- Duplicate content is identical or substantially similar content on multiple URLs, which can be internal or external.
- While not a direct penalty, it can lead to problems like ranking dilution, indexing issues, and weakened backlink profiles.
- Common causes include URL variations, HTTP vs. HTTPS inconsistencies, and scraped content.
- To fix it, use 301 redirects, canonical tags, or “noindex” tags.
- You can find duplicate content using tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, Copyscape, and Siteliner.
Imagine pouring countless hours into crafting high-quality content, only to find out that search engines are struggling to determine which version of your page to rank.
Even worse, your hard-earned traffic could be split across multiple versions of the same page—or worse, given to another site that copied your content.
Duplicate content issues are one of the most misunderstood yet critical SEO challenges businesses face today.
According to a 2020 study by Raven Tools, 29% of all web pages analyzed had some form of duplicate content.
Google itself has acknowledged that duplicate content is a natural part of the web, but when not handled correctly, it can lead to ranking dilution, poor indexing, and a loss in organic visibility.
So, what exactly is duplicate content, and why does it matter?
More importantly, how can you identify and fix these issues to improve your SEO performance?
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about duplicate content issues, including:
- The most common causes (some of which may surprise you)
- How duplicate content impacts search rankings
- Step-by-step methods to detect and fix duplicate content
- Best practices to ensure your content remains unique, authoritative, and optimized for search engines
By the end, you’ll have a clear, actionable plan to tackle duplicate content and improve your site’s search performance.
Let’s get started!
Missed Clicks = Missed Sales.
If you’re not ranking, you’re invisible. Let’s change that before you lose more business!
Contact UsWhat Are Duplicate Content Issues?
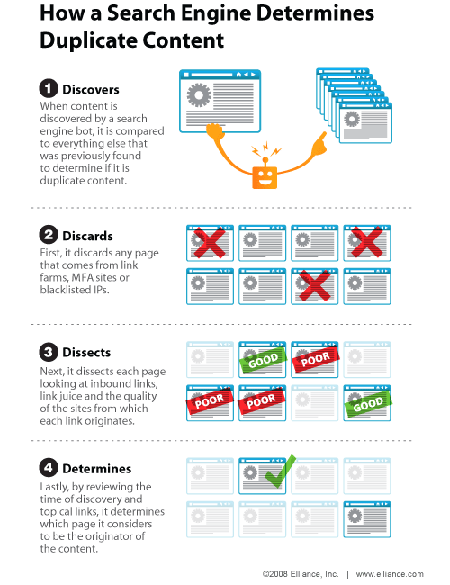
Duplicate content refers to substantially similar or identical content appearing in multiple locations (URLs) on the internet.
When search engines like Google encounter duplicate content, they struggle to determine which version to prioritize in search results.
This can lead to ranking dilution, misattributed authority, and decreased organic visibility.
Internal vs. External Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can exist in two primary forms:
- Internal Duplicate Content – This occurs when multiple pages within the same website contain identical or very similar content. Common causes include:
- URL variations due to tracking parameters or session IDs
- Printer-friendly pages creating duplicate versions
- HTTP vs. HTTPS or WWW vs. non-WWW inconsistencies
- Pagination and category filters on eCommerce sites
- External Duplicate Content – This happens when identical content appears on different domains. Common reasons include:
- Scraped or syndicated content copied by other websites
- Press releases or guest posts republished on multiple platforms
- Product descriptions copied across multiple reseller sites
Is Duplicate Content Always a Problem?
Not all duplicate content is bad. Google has stated that duplicate content itself does not result in a penalty.
Instead, it can cause search engines to consolidate ranking signals and choose a preferred version. However, when not managed properly, it can lead to:
- A loss of control over which page ranks for a keyword
- Search engines choosing the wrong page to display in results
- A weakened backlink profile as links get split across multiple versions
A 2022 study by Semrush found that 50% of eCommerce websites suffer from duplicate content issues, often due to auto-generated product descriptions and poor URL handling.
Understanding these challenges is the first step toward effectively managing duplicate content and optimizing your SEO strategy.
Featured Article: What Is SEO Writing? How to Write SEO-Friendly Content in 2026
Why Do Duplicate Content Issues Matter?
Duplicate content might not always lead to direct penalties, but it can have serious consequences for your website’s SEO performance.
If search engines struggle to determine the most relevant version of a page, your rankings, traffic, and authority can take a hit. Let’s break down why duplicate content matters for both search engines and website owners.
Impact on Search Engines
Search engines like Google aim to provide users with the most relevant, high-quality, and unique content in search results.
When multiple versions of the same content exist, it creates a dilemma: Which version should rank?
Here’s what happens behind the scenes:
- Ranking Dilution: When multiple versions of the same content exist, search engines may split ranking signals (such as backlinks, engagement, and authority) among them instead of consolidating them into one authoritative page.
- Indexing Issues: Google may index a less relevant version of your page, pushing the intended one out of search results.
- Wasted Crawl Budget: If your site has thousands of duplicate pages, Googlebot may spend its crawl budget inefficiently, reducing the frequency of crawling and indexing important pages.
Impact on Website Owners
For businesses and marketers, duplicate content can result in:
- Lower Search Rankings and Visibility
If Google cannot determine the best page to show, it may choose one that isn’t the most optimized, causing fluctuations in rankings. - Traffic Loss and Poor Click-Through Rates (CTR)
If duplicate pages are indexed instead of the primary one, valuable traffic could go to a less important version or even a competitor’s site if they copied your content and optimized better. - Backlink Fragmentation
High-quality backlinks are essential for SEO. When multiple versions of the same content exist, backlinks get distributed among different URLs, weakening the overall authority of your primary page. - Content Syndication Risks
If your content is republished on multiple platforms without proper canonicalization, Google might attribute the authority to an external site instead of yours.
Does Google Penalize Duplicate Content?
No, Google does not issue manual penalties for duplicate content unless it detects intentional manipulation (such as deceptive duplicate pages created to manipulate rankings).
However, the indirect impact—such as ranking loss, indexing issues, and traffic dilution—can be just as damaging.
To avoid these pitfalls, it’s crucial to identify duplicate content early and implement the right fixes.
Featured Article: Best Practices for Header Tags and Content Hierarchy
Common Causes of Duplicate Content Issues
Duplicate content issues don’t just happen by accident—they are often the result of technical mishaps, poor URL structuring, or content being republished across different sites.
Understanding the root causes of duplicate content is the first step toward fixing and preventing these SEO challenges.
-
URL Variations and Tracking Parameters
Issue: Many websites use URL parameters for tracking purposes, filtering products, or sorting content. While these variations may seem minor to users, search engines treat them as separate pages, causing duplicate content problems.
Example:
example.com/product-name(canonical version)example.com/product-name?utm_source=google(tracking parameter)example.com/product-name?sort=price(sorted by price)
Fix: Implement canonical tags to tell search engines which version is the primary one and configure URL parameter settings in Google Search Console. -
HTTP vs. HTTPS & WWW vs. Non-WWW Pages
Issue: If your website is accessible via multiple versions (e.g., HTTP vs. HTTPS or WWW vs. non-WWW), search engines may index both, leading to duplicate content problems.
Example:
http://example.comhttps://example.comhttp://www.example.comhttps://www.example.com
Fix:
- Redirect all versions to the preferred one using 301 redirects.
- Set the preferred domain in Google Search Console.
- Ensure your SSL certificate is properly configured to force HTTPS.
-
Scraped or Copied Content
Issue: If your content is scraped (copied without permission) or syndicated (republished with permission) on other websites, search engines might rank the copied version instead of yours.
Example:
- Your original blog post appears on another site, but they rank higher than you because of stronger authority.
Fix:
- Use
rel="canonical"when syndicating content to signal the original source. - Request removal of stolen content using Google’s DMCA takedown tool.
- Monitor duplicate content using tools like Copyscape or Ahrefs’ Site Explorer.
-
Printer-Friendly and AMP Pages
Issue: Some websites create printer-friendly versions of articles or use AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages), which can result in duplicate content if not properly canonicalized.
Fix:
- Add a canonical tag on printer-friendly or AMP versions pointing to the original page.
- Avoid generating a separate URL for printer-friendly pages if possible.
-
Similar Product Descriptions in E-commerce
Issue: E-commerce sites often have thousands of product pages, many of which feature identical product descriptions, leading to internal duplicate content.
Example:
- If a clothing store has 10 colors of the same t-shirt, each URL may have the same description, causing search engines to see them as duplicate pages.
Fix:
- Write unique product descriptions for each variant where possible.
- Use canonical tags to consolidate ranking signals for similar product pages.
- Implement dynamic content generation to differentiate product pages.
-
Pagination and Category Page Issues
Issue: Websites with paginated content (e.g., blog archives, category pages) often create multiple URLs with similar content, causing indexing problems.
Fix:
- Use
rel="prev"andrel="next"tags to guide search engines through paginated pages. - Ensure category pages have unique meta descriptions and title tags.
- Use canonical tags to consolidate authority when necessary.
- Use
-
Boilerplate Content Across Multiple Pages
Issue: Some websites reuse the same blocks of content (e.g., disclaimers, about sections, author bios, footer text) across multiple pages, which can create partial duplicate content issues.
Fix:
- Ensure each page has unique, valuable content in its main body.
- Use JavaScript to load repetitive content dynamically instead of hardcoding it into every page.
Every Second You Wait, Your Competitors Get Stronger.
They’re climbing the ranks while you’re stuck on page two. Let’s fix that—before it’s too late!
Contact UsHow to Find Duplicate Content on Your Site
Before you can fix duplicate content issues, you need to identify where they exist on your website.
Fortunately, several tools and techniques can help you detect, analyze, and resolve duplicate content problems efficiently.
Below are the best methods to uncover duplicate content, both internally and externally.
-
Using Google Search Operators
One of the quickest ways to check for duplicate content is by using Google search operators. These simple commands help you find pages with similar content indexed by Google.
Search for Exact Phrases on Your Site
Use this query to check if multiple versions of the same content exist on your site:
site:yourdomain.com“specific sentence from your content”If multiple URLs appear in the search results, it means Google has indexed duplicate content, and you need to consolidate them.
Find Indexed Variations of a Page
To check how Google has indexed different versions of a URL, use:
site:yourdomain.com intitle:"Your Page Title"This helps you identify multiple indexed versions of the same page due to URL variations or parameter issues.
-
Google Search Console and Indexing Reports
Google Search Console provides valuable insights into how Google crawls and indexes your pages.
How to Check for Duplicate Content in Google Search Console
- Go to “Coverage” → Look for “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” issues
- This means Google found multiple versions of a page and chose one as the primary version, even if it’s not the one you prefer.
- Check “Performance” → Compare URLs with the Same Keywords
- If multiple pages from your website are competing for the same keywords, they may contain duplicate or similar content.
- Use the URL Inspection Tool
- Enter a URL to see if Google recognizes it as duplicate content or if it has selected another page as the canonical version.
- Go to “Coverage” → Look for “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” issues
-
Site Audits With SEO Tools
Automated SEO tools provide a comprehensive view of duplicate content issues across your website.
Best SEO Tools for Finding Duplicate Content
Tool Features Screaming Frog SEO Spider Crawls your site and detects duplicate title tags, meta descriptions, and content Ahrefs Site Audit Identifies duplicate meta tags, H1s, and body content Semrush Site Audit Flags pages with identical content and suggests fixes Copyscape Checks if your content is copied externally by other websites Siteliner Detects internal duplicate content within your website Using these tools, you can quickly identify duplicate pages, content clusters, and keyword cannibalization issues.
-
Checking for External Duplicate Content (Scraped or Stolen Content)
Sometimes, your content gets copied by other websites, leading to external duplicate content. If search engines determine that another site published the content first (or has a stronger domain authority), it may rank them above you.
How to Detect If Your Content Has Been Copied Elsewhere
- Copyscape (Free & Premium) – Enter your page URL to see if it has been copied on other websites.
- Google Search Operators – Copy a unique sentence from your content and search it in Google using quotation marks (“”) to find exact matches.
- Ahrefs Content Explorer – Shows instances of your content being published elsewhere.
What to Do If Your Content Is Stolen
- Send a Takedown Request – Contact the website owner and request removal.
- Use Google’s DMCA Removal Tool – Submit a Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) request to Google.
- Implement a Canonical Tag – If your content is legitimately syndicated, make sure the original version is canonically linked.
-
Using “Indexed Pages” to Spot Unnecessary Duplicates
In Google Search Console, check how many pages Google has indexed:
- Search
"site:yourdomain.com"in Google – If the number of indexed pages is significantly higher than expected, it could mean Google has indexed unnecessary duplicate versions. - Check for Staging Sites or Test Environments – Some websites accidentally leave development versions of their site indexable.
Fix:
- Use
robots.txtor noindex tags to prevent Google from indexing unnecessary pages. - Redirect old or duplicate URLs to the correct version using 301 redirects.
- Search
Featured Article: The Ultimate Guide to URL Structures: SEO Best Practices & Future Trends
How to Fix Duplicate Content Issues
Now that we’ve identified duplicate content issues, it’s time to implement proven solutions to ensure your website maintains strong SEO performance.
Below are the best strategies to resolve duplicate content problems and improve your site’s ranking potential.
-
Implement 301 Redirects (Best for Merging Duplicate URLs)
A 301 redirect permanently directs traffic from a duplicate URL to the preferred version, consolidating ranking signals and preventing content duplication.
When to Use 301 Redirects
- When multiple URLs lead to the same content (e.g.,
example.com/page1andexample.com/page1?utm_source=google). - If you have HTTP & HTTPS or WWW & non-WWW versions.
- When you merge two similar blog posts into a single authoritative one.
Example: Redirecting non-preferred URLs to the canonical version
Redirect 301 /duplicate-page
https://example.com/correct-pageFix: Use a server-side 301 redirect via your
.htaccessfile (Apache),nginx.conf(NGINX), or redirect settings in your CMS (like WordPress). - When multiple URLs lead to the same content (e.g.,
-
Use Canonical Tags (Best for Similar Content on Multiple URLs)
A
rel="canonical"tag tells search engines which version of a page should be indexed and ranked. This is useful when:- You have duplicate or similar content across multiple URLs.
- Your e-commerce site has product variations or filters.
- Your content is syndicated on multiple sites.
Example of a Canonical Tag in HTML
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/preferred-version">Fix: Add the canonical tag inside the
<head>section of duplicate pages.Important: Ensure the canonicalized page is not blocked by robots.txt or set to noindex, as this can cause indexing conflicts.
-
Use Noindex Tags (Best for Pages You Don’t Want Indexed)
A meta robots
"noindex"tag tells search engines not to index a page while still allowing users to access it. This method is useful when:- You have thin or duplicate content that shouldn’t appear in search results.
- You want to prevent indexing of printer-friendly pages or dynamic URLs.
- Your site has paginated or filtered content that doesn’t need to rank.
Example of a Noindex Tag
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, follow">Fix: Add this tag inside the
<head>section of the pages you don’t want indexed. -
Set Preferred Domain and URL Parameters in Google Search Console
Google allows webmasters to define a preferred domain (WWW or non-WWW) and configure how URL parameters are handled.
Steps to Set a Preferred Domain
- Go to Google Search Console → Settings → Choose “Preferred Domain” (e.g.,
https://example.com). - Use the URL Parameters Tool → Tell Google which URL parameters should be ignored (e.g., session IDs, tracking codes).
- Fixes duplicate indexing issues caused by tracking parameters and variations.
- Go to Google Search Console → Settings → Choose “Preferred Domain” (e.g.,
-
Differentiate Content to Avoid Internal Duplication
Sometimes, duplicate content exists because pages are too similar. Instead of relying on technical fixes alone, make each page unique with:
- Unique Product Descriptions: Instead of copying manufacturer descriptions, write original, SEO-friendly text.
- Custom Meta Titles & Descriptions: Ensure each page has distinct metadata.
- Longer, More Detailed Content: If two pages cover similar topics, expand one and merge the other.
Example Fix for E-Commerce Sites
❌ Ineffective:
example.com/shoes-red→ “Red Shoes, Buy Now”example.com/shoes-blue→ “Red Shoes, Buy Now”
✅ Good:
example.com/shoes-red→ “Red Running Shoes for High Performance – Shop Now”example.com/shoes-blue→ “Blue Sports Shoes for Comfort & Durability”
-
Request Content Removal from Other Sites (If Copied)
If another website steals or scrapes your content, it can outrank your original version.
How to Handle Scraped Content
- Contact the site owner and request removal.
- Use Google’s DMCA Removal Tool (Submit a request here).
- Use Google’s “Request Indexing” tool in Search Console to ensure your page is indexed first.
- Fixes external duplicate content issues caused by stolen content.
-
Managing Duplicate Content in Pagination and Filters
Pagination and category pages can create duplicate content if not handled correctly.
Best Practices for Pagination
- Use rel=”prev” and rel=”next” tags on paginated pages.
- Canonicalize the first page of a paginated series (
?page=1). - Use “noindex” on category filters that create duplicate versions of pages.
Example:
<link rel="prev" href="https://example.com/blog?page=1">
<link rel="next" href="https://example.com/blog?page=3">- Fixes indexing issues caused by paginated content.
In Conclusion
Duplicate content issues can silently impact your website’s SEO, causing ranking dilution, traffic loss, and indexing problems.
While Google doesn’t impose direct penalties for duplicate content, failing to manage it properly can significantly reduce your search visibility.
By implementing 301 redirects, canonical tags, and noindex directives, as well as refining content uniqueness, you can prevent duplicate content from affecting your site’s performance.
Regular audits using tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, and Copyscape will help you identify and resolve duplicate content before it becomes a bigger issue.
The key takeaway? Proactively managing duplicate content is essential for maintaining a strong, authoritative online presence.
By following the strategies outlined in this guide, you can improve your site’s SEO, enhance user experience, and ensure search engines correctly recognize your content.
Every Click You Miss Is Money Lost.
If you’re not ranking, you’re losing potential revenue daily. Let’s fix that—before it’s too late!
Contact UsFAQs
1. Does Google penalize duplicate content?
2. How can I check if my site has duplicate content?
“site:yourdomain.com” along with specific text from your pages can help detect duplicates.3. Should I use canonical tags or 301 redirects to fix duplicate content?
4. What is the best way to prevent duplicate content on an e-commerce site?
- Write unique product descriptions instead of using manufacturer text.
- Use canonical tags for product variations (e.g., different colors, sizes).
- Avoid indexable URL parameters by configuring them in Google Search Console.
- Implement 301 redirects if you have duplicate product pages.

