right Pages
Finding the right keywords is only half the battle.
The other half is knowing where to use them. Keyword mapping is the process of assigning keywords to specific pages on your site, ensuring that each page is optimized for a unique set of relevant search terms.
This improves your chances of ranking and prevents keyword cannibalization—where multiple pages on your site compete for the same term.
Home Page
Your homepage should target broad, high-level terms that reflect your overall brand and value proposition.
These are usually branded terms or high-volume keywords that describe your niche at a macro level—like “affordable home gym equipment” or “organic skincare products.”
Category Pages
Category pages are where you can target medium-tail keywords that describe product groupings.
For example, if you sell fitness gear, a category page might target “adjustable dumbbells” or “resistance bands for beginners.”
These pages are SEO goldmines because they sit between the homepage and product pages in your site structure and often attract users at the consideration stage of the buying process.
Product Pages
These are ideal for long-tail, highly specific keywords that include product names, models, colors, sizes, or use cases.
Someone searching “32 oz stainless steel insulated water bottle” has high purchase intent—and your product page should be optimized for that exact phrase, if applicable.
Use these terms in the product title, description, image alt tags, and meta information.
Blog and Educational Content
Not every keyword deserves a product page. Informational or top-of-funnel keywords should be targeted through blog content, guides, and comparison articles.
For instance, “how to choose the best running shoes” could be a blog post that links to your product pages. This kind of content helps attract traffic earlier in the customer journey and builds topical authority.
Avoid Overlap and Redundancy
Make sure that each page targets a distinct set of keywords. Overlapping keywords between pages can confuse search engines and dilute your rankings.
Use a spreadsheet or keyword mapping tool to track which terms are assigned to which URLs.
Mapping is strategic. When done correctly, it creates a strong keyword-to-page alignment that improves user experience and sends clearer ranking signals to search engines.
Featured Article: What Is Local SEO, and Why Does It Matter?
Advanced Keyword Strategies for E-commerce SEO
Once you’ve covered the basics, it’s time to go beyond the standard approach.
These advanced strategies can help you uncover hidden opportunities, rank for competitive terms, and build a sustainable SEO advantage in your niche.
Keyword Golden Ratio (KGR)
The Keyword Golden Ratio is a method for identifying low-competition keywords that can rank quickly—even for new websites.
The formula compares the number of Google results with the exact phrase in the title to the search volume. If the ratio is below 0.25, the keyword is considered a strong opportunity.
This is particularly useful for long-tail keywords where the competition is lower, and buyer intent is often higher.
While it’s not a silver bullet, using the KGR can help you identify topics that others are overlooking and get content ranked faster.
Long-Tail Targeting for Product Variations
E-commerce stores often carry multiple versions of a product—different sizes, colors, materials, or use cases.
Each of these can be an opportunity to rank for a unique long-tail keyword. For example, instead of just targeting “yoga mat,” you can optimize separate product pages or sections for:
“non-slip yoga mat for hot yoga”
“extra thick yoga mat for bad knees”
“eco-friendly travel yoga mat”
These long-tail variations often have lower competition and appeal to users with specific needs, making them more likely to convert.
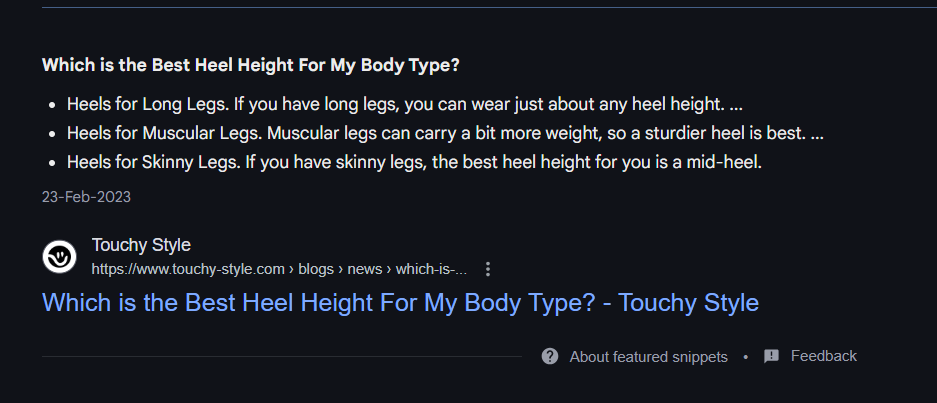
Zero-Click SERPs and Featured Snippets
Google is increasingly showing featured snippets, People Also Ask boxes, and other elements that can steal clicks away from organic results. But these features also represent an opportunity.
By formatting your content clearly—using lists, tables, and concise answers—you increase the chance of being featured in these areas.
For example, writing a blog post titled “5 Best Protein Powders for Women” with bullet points and clear headings could land you a featured snippet for related searches.
Gap Analysis: Find What Your Competitors Missed
Gap analysis is the process of identifying keywords your competitors are ranking for—but you’re not. Many keyword tools allow you to enter your domain and compare it to one or more competitors.
This can reveal content gaps, overlooked product terms, or informational queries that you haven’t covered yet.
When you find these gaps, prioritize them based on intent and relevance, then create targeted pages or blog content to fill them.
It’s one of the most efficient ways to catch up or even leap ahead of competitors without reinventing your strategy from scratch.
Evergreen and Seasonal Planning
Some keywords perform year-round, while others spike during specific seasons. Smart stores create content calendars that reflect both.
Evergreen content keeps delivering traffic over time, while seasonal content—like “best gifts for runners” or “summer skincare essentials”—can drive short-term spikes in traffic and sales.
Combining both ensures a steady flow of relevant traffic all year long.
Rank for What People Actually Type
Generic keywords don’t sell. Nexa Growth helps you target the keywords that close the deal.
Contact UsTools to Supercharge Your E-commerce Keyword Research
Even the most skilled marketers rely on the right tools to streamline keyword research, uncover hidden opportunities, and analyze competitors.
There’s no single “best” tool—it depends on your goals, platform, and budget. Below is a curated mix of industry-standard platforms and niche-specific options that can help you build a smarter e-commerce SEO strategy.
Ahrefs
Ahrefs is a powerful all-in-one SEO suite. Its Keyword Explorer tool provides detailed metrics on search volume, keyword difficulty, clicks, and return rate.
What sets it apart is its robust competitor analysis features.
You can easily reverse-engineer top-performing pages from your competitors, identify content gaps, and see what keywords are driving their traffic.
Ahrefs also includes a SERP overview for each keyword, showing who ranks, how strong their backlinks are, and what you’re up against.
Semrush
Semrush is another industry favorite, known for its broad feature set and user-friendly interface. In addition to keyword research, it offers tools for site audits, backlink analysis, and position tracking.
Its Keyword Magic Tool makes it easy to generate thousands of keyword ideas, and the Keyword Gap tool is excellent for comparing your domain with up to five competitors to find untapped opportunities.
Google Keyword Planner
This free tool from Google Ads is useful for getting basic search volume data and discovering new keyword variations.
While the volume ranges are often broad, it’s still a good starting point for brainstorming seed keywords and understanding advertising competition.
If you’re running paid search campaigns alongside your organic strategy, this tool is especially valuable.
Google Search Console
This is one of the most underrated tools for keyword discovery.
Google Search Console shows you which queries are already driving impressions and clicks to your site—even if you’re not ranking on the first page yet.
Use it to identify low-hanging fruit: keywords where you rank on page 2 or 3 and can move up with a bit of optimization.
Helium 10 and Jungle Scout (for Amazon sellers)
If you sell on Amazon, traditional keyword tools aren’t enough.
Helium 10 and Jungle Scout are tailored to Amazon SEO, helping you discover high-converting keywords based on actual Amazon search data.
These platforms also provide competitive insights, product trends, and backend keyword optimization tools for listings.
Keywords Everywhere
This browser extension overlays keyword data directly into your Google search results.
It shows metrics like volume, CPC, and competition in real time, helping you validate keyword ideas without jumping between tools. It’s lightweight, affordable, and great for day-to-day research.
Featured Article: What Is E-commerce SEO? How Is It Different?
Optimizing Your E-commerce Site Using Keywords
Once you’ve built a strong keyword list and mapped those keywords to the right pages, the next step is execution—actually integrating those terms into your site in ways that boost visibility without hurting usability.
Effective on-page optimization is both technical and creative. It’s not just about sprinkling keywords around—it’s about positioning them where they matter most.
Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
Your title tag is often the first thing a searcher sees. It should include your primary keyword and communicate what the page is about. Keep it under 60 characters to avoid truncation in search results.
Meta descriptions don’t directly impact rankings, but they do influence click-through rates.
Write clear, compelling descriptions that naturally include your keywords and entice users to click. Aim for 150–160 characters.
URLs
Clean, readable URLs help both users and search engines. Use keywords in your URLs where appropriate, but avoid keyword stuffing. For example:
yourstore.com/mens-running-shoes
is better than
yourstore.com/product?id=29374
Headings (H1, H2, H3)
Use headings to structure your content and make it easier to scan. Your H1 tag should contain the primary keyword for the page. Subheadings (H2s and H3s) can include secondary or related terms.
This structure not only improves SEO but also enhances readability—especially important for mobile users.
Product Descriptions
Too many e-commerce stores use manufacturer-provided descriptions, which can lead to duplicate content issues.
Create unique, keyword-rich descriptions for each product. Focus on benefits as well as features, and include relevant long-tail keywords where they make sense.
Avoid keyword stuffing by writing naturally. If your product solves a problem or caters to a niche audience, describe it in those terms.
Image Alt Text and File Names
Images are a key part of e-commerce pages, and optimizing them can drive traffic from image search as well. Use descriptive file names and alt text that include relevant keywords.
For example, instead of img123.jpg, use womens-black-ankle-boots.jpg.
Internal Linking
Linking related products, categories, and blog posts to each other helps distribute page authority and keeps users engaged longer.
Use descriptive anchor text that includes keywords. For instance, link with “view all waterproof hiking boots” instead of just “click here.”
Structured Data and Schema Markup
Implement schema markup to enhance your product listings in search results with rich snippets. These can include ratings, price, availability, and more.
This doesn’t directly affect rankings but can significantly improve click-through rates by making your listings stand out.
Your Products Deserve to Be Found
With expert keyword research, we help each item get discovered in the moments that matter most.
Contact UsMeasuring Results and Refining Your Keyword Strategy
Keyword research for e-commerce doesn’t end once your pages are optimized. Continuous tracking, analysis, and adjustment are key to long-term success.
The digital landscape changes rapidly, and your SEO strategy must evolve along with it. Here’s how to measure your results and refine your approach to stay ahead of the competition.
Track Keyword Rankings
The first step in evaluating your keyword strategy is to monitor your rankings.
Tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, and Google Search Console provide detailed reports on how your pages are performing for your target keywords.
Track both the rankings for individual keywords and the overall search visibility of your site.
Pay attention to:
- Movements in rankings: Are your target keywords moving up or down? Regularly tracking changes helps you understand what’s working and what’s not.
- Top-performing pages: Identify which pages are bringing in the most traffic and focus on optimizing those further. If certain product or category pages are driving sales, ensure they’re fully optimized and maintained.
Analyze Organic Traffic
Keyword rankings are important, but traffic numbers tell you how well your site is converting visitors. Google Analytics can show you which keywords and pages are driving organic traffic.
By identifying patterns in the traffic—such as time on page, bounce rate, and conversion rate—you can better understand user behavior and make more informed decisions.
Look for:
- High-traffic, low-conversion pages: If a page is getting significant traffic but not converting, it might need better copy, CTAs, or clearer navigation to product pages.
- Content gaps: Is there a keyword cluster with lots of traffic but not much content? It could be time to add more targeted blog posts, guides, or category pages.
Measure Conversions and Revenue
At the end of the day, traffic doesn’t matter if it doesn’t lead to sales.
Track the conversion rate for the keywords you’re targeting. Google Analytics, combined with e-commerce platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce, can help track conversions from organic search.
Some key metrics to monitor:
- Revenue per visit (RPV): This helps you understand how much revenue each visit generates from organic traffic.
- Goal completions: Track specific goals like adding a product to the cart, initiating checkout, or completing a purchase.
- Customer lifetime value (CLV): Use keyword performance data to identify which keywords bring in high-value customers who return and make repeat purchases.
Refine Your Keyword Strategy
Based on the data you gather, it’s time to adjust your keyword strategy.
If certain keywords aren’t delivering the desired results, try experimenting with different variations, adjusting on-page optimization, or updating content.
Here are some tips for refining your strategy:
- Focus on high-intent keywords: If you’re targeting informational keywords but not seeing conversions, it might be time to focus more on transactional or commercial keywords that reflect buyer intent.
- Adjust for seasonality: If you see dips in traffic due to seasonal changes, update your content and product pages to align with demand shifts. For example, prepare in advance for holidays or annual events.
- Repurpose top-performing content: If a blog post or product page is performing well, consider repurposing that content into videos, infographics, or social media posts to reach a broader audience.
Conclusion
Keyword research for e-commerce is an ongoing process that requires a combination of creativity, strategy, and constant refinement.
By understanding your audience, analyzing competitors, and using the right tools, you can uncover valuable keywords that drive targeted traffic and boost conversions.
It’s important to remember that SEO success doesn’t happen overnight.
Consistently optimizing your website and tracking your performance will allow you to adjust your strategy, stay ahead of the competition, and ultimately achieve sustainable growth.
Whether you’re just starting your e-commerce journey or looking to refine your existing strategy, effective keyword research is the foundation of driving organic traffic and reaching the right customers at the right time.
Keep experimenting, learning, and adapting—and you’ll be on your way to long-term SEO success.
Your SEO Strategy Starts With the Right Words
We research, segment, and prioritize the keywords that drive bottom-line results.
Contact Us
