- Entity-Based SEO focuses on optimizing content around real-world concepts and their relationships rather than just keywords.
- Building a content strategy based on entities improves Google’s understanding and topical authority, boosting rankings.
- Using structured data and schema markup helps search engines recognize entities and enhances chances of rich search results.
- Staying updated with evolving entity relationships and semantic search trends is key to maintaining long-term SEO success.
In a world where over 8.5 billion searches are conducted on Google each day, traditional keyword-focused SEO is no longer enough to keep up with how modern search engines process information.
Google has evolved from merely matching strings of text to understanding the meaning behind them—what SEOs now refer to as semantic search.
At the core of this evolution is a concept that’s becoming increasingly critical: entity-based SEO. Entity-based SEO shifts the focus from keywords to the entities behind those words—distinct, identifiable concepts like people, places, things, and ideas.
This transformation is not theoretical. It’s already well underway. According to Google, its Knowledge Graph contains over 500 billion facts about 5 billion entities, and it plays a key role in how search results are generated.
When used effectively, entity-based SEO helps establish topical authority, improves contextual relevance, and increases your visibility in rich results like featured snippets and People Also Ask boxes. More importantly, it aligns your content with the way Google’s algorithms think.
This guide will show you how to master entity-based SEO—from understanding what entities are, to structuring your content around them, to using advanced tools that uncover entity gaps your competitors missed.
Whether you’re a content strategist, SEO professional, or digital marketer, embracing this approach is no longer optional—it’s essential for staying competitive in search.
In the sections ahead, we’ll break down what entities are, how they differ from traditional keywords, how Google uses them to rank content, and how you can leverage them to future-proof your SEO strategy.
Be Understood, Not Just Indexed
Nexa Growth uses Entity-Based SEO to help search engines understand your brand—not just your keywords.
Contact UsWhat Makes Entity-Based SEO Different?
For years, SEO success was largely dictated by keyword density, exact-match phrases, and backlink quantity. But Google’s algorithm updates—from Hummingbird to BERT to MUM—have progressively moved the needle toward understanding user intent and content meaning.
Entity-based SEO is the logical progression of that trend. Unlike keywords, which can be vague or context-dependent, entities are unambiguous.
For example, the word “Apple” as a keyword could refer to a fruit, a technology company, or even a music label.
But when Google recognizes “Apple Inc.” as an entity—connected to a company founded by Steve Jobs, headquartered in Cupertino, producing iPhones—it disambiguates the term using context.
This is what allows Google to return more accurate and relevant results, even for complex or ambiguous queries. This shift is particularly important in the age of voice search and AI-generated content.
Over 70% of all Google searches are now believed to be semantic in nature, meaning they rely on the understanding of context and intent, not just keywords. As search evolves, so too must our strategies.
By optimizing for entities, you’re helping search engines form a more complete and accurate understanding of your content. This leads to better rankings, richer search features, and greater long-term visibility.
Featured Article: How Long Does SEO Take to Show Results? A Realistic Timeline
What Is an Entity in SEO?
An entity is a clearly defined thing or concept that is singular, unique, and distinguishable. In the context of SEO and Google’s search algorithm, an entity could be a person, organization, place, product, idea, event, or even an abstract concept.
What defines an entity is its ability to stand on its own and be recognized independently within a structured knowledge framework like Google’s Knowledge Graph. Google defines an entity as “a thing or concept that is singular, unique, well-defined, and distinguishable.”
This means that, unlike simple keywords, which are just strings of text, entities carry context, attributes, and relationships.
For example: “Barack Obama” is not just a combination of words; it’s an entity with a known birthdate, nationality, spouse, political role, and connections to other entities like “United States,” “Michelle Obama,” and “Democratic Party.”
Entities allow Google to go beyond matching words to understanding what those words represent and how they connect to other ideas across the web.
Entity vs. Keyword: What’s the Difference
While keywords are essential for helping Google surface content, they are limited in their ability to express meaning. Keywords rely on string matches, while entities rely on semantic understanding.
For example, someone searching for “best banks for students” might use various phrasings—“top student checking accounts,” “good college bank,” “student-friendly banking”—but Google understands the intent by connecting the query to the entity “student banking services.”
Optimizing content around entities ensures you’re still relevant across all these variations, even if you never use those exact keyword strings.
Be Understood, Not Just Indexed
Nexa Growth uses Entity-Based SEO to help search engines understand your brand—not just your keywords.
Contact UsWhat Makes Entity-Based SEO Different?
For years, SEO success was largely dictated by keyword density, exact-match phrases, and backlink quantity.
But Google’s algorithm updates—from Hummingbird to BERT to MUM—have progressively moved the needle toward understanding user intent and content meaning.
Entity-based SEO is the logical progression of that trend. Unlike keywords, which can be vague or context-dependent, entities are unambiguous. For example, the word “Apple” as a keyword could refer to a fruit, a technology company, or even a music label.
But when Google recognizes “Apple Inc.” as an entity—connected to a company founded by Steve Jobs, headquartered in Cupertino, producing iPhones—it disambiguates the term using context.
This is what allows Google to return more accurate and relevant results, even for complex or ambiguous queries. This shift is particularly important in the age of voice search and AI-generated content.
Over 70% of all Google searches are now believed to be semantic in nature, meaning they rely on the understanding of context and intent, not just keywords. As search evolves, so too must our strategies.
By optimizing for entities, you’re helping search engines form a more complete and accurate understanding of your content. This leads to better rankings, richer search features, and greater long-term visibility.
Featured Article: Internal Linking for SEO: The Complete Guide for 2026
Why Entities Matter for SEO
The reason entity-based SEO is gaining traction is simple: entities help search engines understand content at a deeper, more contextual level. While keywords tell Google what words are on a page, entities tell it what the content actually means.
Let’s explore the core reasons why entities are now central to modern SEO:
Google’s Knowledge Graph Powers Smarter Search
Google’s Knowledge Graph—containing over 500 billion facts about billions of entities—acts as the backbone of semantic search.
Instead of treating search queries as strings of keywords, the Knowledge Graph allows Google to map relationships between entities.
For example, if a user searches for “Where was Barack Obama born?”, Google doesn’t look for pages containing the words “Barack,” “Obama,” and “born.”
Instead, it connects the entity “Barack Obama” with the attribute “birthplace” and retrieves the correct answer, “Honolulu, Hawaii.” This entity-driven approach powers featured snippets, knowledge panels, and conversational AI results.
Entities Help Google Disambiguate Meaning
Keywords are often ambiguous. The word “Amazon” could refer to the e-commerce giant, the river, or even the rainforest. Without entities, Google would struggle to determine user intent. Entities eliminate this problem.
When Google recognizes “Amazon Inc.” as a company entity and “Amazon River” as a geographical entity, it uses context—such as user behavior, query history, and related terms—to deliver the right result.
This makes search results more accurate and reduces irrelevant results, which improves user satisfaction and trust.
Entities Build Topical Authority
Modern SEO isn’t just about ranking for a single keyword—it’s about becoming the go-to resource within a topic cluster. Entities make this possible.
By consistently publishing content that connects multiple entities within a niche, you help Google understand that your website has depth and authority in that domain.
For instance, a healthcare site covering entities like “diabetes,” “insulin,” “blood sugar monitoring,” and “nutrition for diabetics” will be seen as a topical authority in diabetes management. Over time, this leads to higher rankings across a wide range of related searches, not just one or two keywords.
Structured Data Enhances Entity Recognition
Structured data (schema markup) is one of the most powerful ways to signal entities to Google directly. By tagging entities in your content—like marking a person, organization, product, or event—you help search engines classify and connect information faster.
For example, using schema to identify a recipe’s “ingredients,” “cooking time,” and “calories” doesn’t just improve indexing—it also increases your chances of appearing in rich results like recipe cards. This structured clarity makes your content machine-readable, boosting visibility and click-through rates.
Search Has Evolved. Has Your SEO?
Entity-Based SEO by Nexa Growth helps you speak the language of Google’s Knowledge Graph.
Contact UsHow Google Uses Entities in Its Algorithm
To fully grasp the importance of entity-based SEO, it’s essential to understand how Google incorporates entities into its search algorithm.
With the rise of semantic search, natural language processing (NLP), and artificial intelligence, Google has shifted from being a keyword-matching engine to a meaning-matching engine.
Instead of simply scanning for repeated keywords, it now seeks to understand the context and relationships behind the words.
A major driver of this shift is Google’s use of advanced NLP models like BERT and MUM, which help the algorithm interpret language the way humans do.
These models allow Google to break down sentences, identify entities within them, and understand how those entities connect. For example, if a user searches “best ways to manage diabetes with diet,” Google doesn’t just see the keywords “manage,” “diabetes,” and “diet.”
It recognizes the entity “diabetes” as a medical condition, links it to the entity “dietary management,” and retrieves results that answer the query holistically.
Beyond individual recognition, entity relationships are at the heart of relevance. Google’s Knowledge Graph maps how entities are connected, ensuring that the search engine can disambiguate meaning and serve the most accurate results.
For instance, when someone searches for “Apple revenue,” Google understands that the entity in question is “Apple Inc.,” the company, not “apple,” the fruit. This level of precision is only possible because of the web of entity relationships Google has built.
Machine learning and the Knowledge Graph work together to continually refine this process.
The Knowledge Graph contains billions of facts about people, places, organizations, and concepts, and machine learning helps Google update and expand it in real time as new information emerges.
This means search results aren’t just based on keyword frequency—they’re informed by a dynamic, evolving graph of knowledge.
Most importantly, Google now prioritizes contextual relevance over exact matches. A page doesn’t need to contain the exact phrasing of a query to rank; instead, it must demonstrate a strong understanding of the topic and its related entities.
This is why entity-driven content often outranks keyword-stuffed pages—it aligns with how Google interprets meaning, not just how it counts words.
In short, Google’s reliance on entities allows it to deliver more accurate, user-focused results.
For marketers and SEO professionals, this means the path to visibility lies in optimizing around entities and their relationships, not just keywords.
Featured Article: What Is Schema Markup & How to Implement It in 2026
How to Build a Content Strategy Around Entities
Creating content that ranks in today’s semantic search environment requires more than keyword targeting. It involves mapping out the entity landscape surrounding a topic and structuring your content to reflect the relationships between those entities.
Here’s how to do it step by step:
Identify Core and Supporting Entities
Start by identifying the primary entity your content will focus on. For example, if your topic is “digital marketing,” the core entity is “digital marketing.” From there, expand into supporting entities—related concepts that strengthen topical depth.
These might include “SEO,” “content marketing,” “PPC advertising,” and “social media strategy.” Tools like Google’s Knowledge Graph API, Wikidata, and entity extraction platforms (e.g., InLinks, MarketMuse, or Clearscope) can help you discover related entities and ensure your content covers the full semantic spectrum.
Structure Content With Entity Relationships in Mind
Google doesn’t just look at which entities are mentioned—it cares about how they are connected. Structuring your content to highlight these relationships gives your page semantic depth. For example, when writing about “content marketing,” don’t just list it.
Show how it ties into “SEO,” “buyer’s journey,” and “lead generation.” Use subheadings, internal links, and contextual explanations to demonstrate these relationships, creating a content graph that mirrors how Google organizes knowledge.
Use Structured Data to Mark Up Entities
Schema markup is a powerful way to explicitly signal entities to search engines.
By marking up content elements like “Organization,” “Person,” “Product,” “Event,” or “FAQ,” you make it easier for Google to recognize and connect entities.
This not only helps with indexing but also increases your eligibility for rich search features such as knowledge panels, carousels, and featured snippets. For example, a local business can use “LocalBusiness” schema to connect its entity with attributes like address, reviews, and opening hours.
Optimize for Entity-Based Search Features
Entity-driven SEO directly influences how your content appears in Google’s advanced search features.
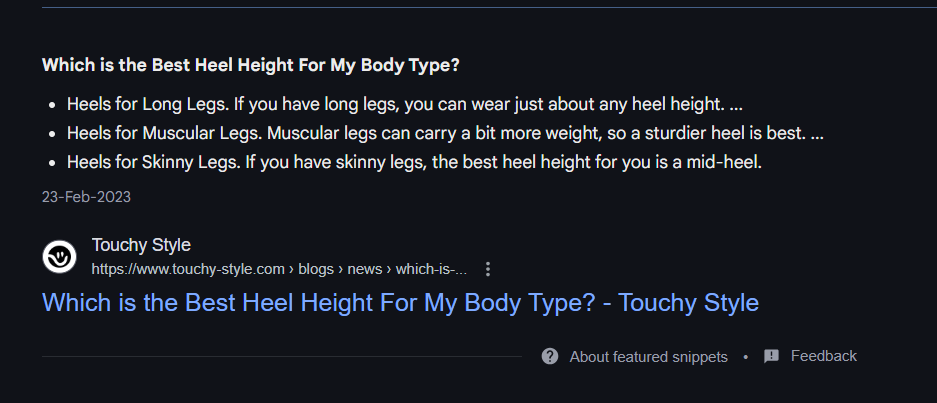
Featured snippets, People Also Ask (PAA) boxes, knowledge panels, and voice search results are all powered by entity understanding.
To optimize for these, create content that answers specific questions, includes concise definitions, and uses Q&A-style formatting where appropriate.
The more clearly your content matches entity-based queries, the higher your chances of being pulled into these high-visibility placements.
Update and Expand as the Entity Graph Evolves
Entities and their relationships are not static—they evolve as knowledge grows and industries shift.
To stay ahead, regularly audit your content to add new supporting entities, update outdated relationships, and expand coverage where gaps exist.
For example, if you wrote about “AI in marketing” three years ago, you should now include emerging entities like “generative AI,” “ChatGPT,” or “AI-driven personalization.” Keeping your entity graph fresh ensures long-term relevance and continued visibility in search.
Build Authority That Machines Recognize
We map your content to entities, so Google knows exactly who you are and what you do.
Contact UsHow to Go Beyond SEO Tools: Manual Entity Mapping for Competitive Advantage
SEO tools are helpful for surface-level optimization, but they often fail to capture the full semantic depth of a topic.
To stand out in competitive SERPs, you need to think like Google and understand how entities connect conceptually, not just linguistically.
Approaches include:
- Analyze Top-Ranking Content Through an Entity Lens
- Use Wikipedia as a Semantic Blueprint
- Expand Topical Coverage Using Ontologies and Taxonomies
- Apply Entity Salience to Prioritize Focus
- Build a Custom Internal Entity Graph
Featured Article: What Is Technical SEO and Why Does It Matter?
How to Optimize Your Content for Entities
Once you’ve identified the right entities and structured your content strategy, the next step is execution.
Some best practices include:
- Structure Content Around Entity Clusters
- Use Semantic HTML and Clear Headings
- Provide Clear, Fact-Based Definitions
- Use Internal Linking to Reinforce Entity Relationships
- Add Schema Markup to Highlight Entities
- Optimize for Entity-Based SERP Features
SEO That Speaks Google’s Language
With structured data and semantic relationships, Nexa Growth helps you rank where it counts.
Contact UsConclusion
Entity-based SEO represents the future of search. While keywords still matter, search engines now prioritize meaning, context, and relationships between concepts.
By aligning your content with entities, you’re not just optimizing for algorithms—you’re optimizing for how Google and users understand knowledge.
The shift toward entities means success in SEO is no longer about stuffing keywords but about building topical authority, mapping out entity connections, and leveraging structured data to help search engines interpret your content.
Websites that embrace entity-driven strategies gain long-term advantages: higher visibility in rich features, stronger authority within their niche, and resilience as Google continues evolving toward semantic and AI-powered search.
If you want your content to thrive in today’s competitive landscape, think beyond keywords. Think entities. The brands that master entity-based SEO now will be the ones shaping the search results of tomorrow.
Want to Rank Higher? Think Deeper.
Entity SEO aligns your content with Google's AI-driven understanding of topics and intent.
Contact Us