- E-commerce SEO is the process of optimizing an online store to improve its search engine visibility and increase sales.
- Organic search is a powerful channel for e-commerce, accounting for over 53% of all trackable website traffic.
- Key pillars of a successful strategy include smart keyword research, technical SEO, and site architecture.
- E-commerce SEO differs from traditional SEO due to a large number of product pages and complex site structures.
- Best practices include creating unique product content, refreshing existing content, and targeting high-intent keywords to convert traffic into sales.
If you run an online store, showing up in search results isn’t optional—it’s essential.
E-commerce SEO is the process of optimizing your online store to improve its visibility in search engines like Google, Bing, and others.
The goal is simple: to attract more qualified traffic, convert that traffic into paying customers, and ultimately increase revenue without relying heavily on paid ads.
Organic search is one of the most powerful channels for e-commerce growth. According to a study by BrightEdge, over 53% of all trackable website traffic comes from organic search.
For e-commerce sites specifically, Google remains the top source of discovery, with product searches starting on Google more often than on Amazon.
That means ranking on the first page for relevant search terms can directly impact your sales volume.
Unlike traditional SEO, e-commerce SEO has unique challenges and opportunities.
You’re not just optimizing a few service pages and blog posts—you’re dealing with hundreds or thousands of product pages, complex site structures, and technical considerations like canonical tags, duplicate content, and crawl efficiency.
In this guide, you’ll learn exactly how e-commerce SEO works, why it matters, and how to build a strategy that improves rankings, drives qualified traffic, and boosts conversions in 2026 and beyond.
Whether you’re a B2B or B2C business, selling niche products or managing a large catalog, this guide will walk you through every critical element.
Ready to build an online store that ranks, converts, and scales? Let’s get started.
Don’t Get Lost in a Sea of Products
Nexa Growth helps your store and product pages rank higher—so you attract shoppers, not just traffic.
Contact UsWhat Is E-commerce SEO and Why Does It Matter?
E-commerce SEO is the practice of optimizing an online store to increase its visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs) for relevant keywords.
It involves a combination of strategies, including keyword research, technical optimization, content creation, and link building, all tailored to the structure and needs of an e-commerce website.
The ultimate goal is to drive more organic traffic to product and category pages, helping customers find your store when they’re actively searching for the products you sell.
Unlike paid ads, which stop bringing in traffic once the budget runs out, organic SEO continues to deliver long-term results with consistent effort.
E-commerce SEO matters because most online shoppers begin their journey with a search engine. According to Think with Google, 49% of shoppers say they use Google to discover new items or products.
If your store isn’t appearing near the top of those results, you’re missing out on significant sales opportunities.
Additionally, SEO offers higher ROI compared to many other channels. Organic traffic tends to be more qualified since users are actively searching for products you offer.
Plus, investing in SEO builds equity in your website over time, making your brand more resilient to market fluctuations and rising advertising costs.
By prioritizing e-commerce SEO, you’re not just improving your search rankings—you’re aligning your business with the way people shop today.
It positions your store to compete effectively, grow sustainably, and reduce reliance on short-term promotional tactics.
Featured Article: How to Write Meta Descriptions: Tips and Examples 2026
How E-commerce SEO Works
E-commerce SEO works by aligning your website with how search engines evaluate and rank content.
Search engines like Google aim to provide users with the most relevant, high-quality results for their queries.
For e-commerce websites, this means optimizing not only for relevance and authority but also for technical performance and user experience.
The process begins with crawling, where search engine bots scan your site’s pages. Then comes indexing, where those pages are stored in the search engine’s database.
Finally, in the ranking stage, the engine decides which pages to show for a given search query, and in what order.
E-commerce sites must ensure that product, category, and informational pages are all easily crawlable, indexable, and optimized for the right keywords.
Here’s how the core elements work together:
- Keyword targeting helps ensure your product and category pages appear in searches with purchase intent. These include terms like “buy running shoes online” or “best DSLR cameras under $1000.”
- On-page SEO involves optimizing titles, meta descriptions, headers, and product descriptions to be both keyword-relevant and user-friendly.
- Technical SEO ensures your site loads fast, is mobile-friendly, uses clean URLs, and avoids issues like duplicate content or broken links that can harm rankings.
- Site structure and internal linking help search engines understand the relationship between pages and distribute authority across the site, making it easier for important pages to rank.
- Content and backlinks boost authority by signaling to search engines that your site is trustworthy and valuable. Blogs, buying guides, and educational resources also help capture traffic earlier in the customer journey.
Google uses over 200 ranking factors, and while not all of them are disclosed, experience shows that well-structured, content-rich, and technically sound e-commerce websites perform better.
With more than 12 to 24 million e-commerce sites online globally, a well-executed SEO strategy helps you stand out in a crowded digital marketplace.
Featured Article: How Does SEO Work? (Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking Explained)
B2B vs. B2C E-commerce SEO: What’s the Difference?
While the fundamentals of SEO apply to both B2B (business-to-business) and B2C (business-to-consumer) e-commerce websites, the strategies and tactics often differ due to variations in buyer behavior, search intent, and sales cycles.
Search intent is one of the most significant differences. B2C customers typically look for immediate purchases.
Their queries often include product-focused keywords such as “best wireless earbuds” or “buy yoga mat online.” These are shorter sales cycles with decisions made quickly, often on emotion, price, or brand recognition.
In contrast, B2B buyers conduct more extensive research before committing to a purchase.
Their queries are more specific and technical, and they often search for solutions rather than products, like “bulk order inventory management software” or “industrial-grade 3D printers for manufacturing.”
Sales cycles in B2B can span weeks or even months, involving multiple decision-makers.
Keyword strategy also varies.
B2C SEO usually focuses on high-volume, transactional keywords, while B2B SEO leans more heavily into long-tail keywords and informational content.
A B2B site might need to rank for terms relevant to case studies, white papers, or comparison pages to educate prospects.
Content formats reflect these differences. B2C content often includes short product descriptions, customer reviews, and visually rich media.
B2B websites benefit from in-depth content like technical documentation, industry-specific blog posts, and gated assets such as PDFs or webinars that capture leads.
Site structure and navigation also play a role. B2C sites often prioritize ease of use and fast checkout, while B2B sites might emphasize request-a-quote features, contact forms, or account-based pricing.
Ultimately, both B2C and B2B e-commerce SEO aim to connect searchers with solutions. But understanding the buyer’s mindset and tailoring your SEO approach accordingly can make a significant difference in rankings, traffic quality, and conversion rates.
Don’t Let Your Competitors Outrank You on Your Own Products
We help you reclaim rankings, visibility, and sales with laser-focused SEO for your store.
Contact Us7 Core Pillars of a Successful E-commerce SEO Strategy
Building an effective e-commerce SEO strategy requires more than just plugging in keywords.
It’s a holistic effort that spans technical performance, content, site architecture, user experience, and off-site authority.
Here are the seven foundational pillars that every successful e-commerce SEO plan should include:
-
Smart Keyword Research
Keyword research is the foundation of e-commerce SEO. The goal is to identify the terms your potential customers are using when searching for products like yours. These include:
- Transactional keywords: “buy leather boots,” “cheap gaming laptop”
- Navigational keywords: “Nike running shoes,” “IKEA bed frame”
- Informational keywords: “how to choose a DSLR camera,” “best phones under $500”
It’s important to research keywords at the product, category, and blog content level. Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Semrush, Ahrefs, and Amazon’s autocomplete suggestions to find terms with strong intent and manageable competition.
Don’t overlook long-tail keywords—they may have lower search volume but typically come with higher intent and better conversion rates.
-
Technical SEO for E-commerce
Technical SEO ensures that search engines can properly crawl, index, and understand your website.
For e-commerce, this is particularly critical due to the volume of product pages and frequent changes in inventory.
Key areas to focus on include:
- Site speed: Load times under 3 seconds are crucial
- Mobile-friendliness: Over 60% of shoppers browse via mobile
- Secure browsing: HTTPS is a must
- Structured data: Use schema markup to enhance product listings with reviews, prices, and availability
- Canonical tags: Prevent duplicate content caused by filters and sorting
- XML sitemaps and robots.txt: Help search engines index your pages properly
Crawl errors, broken links, and slow-loading pages all hurt rankings and user experience. Regular technical audits help keep your site healthy.
-
Site Architecture & Internal Linking
A clear and logical site structure not only helps users navigate but also allows search engines to crawl your site more efficiently. A strong e-commerce site structure typically follows a simple hierarchy:
- Homepage → Category Pages → Subcategory Pages → Product Pages
Each level should include optimized internal links using keyword-rich anchor text. Implement breadcrumb navigation to reinforce site hierarchy and enhance internal linking.
Avoid creating orphan pages (pages not linked from anywhere on the site), and use filters and facets carefully to avoid generating too many duplicate URLs.
-
On-Page Optimization
On-page SEO involves optimizing individual elements on each page to ensure they’re relevant, user-friendly, and keyword-aligned. For e-commerce, focus on:
- Title tags and meta descriptions: Include primary keywords and calls to action
- Product descriptions: Write unique, benefit-focused copy instead of copying manufacturer content
- Header tags (H1, H2, etc.): Organize content clearly
- Image optimization: Use descriptive alt text and compress files for fast loading
- URL structure: Keep URLs short, readable, and keyword-rich
Each product and category page should be treated as a potential landing page—optimized not only for search engines, but also for users looking to convert.
-
Content Marketing for E-commerce
Content marketing supports e-commerce SEO by attracting traffic at earlier stages in the buyer journey and by earning backlinks. High-performing content formats include:
- Buying guides and product comparisons
- “How-to” blog posts
- Seasonal gift guides
- FAQs and troubleshooting articles
Use content to build topical authority around your niche. For example, a fitness equipment store could publish articles on home workout routines, gear maintenance, and nutrition tips.
Content also keeps users engaged, reduces bounce rates, and opens opportunities to rank for informational keywords that your competitors may overlook.
-
UX & Conversion-Focused Design
Google takes user signals into account when ranking pages, so SEO and user experience (UX) go hand in hand. A well-optimized product page should also convert. Best practices include:
- Fast-loading, mobile-responsive pages
- Clear CTAs (e.g., “Add to Cart,” “Buy Now”)
- Trust signals like reviews, security badges, and return policies
- Simple, intuitive navigation and search functions
- Persistent shopping cart visibility
Reducing friction across the shopping experience not only improves SEO but also boosts sales.
-
Backlink Building
Backlinks from reputable websites signal authority and trust to search engines. While more challenging for e-commerce than for other types of sites, link building is still essential. Strategies include:
- Publishing link-worthy content like data studies, tools, and guides
- Reaching out to industry blogs, reviewers, and influencers
- Getting listed in relevant directories
- Earning links from suppliers or brand partners
- Reclaiming unlinked brand mentions
A strong backlink profile increases your domain authority and helps category and product pages rank more effectively.
Featured Article: How Long Does SEO Take to Show Results? A Realistic Timeline
E-commerce SEO Best Practices for 2026
SEO is constantly evolving, and what worked two years ago may not be enough today. As search engines get smarter and competition grows, staying ahead means adopting up-to-date, effective tactics.
Here are the best practices to follow to ensure your e-commerce site ranks well and drives sustainable growth.
-
Define Buyer Personas Before Starting Keyword Research
Knowing your audience is essential for targeting the right keywords. Develop clear buyer personas based on demographics, purchase behaviors, pain points, and search habits.
Are your customers looking for the cheapest option, the most premium product, or expert advice?
Understanding their motivations allows you to match content and product listings with the specific terms they use in search, making your SEO far more targeted and effective.
-
Create Unique and Valuable Product Content
One of the biggest mistakes in e-commerce is duplicating manufacturer descriptions across hundreds of product pages. Search engines value originality, and duplicate content can hurt your rankings.
Write unique product titles and descriptions for each item. Highlight benefits, answer common questions, and use customer-friendly language. Where possible, include keywords naturally without stuffing.
-
Update and Refresh Content Regularly
Outdated content can lead to traffic drops and lower conversions. Set up a content review schedule—especially for blog posts, buying guides, and category pages.
Refreshing older pages with updated statistics, trends, and optimized keywords can improve rankings without the need to publish entirely new content.
It also signals to search engines that your site is active and relevant.
-
Target Low-Volume, High-Intent Keywords
High-volume keywords are attractive, but they often come with fierce competition. Low-volume, long-tail keywords—like “eco-friendly hiking boots for women” or “organic dog treats subscription box”—can drive highly qualified traffic.
These keywords tend to reflect specific intent, which means users are closer to converting. Incorporating them into product and blog content is a smart way to capture untapped demand.
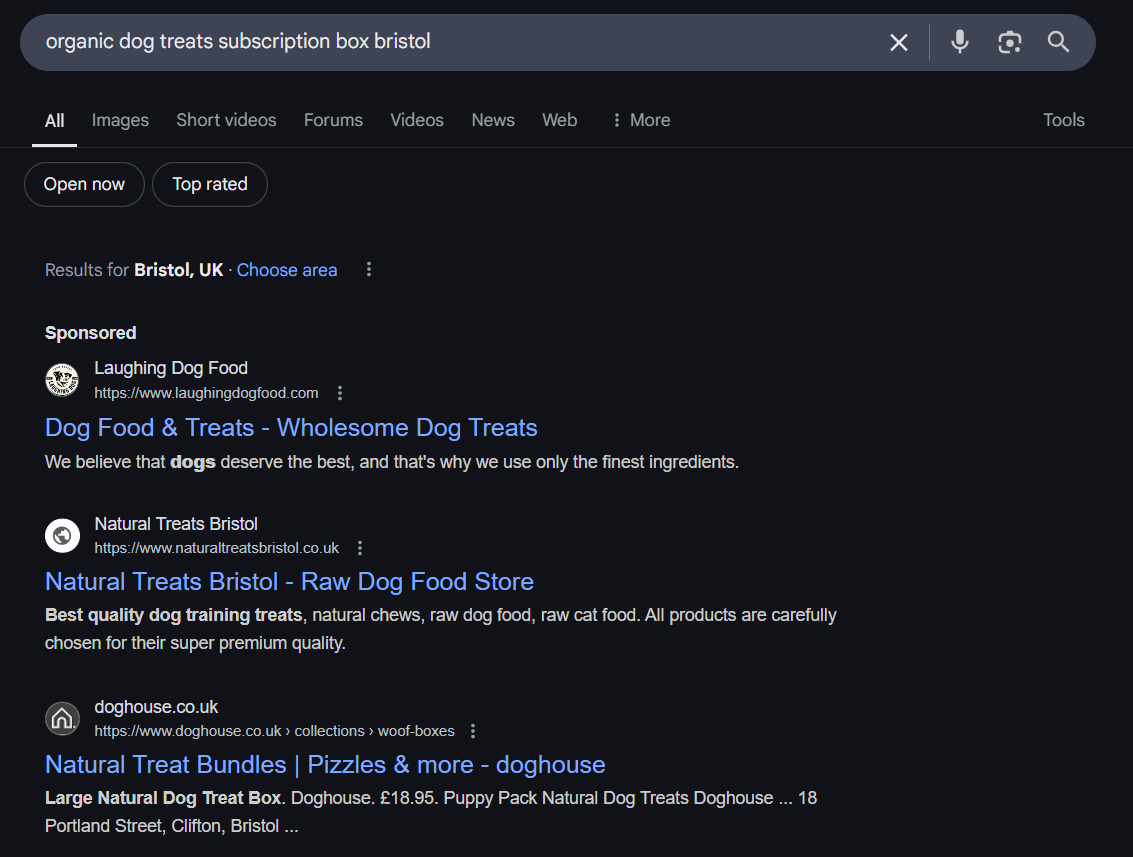
An Example of a Long-Tail Keyword -
Build High-Quality Backlinks With Content Worth Sharing
The best backlinks come from content that provides real value. Create in-depth guides, data reports, product comparisons, or interactive tools that your industry will want to reference and link to.
Promote your content through outreach, social channels, and partnerships with influencers or bloggers. Link building is about building relationships and authority, not shortcuts.
-
Optimize for Search Features and Rich Results
Google is showing more than just blue links in its results—product carousels, FAQ boxes, reviews, and pricing data now take up significant SERP space. Use schema markup (structured data) to enhance your product listings with:
- Product name and image
- Ratings and reviews
- Price and availability
- FAQs and shipping info
Rich results increase visibility, click-through rates, and trust in your listings.
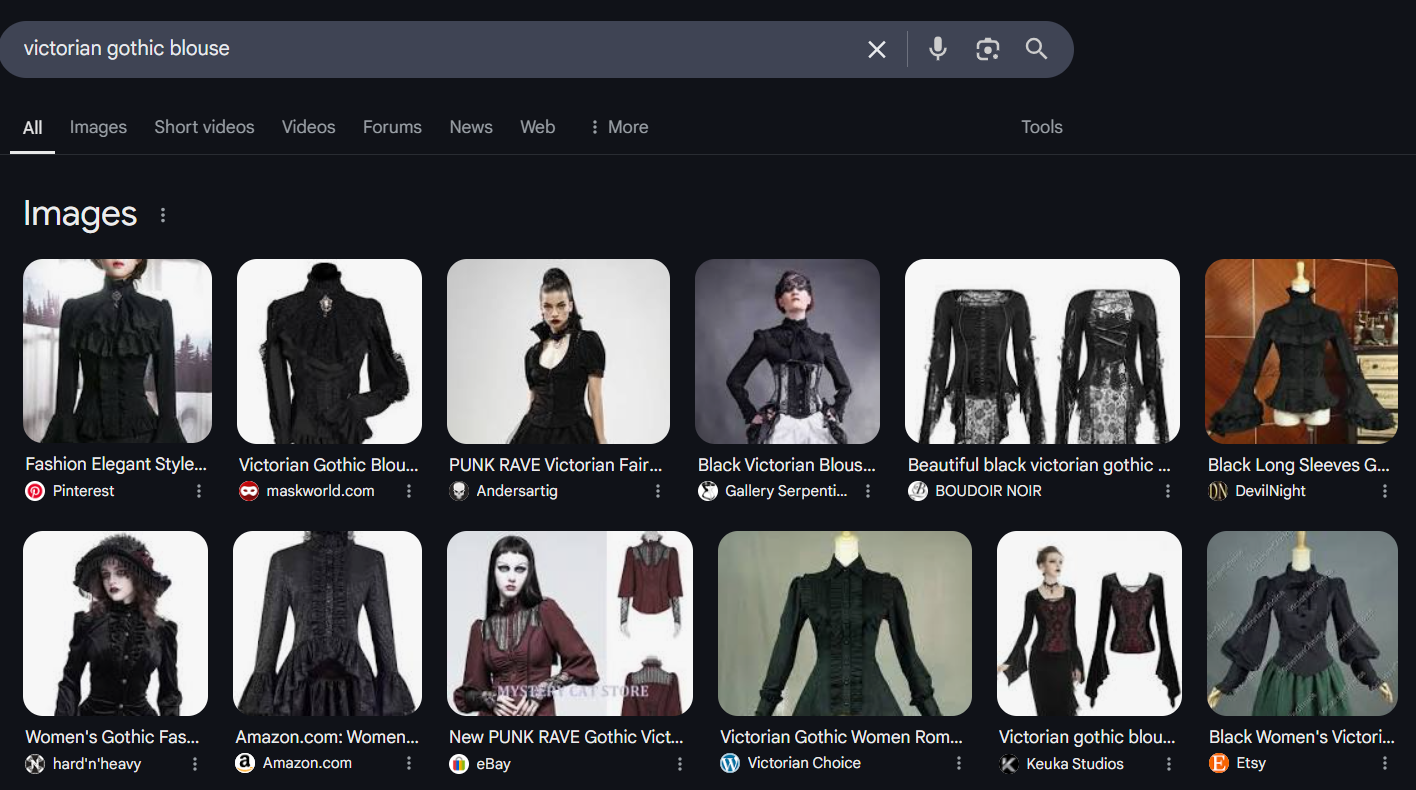
Google’s Rich Results -
Improve Core Web Vitals and Mobile Experience
Core Web Vitals—metrics related to page speed, interactivity, and visual stability—are now ranking factors. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse to monitor and improve:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- First Input Delay (FID)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Since the majority of shoppers use mobile devices, prioritize responsive design, fast-loading images, and seamless mobile navigation.
Featured Article: Core Web Vitals: How to Optimize for Better Performance in 2026
Common E-commerce SEO Challenges and How to Overcome Them
E-commerce SEO offers high rewards, but it’s not without its challenges. Online stores deal with unique complexities—from massive product catalogs to technical issues and duplicate content.
Understanding these obstacles and addressing them proactively is key to long-term SEO success.
-
Thin or Duplicate Product Content
Many e-commerce sites rely on manufacturer descriptions or copy the same text across multiple products with slight variations. This creates thin or duplicate content, which search engines tend to deprioritize.
Solution: Invest time in writing unique, helpful product descriptions. Where appropriate, add comparison tables, FAQs, user-generated content, or videos. This not only boosts SEO but also improves conversion rates by providing more value to the shopper. -
Complex Site Architecture and Poor Crawlability
With thousands of products, filters, and category levels, it’s easy for your site structure to become bloated and difficult for search engines to crawl efficiently.
Unoptimized navigation can result in orphaned pages, crawl traps, and wasted crawl budgets.
Solution: Use a flat, logical site architecture that limits the number of clicks from the homepage to product pages. Set clear internal linking strategies and submit a dynamic XML sitemap. Use tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to audit crawlability regularly. -
Slow Page Load Times
Page speed is a confirmed ranking factor and directly affects bounce rates and conversions. If your site takes too long to load—especially on mobile—users are likely to leave before engaging.
Solution: Compress images, use lazy loading, implement a content delivery network (CDN), and minimize JavaScript where possible. Monitor performance through Google PageSpeed Insights and prioritize fixing issues that impact Core Web Vitals. -
Poorly Managed Faceted Navigation and Filters
Filters like size, color, and price can generate thousands of unique URLs, which may cause duplicate content and indexing issues if not handled correctly.
Solution: Use canonical tags, noindex directives, or parameter handling in Google Search Console to control how filter-generated URLs are crawled and indexed.Create SEO-friendly landing pages for high-value filtered combinations when relevant.
-
Inconsistent URL Structures and Broken Links
Messy URLs or outdated internal links can confuse both users and search engines. Broken links negatively affect user experience and diminish the perceived quality of your site.
Solution: Create clean, keyword-rich URLs without unnecessary parameters. Regularly audit internal and external links, and implement 301 redirects where needed.Maintain consistency in how URLs are formatted across your entire site.
-
Limited Link Building Opportunities
Compared to blogs or service sites, e-commerce stores may struggle to earn backlinks because their content is perceived as purely commercial.
Solution: Develop a content strategy that includes educational resources, buyer’s guides, expert roundups, and original research.These assets can attract natural backlinks and position your brand as a thought leader in your niche.
-
Tracking and Measuring ROI
SEO takes time, and it’s not always easy to connect improvements in rankings with sales outcomes, especially for long-tail or assisted conversions.
Solution: Set up proper attribution tracking using Google Analytics 4 and Search Console.Track SEO-specific KPIs like organic sessions, click-through rates, keyword positions, and revenue from organic traffic. Use dashboards to visualize performance trends over time.
Featured Article: Technical SEO Audit: The Complete Step-by-Step Guide (2026 Edition)
Key SEO KPIs for E-commerce Success
To evaluate the effectiveness of your e-commerce SEO efforts, it’s crucial to track the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
These metrics help you understand how well your website is performing in search results, how it’s driving traffic, and, most importantly, how that traffic converts into sales.
Here are the most important KPIs to monitor:
-
Organic Traffic
Organic traffic is the primary indicator of SEO success. It shows how many visitors are coming to your site via search engines.
Tracking the volume of organic traffic over time helps you gauge how well your SEO efforts are improving visibility and attracting relevant visitors.
What to track: Overall organic sessions, by page or category, and growth trends.Why it matters: An increase in organic traffic signals that your site is ranking higher for your target keywords and reaching more potential customers.
-
Keyword Rankings
Tracking how well your site ranks for specific keywords is fundamental to understanding the impact of your SEO strategy.
Focus on both high-volume and long-tail keywords related to your products and categories.
What to track: Keyword ranking changes, keyword visibility, and position in search results for primary product or category terms.Why it matters: If your rankings improve for targeted keywords, it directly correlates with an increase in organic traffic and conversions.
-
Click-Through Rate (CTR)
CTR is the percentage of people who click on your website from the search results compared to how many saw your link.
A higher CTR indicates that your titles, meta descriptions, and other on-page elements are compelling and relevant to users’ queries.
What to track: CTR for product pages, category pages, and blog posts.Why it matters: Improving CTR can help you drive more traffic and improve your ranking by signaling to search engines that your pages meet users’ needs.
-
Bounce Rate
Bounce rate refers to the percentage of visitors who land on a page and then leave without interacting with the site further.
A high bounce rate may indicate that users aren’t finding what they expect or that the page isn’t optimized for engagement.
What to track: Bounce rates for key landing pages, such as product and category pages.Why it matters: A lower bounce rate is a sign of good user experience and relevant content. Reducing bounce rates can help improve rankings and conversions.
-
Conversion Rate
Conversion rate is the percentage of visitors who take a desired action on your site, such as making a purchase, signing up for an email list, or completing a contact form.
What to track: Conversion rates for different product categories, landing pages, and traffic sources.Why it matters: Conversion rate optimization (CRO) and SEO work together. If your SEO drives traffic but you have a low conversion rate, you may need to optimize your site’s usability and user journey.
-
Average Order Value (AOV)
Average order value (AOV) is the average amount of money each customer spends per transaction.
Increasing AOV is an important metric for e-commerce stores looking to boost revenue without necessarily increasing traffic.
What to track: AOV over time, segmented by product category or traffic source.Why it matters: A higher AOV leads to greater revenue per sale, helping to offset marketing costs and improve ROI.
-
Organic Revenue
Organic revenue is the total revenue generated from organic search traffic. It’s a clear indication of how well your SEO strategy is converting visitors into actual sales.
What to track: Revenue from organic traffic, segmented by product categories and key landing pages.Why it matters: Organic revenue is the ultimate KPI for e-commerce SEO success, as it directly correlates with profitability. Monitoring this metric ensures that SEO investments lead to real business results.
-
Pages per Session
Pages per session is the average number of pages a user visits during a single session on your website.
A higher pages per session figure indicates that visitors are exploring multiple products or categories, which often leads to higher conversion rates.
What to track: Pages per session for key landing pages, product pages, and blog content.Why it matters: A higher pages per session rate signals good site navigation and user engagement, which can lead to better rankings and increased sales.
Featured Article: Mobile-First Indexing: How to Optimize Your Site in 2026
Conclusion: Putting Your E-commerce SEO Strategy into Action
Developing and implementing an effective e-commerce SEO strategy requires ongoing effort, consistency, and adaptation to ever-evolving search engine algorithms.
By focusing on key SEO pillars—such as technical optimization, content creation, user experience, and building authority—you’ll be able to build a solid foundation for long-term online visibility and success.
As the e-commerce landscape grows more competitive, it’s essential to stay on top of SEO trends and continuously optimize your website to meet user expectations.
SEO is not a one-time task; it’s a continuous process of refinement, testing, and adapting to changes in search behavior, algorithms, and your own business goals.
Remember, a successful e-commerce SEO strategy isn’t just about ranking higher for keywords—it’s about converting that traffic into sales, fostering customer loyalty, and driving sustainable growth.
By tracking the right KPIs, creating valuable content, and leveraging best practices, your online store can rise above competitors and capture valuable organic traffic.
Technical SEO Issues Are Costing You Customers
Slow speed, indexing errors, or bad site structure? We fix it all—so your eCommerce store performs like it should.
Contact Us
