- A technical SEO audit is an evaluation of a website’s infrastructure to optimize it for search engines and user experience.
- Technical SEO is the foundation of a website’s search visibility, and a flawed site can limit ranking potential.
- An audit can resolve common issues like slow site speed, broken links, duplicate content, and crawlability problems.
- You can use tools like Screaming Frog to check for broken links and canonical tag conflicts.
- All important pages should be accessible within three clicks from the homepage to improve navigation and crawlability.
Search engine optimization (SEO) has evolved beyond just keywords and backlinks.
While content and on-page SEO are essential, technical SEO forms the foundation of a website’s search visibility.
Without a technically sound website, even the best content can struggle to rank.
In fact, according to a study by Ahrefs, 90.63% of all web pages get no organic traffic from Google—and technical SEO issues are often a key reason why.
Search engines need to efficiently crawl, index, and understand your site’s content, and any technical barriers can significantly impact rankings.
Google’s algorithm updates continue to emphasize Core Web Vitals, mobile-friendliness, structured data, and site security.
A poorly optimized website can experience drops in rankings, higher bounce rates, and lower conversion rates, directly impacting business growth.
Even small technical errors—like broken links, duplicate content, improper redirects, or crawl errors—can prevent search engines from indexing your site correctly.
These hidden issues can quietly sabotage your rankings, often without you even realizing it.
This guide will walk you through a 10-step technical SEO audit covering everything from crawlability and indexability to Core Web Vitals, structured data, and advanced SEO techniques.
Whether you’re an SEO professional or a business owner looking to optimize your site, this comprehensive audit will ensure your website is in top shape for search engines.
Let’s dive into the exact steps you need to take to perform a successful technical SEO audit in 2026
Is Your Website Holding You Back?
Discover what’s slowing you down with a comprehensive Technical SEO Audit!
Contact UsWhat is a Technical SEO Audit and Why is it Important?
A technical SEO audit is a comprehensive evaluation of your website’s infrastructure, ensuring it is optimized for search engine crawling, indexing, and user experience.
Unlike content and link-building strategies, which focus on what appears on the page, technical SEO ensures that search engines can effectively discover, understand, and rank your content.
Why Does Technical SEO Matter?
Search engines like Google use over 200 ranking factors to determine how pages appear in search results.
While high-quality content and backlinks are crucial, a technically flawed site can limit your ability to rank, no matter how strong your content is.
A study by Backlinko analyzing 11.8 million Google search results found that websites with strong technical SEO tend to rank higher, even if their content is comparable to competitors.
Common technical SEO issues—such as slow site speed, broken links, duplicate content, poor mobile usability, and crawlability issues—can prevent Google from indexing your pages properly. As a result, your rankings can drop, and you may miss out on valuable organic traffic.
The Key Benefits of a Technical SEO Audit
Performing a technical SEO audit ensures that your website meets Google’s technical guidelines, ultimately leading to better search rankings, improved user experience, and increased conversions.
Here’s how:
-
Helps Search Engines Crawl and Index Your Site Efficiently
Googlebot and other search engine crawlers scan websites to determine their relevance and ranking potential. If your website has blocked pages, noindex tags, or broken links, search engines may struggle to index your content correctly, leading to ranking issues.
-
Improves Website Performance and Page Speed
Google considers page speed a direct ranking factor, and 53% of mobile users leave a page if it takes more than 3 seconds to load. Technical SEO audits help you identify slow-loading pages, optimize images, and fix server issues that could be slowing down your site.
-
Ensures Mobile-Friendliness
With over 60% of Google searches now conducted on mobile devices (Statista), mobile optimization is no longer optional. Google’s Mobile-First Indexing means that if your website isn’t mobile-friendly, your rankings will suffer. A technical audit checks for responsive design, viewport configurations, and mobile usability errors.
-
Fixes Crawl Errors and Broken Links
404 errors, improper redirects, and broken links can hurt user experience and confuse search engines. A thorough technical audit helps identify and fix these issues to ensure a smooth user journey.
-
Strengthens Security and HTTPS Implementation
Google has made HTTPS encryption a ranking factor, and non-secure websites (HTTP) now display warnings in browsers like Chrome. An audit ensures proper SSL certification, mixed content fixes, and secure browsing standards.
-
Helps Detect and Fix Duplicate Content Issues
Duplicate content can dilute page authority and confuse search engines, leading to lower rankings. By identifying duplicate pages, incorrect canonical tags, and parameterized URLs, a technical SEO audit helps consolidate ranking signals and prevents keyword cannibalization.
Who Should Conduct a Technical SEO Audit?
A technical SEO audit is essential for website owners, marketers, and SEO professionals looking to improve rankings and site health.
Whether you’re running a small business website, an e-commerce store, or a large enterprise site, regular audits ensure that your site remains optimized for search engines and users alike.
How Often Should You Perform a Technical SEO Audit?
The frequency of a technical SEO audit depends on the size and complexity of your website. However, here’s a general guideline:
- Small to medium websites: Every 3 to 6 months
- Large enterprise websites: Every 1 to 3 months
- E-commerce websites: Every 1 to 2 months (due to frequent product updates)
- After major website changes: Immediately following any website redesign, migration, or significant updates
Now that you understand the importance of a technical SEO audit, let’s dive into the 10-step process to perform a complete audit and optimize your website for search engines.
This section effectively educates the reader on what a technical SEO audit is, why it matters, and its benefits while incorporating relevant statistics and real-world examples.
Featured Article: The Ultimate Guide to URL Structures: SEO Best Practices & Future Trends
How to Perform a Technical SEO Audit in 10 Steps
Now that you understand the importance of a technical SEO audit, it’s time to walk through the step-by-step process to identify and fix technical SEO issues.
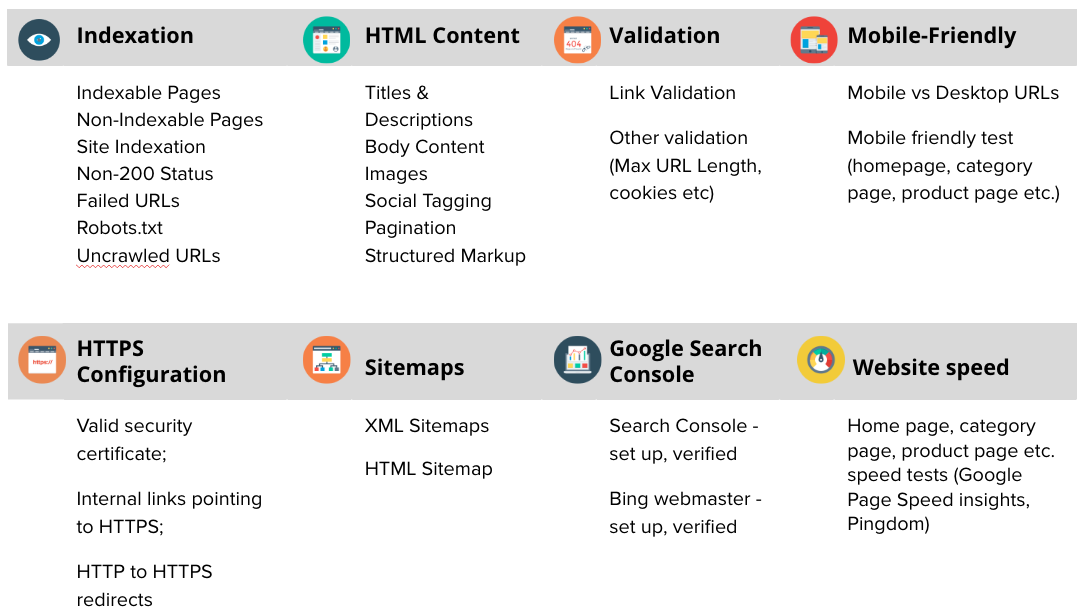
Each step in this guide is designed to ensure that your website is fully optimized for crawlability, indexability, performance, and user experience.
-
-
Crawlability and Indexability: Ensure Your Site Can Be Found
Search engines must efficiently crawl and index your website to rank your pages in search results.
No matter how well-optimized your content is, if Googlebot cannot access your pages, they won’t appear in search results.
That’s why ensuring your site is fully crawlable and indexable is a crucial step in technical SEO.
A website’s crawlability refers to how easily search engine bots can navigate and discover pages, while indexability determines whether those pages can be stored and ranked in Google’s database.
Misconfigurations in robots.txt, sitemaps, redirects, or canonical tags can create significant barriers, preventing search engines from indexing key pages.
Let’s explore how to resolve these issues effectively.
-
Check Robots.txt for Restrictions
The robots.txt file is a simple text file located in your website’s root directory that tells search engines which pages they can and cannot crawl.
While this can help prevent search engines from accessing irrelevant pages (such as admin areas or login pages), improper configurations can accidentally block essential content from being indexed.
How to Check and Fix Robots.txt Issues
- Open Google Search Console > Robots.txt Tester to check for disallowed pages.
- Ensure that important sections, such as /blog/, /products/, or /services/, are not blocked.
- A well-structured robots.txt file should only block non-public pages and should look something like this:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Disallow: /cart/
Allow: /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php- If you notice that an essential page is blocked, remove the Disallow directive for that page to ensure it can be crawled and indexed.
- Use Google’s Robots Testing Tool to validate any changes before deployment.
-
Audit Your XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is a roadmap that guides search engines through your website’s most important pages.
A well-optimized sitemap ensures efficient indexing, helping Google recognize canonical versions of pages while avoiding duplicate content issues.
How to Optimize Your XML Sitemap
- Ensure your sitemap includes only indexable pages—remove any 404 errors, redirects, or no-index pages.
- Submit your sitemap via Google Search Console > Sitemaps to inform search engines of its location.
- Use tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to identify orphaned pages (pages with no internal links). Orphaned pages might exist in the sitemap but are not easily discoverable by search engine bots.
- Regularly update your sitemap whenever new content is published to help search engines find new pages faster.
-
Perform a Site Crawl to Detect Indexing Issues
A site crawl mimics how search engine bots navigate your website, helping you identify technical barriers that could prevent pages from being indexed.
Using SEO audit tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs Site Audit, or SEMrush, conduct a full website crawl and review the following:
- Broken links (404 errors): Identify and fix any broken internal or external links to avoid negative SEO impact.
- Redirect chains (301/302 loops): Ensure that redirects are clean and do not lead to unnecessary loops, slowing down search engines.
- Blocked pages: Check if important pages are mistakenly blocked by robots.txt, meta no-index tags, or incorrect HTTP headers.
- Canonical tag conflicts: If multiple versions of a page exist, ensure proper canonicalization to avoid duplicate content issues.
By resolving these crawl errors, you can improve site accessibility and increase the chances of pages being indexed correctly.
-
Analyze the Google Search Console Coverage Report
Google Search Console provides a detailed coverage report that reveals which pages are indexed, which are blocked, and which have indexing issues. To check this:
- Go to Google Search Console > Pages to review the indexing status of your site.
- Look for the following:
- Indexed, not submitted in sitemap: These pages are in Google’s index but are missing from your sitemap. Add them to improve discoverability.
- Discovered but not indexed: These pages have been found by Google but have not been indexed. This could indicate quality issues, duplicate content, or slow loading times.
- Excluded pages: Review any pages Google has chosen not to index. Some exclusions are intentional (e.g., pages with a no-index tag), but others might be accidental blocks that need fixing.
-
-
Site Architecture and Internal Linking Optimization
A well-structured website is essential for both user experience and search engine optimization (SEO).
A strong site architecture ensures that content is organized logically, making it easier for search engines to crawl, index, and distribute link equity effectively.
It also helps users navigate the site seamlessly, reducing bounce rates and increasing engagement.
A poorly structured website, on the other hand, can lead to orphaned pages, inefficient crawl paths, and lower rankings in search results.
To avoid this, your website should follow a clear hierarchy, maintain a logical URL structure, and leverage internal linking strategies to guide both users and search engines.
-
Optimize Your Site Hierarchy and Navigation
A well-defined site hierarchy ensures that all important pages are easily accessible, making it easier for both users and search engines to navigate. A properly structured website should adhere to the following best practices:
- Ensure every page is reachable within three clicks from the homepage.
- Deeply buried pages make it difficult for search engines to crawl content efficiently.
- Use a logical and descriptive URL structure.
- Instead of using generic or auto-generated URLs like
/p123x/, use clear and structured URLs such as/services/seo-audit/.
- Instead of using generic or auto-generated URLs like
- Keep navigation menus simple and intuitive.
- Avoid excessive dropdowns or complex menu structures that can overwhelm users and confuse search engines.
- Create a structured hierarchy with categories and subcategories.
- Example:
- Homepage → SEO Services → Technical SEO Audit
- This helps distribute link equity from top-level pages to deeper pages, improving their chances of ranking.
- Example:
By implementing these strategies, you ensure that search engines can easily discover and understand your content, improving both crawlability and user experience.
- Ensure every page is reachable within three clicks from the homepage.
-
Identify and Fix Internal Linking Issues
Internal linking plays a crucial role in SEO and site architecture as it helps search engines understand the relationship between different pages and distribute ranking signals effectively.
Internal links also encourage users to explore more pages, increasing dwell time and reducing bounce rates.
However, poor internal linking practices can lead to issues such as orphaned pages, broken links, and inefficient link distribution.
How to Fix Internal Linking Issues
-
- Use an SEO crawler (Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or SEMrush) to identify orphan pages.
- Orphan pages have no internal links pointing to them, making it difficult for search engines to find and index them.
- Ensure every important page is linked at least once from another relevant page.
- Fix broken internal links (404 errors or redirects).
- Broken links disrupt user experience and prevent link equity from passing correctly.
- Regularly audit internal links and replace broken links with valid URLs.
- Use contextual internal links with descriptive anchor text.
- Instead of using vague text like “click here”, use keyword-rich anchor text like “learn more about technical SEO audits”.
- Contextual links provide search engines with additional context about the linked page, improving relevancy and rankings.
- Use an SEO crawler (Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or SEMrush) to identify orphan pages.
By refining your site architecture and internal linking strategy, you make your website easier to navigate, more search-friendly, and better optimized for rankings.
These optimizations enhance both SEO performance and user engagement, making them a critical component of any technical SEO audit.
-
-
-
Page Speed Optimization and Core Web Vitals
Page speed is a critical ranking factor in Google’s algorithm, directly influencing user experience (UX), bounce rates, and conversions.
A slow-loading website can frustrate users, leading them to abandon the page before it even loads.
In fact, according to Google, 53% of mobile users leave a site if it takes longer than three seconds to load.
Google has placed increasing emphasis on Core Web Vitals, a set of metrics that measure page loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability.
Websites that meet these performance benchmarks are more likely to rank higher and provide a better experience for visitors.
To improve your site’s speed and optimize Core Web Vitals, follow these actionable steps.
-
Use Google PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse
The first step in page speed optimization is diagnosing your website’s performance issues. Google provides two powerful tools for this:
- Google PageSpeed Insights – Evaluates page speed for both mobile and desktop versions and provides recommendations for improvement.
- Google Lighthouse – A more advanced tool that analyzes page performance, accessibility, and best practices in addition to SEO.
How to Use These Tools Effectively
- Run a test on Google PageSpeed Insights to get an overview of speed issues.
- Review the Core Web Vitals assessment, focusing on the three main metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures how quickly the largest visible content loads.
- First Input Delay (FID): Evaluates the time it takes for a page to become interactive.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Checks for unexpected layout shifts that disrupt user experience.
- Use Lighthouse within Chrome DevTools for a more detailed performance audit.
By identifying problem areas, you can prioritize optimizations that will have the greatest impact on speed and usability.
-
Optimize for Core Web Vitals
Google’s Core Web Vitals are key indicators of a site’s user experience. Here’s how to optimize each metric effectively.
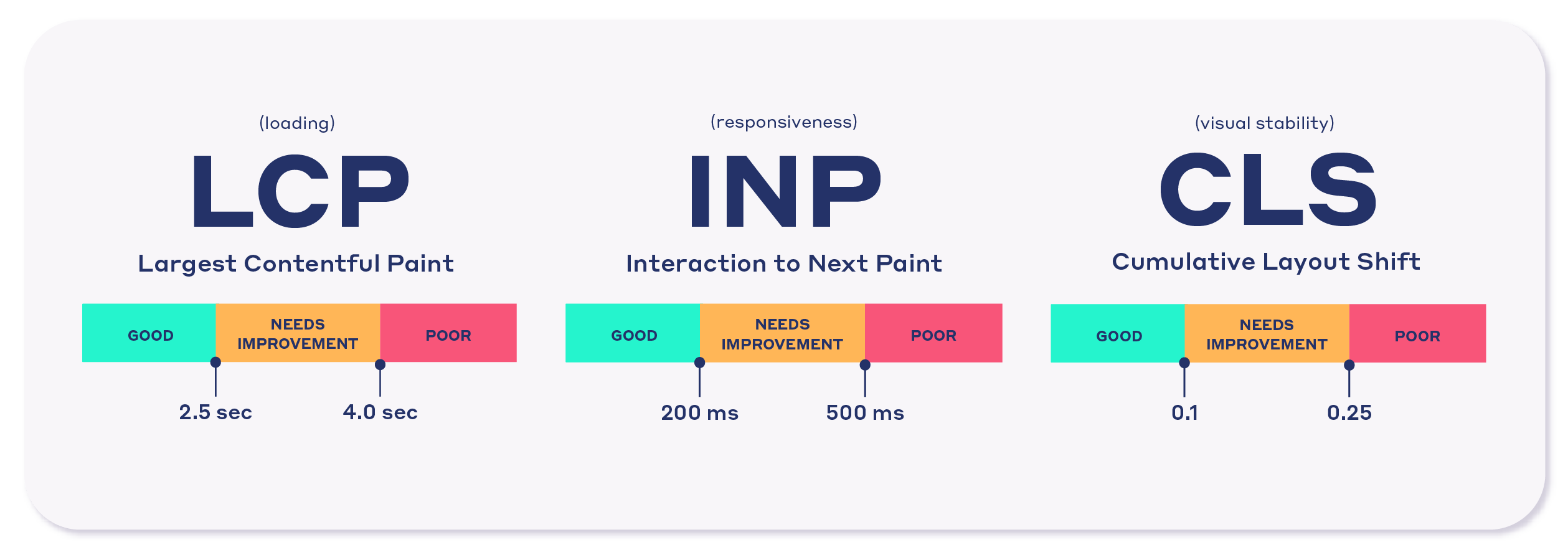
Core Web Vitals- A Visual by NitroPack Improve Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
LCP measures the time it takes for the largest visible element (such as an image or headline) to load. A good LCP score is under 2.5 seconds.
- Compress images using WebP or JPEG 2000 formats to reduce file size.
- Enable lazy loading to delay the loading of images until they are needed.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to distribute content across multiple servers and speed up delivery.
- Optimize server response times by using faster hosting and reducing unnecessary redirects.
Reduce First Input Delay (FID)
FID measures the time it takes for a user to interact with the page (e.g., clicking a button) after it loads. A good FID score is under 100 milliseconds.
- Minimize JavaScript execution time by reducing unused JavaScript and deferring non-essential scripts.
- Use browser caching to store resources locally and reduce load times.
- Optimize third-party scripts (e.g., chatbots, tracking pixels) to prevent slowdowns.
Fix Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
CLS measures unexpected shifts in page layout, such as images or ads that suddenly move after loading. A good CLS score is under 0.1.
- Specify image dimensions (width and height) in the HTML to prevent reflow issues.
- Avoid inserting dynamic content above existing content (e.g., ads or pop-ups that load after page rendering).
- Use font-display: swap to prevent Flash of Unstyled Text (FOUT) when loading web fonts.
Page speed optimization and Core Web Vitals improvements are essential for both SEO and user experience.
A fast-loading, stable website not only ranks higher in Google but also reduces bounce rates and improves conversions.
Don’t Let SEO Issues Cost You Traffic!
Our expert Technical SEO Audit finds and fixes problems before they hurt your rankings.
Contact Us -
-
Mobile-Friendliness and Responsive Design
With Google’s mobile-first indexing, ensuring that your website is fully optimized for mobile devices is no longer optional—it’s essential.
Since over 60% of Google searches come from mobile devices, Google primarily uses the mobile version of your website for indexing and ranking.
A site that doesn’t provide a smooth mobile experience can suffer from lower rankings, high bounce rates, and lost conversions.
A mobile-friendly website should be easy to navigate, load quickly, and function properly across different screen sizes.
Here’s how to ensure your site meets Google’s mobile usability standards.
-
Test Your Website for Mobile-Friendliness
Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool was previously a popular way to check a website’s mobile usability, but it has been discontinued. Instead, you can use alternative tools like:
- Google Search Console > Mobile Usability Report – This feature highlights mobile-specific errors like small fonts, clickable elements being too close, and content wider than the screen.
- PageSpeed Insights (https://pagespeed.web.dev/) – While primarily focused on page speed, this tool also provides insights into mobile usability issues.
- Browser Developer Tools (Chrome DevTools) – You can simulate mobile devices in Chrome by opening DevTools (right-click on a webpage > Inspect > Toggle Device Toolbar).
Common Mobile Usability Issues and How to Fix Them
- Text that’s too small to read: Increase font size to at least 16px for body text.
- Buttons too close together: Ensure that tap targets (buttons, links) are at least 48px in height and width.
- Viewport scaling issues: Add the following meta tag in your HTML to ensure proper scaling across devices:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">- Unresponsive layouts: Use flexible grids, CSS media queries, and responsive images to adapt content for different screen sizes.
-
HTTPS and Security Audits
Google prioritizes secure websites, and sites that are not encrypted with HTTPS may show a “Not Secure” warning in browsers like Chrome. If your site is still using HTTP, switching to HTTPS is critical for both SEO rankings and user trust.
Why HTTPS Matters for SEO and UX
- Google has confirmed HTTPS as a ranking factor. Secure websites may see a slight ranking boost.
- Protects user data by encrypting information exchanged between the user and the website.
- Prevents browser security warnings, which can deter users from visiting your site.
-
Find and Fix Mixed Content Issues
Even if your website has an SSL certificate, mixed content issues can still occur. This happens when some resources (images, scripts, stylesheets) load over HTTP instead of HTTPS, creating security vulnerabilities.
How to Identify and Fix Mixed Content Errors
- Use Google Search Console > Security Issues to check for errors.
- Open Chrome DevTools (F12 > Console) to detect HTTP resources causing warnings.
- Update all internal links, images, and scripts to use HTTPS.
- Ensure third-party plugins and embeds (such as YouTube videos, fonts, and ads) are also using HTTPS.
-
-
Duplicate Content and Canonicalization Issues
Duplicate content is a common SEO problem that occurs when identical or highly similar content appears on multiple URLs.
Search engines struggle to determine which version to rank, leading to keyword cannibalization, diluted ranking signals, and lower visibility in search results.
Google does not penalize duplicate content unless it’s deliberately manipulative, but it can impact SEO performance by splitting ranking authority between multiple versions of the same page.
Identifying and resolving duplicate content issues ensures that your website maintains a strong SEO foundation.
Identify and Fix Duplicate Content Issues
To detect and resolve duplicate content problems, follow these steps:
-
Use Screaming Frog to Find Duplicate Titles and Meta Descriptions
- Run a full website crawl using Screaming Frog SEO Spider to identify duplicate title tags, meta descriptions, and content.
- Check for pages with similar or identical H1 tags and body content, which may indicate duplicate content issues.
-
Implement Canonical Tags to Consolidate Duplicate Pages
A canonical tag (rel=”canonical”) tells search engines which version of a page is the primary source. This prevents multiple URLs from competing for rankings.
Example of a Canonical Tag:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/preferred-page">- Add canonical tags to similar or duplicate pages to point to the preferred version.
- Ensure that paginated pages, session IDs, and URL parameters use proper canonicalization.
By properly managing duplicate content and using canonical tags, you help Google consolidate ranking signals, ensuring that your most important pages rank higher in search results.
-
-
Check and Optimize Meta Tags
Meta tags play a crucial role in on-page SEO, influencing how search engines and users perceive your content.
They provide context about a webpage and directly impact click-through rates (CTR). Optimizing meta tags ensures that each page is unique, compelling, and aligned with search intent.
Best Practices for Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
Here are some best practices for title tags and meta descriptions:
Optimize Title Tags
Title tags are one of the most important on-page SEO elements, as they influence both rankings and CTR.
- Keep title tags under 60 characters to prevent truncation in search results.
- Include primary keywords naturally, ideally at the beginning of the title.
- Make titles compelling to encourage users to click.
Example of an Optimized Title Tag:
<title>Technical SEO Audit: A 12-Step Guide to Better Rankings</title>Craft Unique and Engaging Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions provide a brief summary of the page’s content and help improve CTR. While not a direct ranking factor, they influence user behavior and search visibility.
- Keep meta descriptions under 160 characters to ensure they display properly.
- Write a compelling summary that encourages clicks.
- Include relevant keywords naturally to align with search intent.
Example of an Optimized Meta Description:
<meta name="description" content="Learn how to conduct a technical SEO audit with this step-by-step guide. Improve your site’s crawlability, speed, and rankings today.">Key Takeaways for Optimizing Meta Tags:
- Each page should have a unique title and meta description.
- Avoid duplicate metadata, which can confuse search engines.
- Use action-oriented language to improve engagement and CTR.
Featured Article: The Importance of Title Tags and How to Optimize Them
-
Structured Data and Schema Markup Optimization
Structured data helps search engines better understand your content and improves the chances of appearing in rich snippets.
By implementing schema markup, you can enhance search visibility and improve user experience.
How to Add Structured Data Using JSON-LD
JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is the preferred format for adding structured data. It helps search engines categorize content and display it in an enhanced format in search results.
Common types of structured data include:
- FAQ Schema – Helps display questions and answers directly in search results.
- Product Schema – Enhances product pages by displaying prices, reviews, and availability.
- Article Schema – Helps Google identify news articles, blogs, and how-to guides.
Example of FAQ Schema Using JSON-LD:
<script type="application/ld+json">{ "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "FAQPage", "mainEntity": [{ "@type": "Question", "name": "What is a technical SEO audit?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "A technical SEO audit is a process of evaluating a website's technical elements to improve search visibility and performance." } }]}</script>How to Validate Schema Markup
After adding structured data, it’s important to test and validate it to ensure correct implementation.
- Use Google’s Rich Results Test (Google Rich Results Test) to check if your schema is correctly formatted.
- Use Google Search Console’s Schema Report to identify any errors in structured data implementation.
By implementing structured data correctly, you enhance search appearance, increase CTR, and improve rankings, making it an essential part of technical SEO optimization.
-
Status Code and Redirects Audit
Website status codes and redirects play a critical role in SEO and user experience. They determine how search engines and browsers handle webpage requests.
If a site has excessive redirects, broken links, or server errors, it can negatively impact crawlability, indexability, and rankings.
By auditing status codes and redirect issues, you ensure that users and search engines can access your content without errors or unnecessary redirections.
Find and Fix 3XX, 4XX, and 5XX Errors
HTTP status codes indicate the response a web server returns when a browser or search engine requests a page. Below are the most common status codes that impact SEO and how to fix them.
3XX Redirect Issues (Redirection Errors)
301 and 302 redirects tell search engines that a page has been permanently or temporarily moved. While 301 redirects pass link equity (SEO value), 302 redirects do not—which can lead to ranking losses if misused.
Common Redirect Issues to Look For:
- Redirect Chains: When a URL redirects multiple times before reaching its final destination. This slows down crawling and can dilute link equity.
- Redirect Loops: When two or more pages redirect to each other indefinitely, preventing the page from loading.
How to Fix Redirect Issues:
- Use Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to identify and audit redirects.
- Replace redirect chains with a direct 301 redirect from the original URL to the final destination.
- Ensure 302 redirects are only used for temporary page moves—otherwise, replace them with 301 redirects.
4XX Errors (Client-Side Errors)
4XX errors occur when a requested page does not exist or is inaccessible. The most common is the 404 Not Found error, which happens when a page has been deleted, moved, or linked incorrectly.
Why 4XX Errors Harm SEO:
- Broken links lead to poor user experience and higher bounce rates.
- Search engines may drop pages from their index if they consistently return 404 errors.
- Internal links pointing to 404 pages create crawl inefficiencies.
How to Fix 4XX Errors:
- Use Google Search Console > Coverage Report to identify 404 pages.
- Fix broken internal links by updating them with the correct URLs.
- Implement 301 redirects for deleted pages that still receive traffic.
- If a page is intentionally removed, serve a 410 Gone status instead of a 404.
5XX Errors (Server-Side Issues)
5XX errors indicate server failures, preventing users and search engines from accessing a site. The most common are:
- 500 Internal Server Error – General server malfunction.
- 503 Service Unavailable – Server temporarily down.
- 504 Gateway Timeout – Slow server response.
How to Fix 5XX Errors:
- Monitor server uptime using tools like UptimeRobot or Google Search Console.
- Check server logs to identify frequent 5XX errors.
- Contact your hosting provider if server errors persist.
By proactively fixing status code errors, you improve site crawlability, retain search rankings, and provide a smoother user experience.
-
Log File Analysis for Advanced SEO
A log file is a record of all requests made to a web server, including visits from search engine bots like Googlebot, Bingbot, and others.
Analyzing log files helps uncover crawl behavior, detect wasted crawl budget, and optimize indexing.
Why Log Files Matter and How to Analyze Them
Log file analysis provides insights into how search engines interact with your site:
- Which pages Googlebot crawls most often.
- How frequently search engine bots visit your site.
- Which pages are wasting crawl budget (e.g., bots crawling non-important pages excessively).
- Errors encountered by Googlebot during crawling.
How to Conduct a Log File Analysis
- Extract and Analyze Log Files
- Download log files from your hosting provider or use Google Search Console’s Crawl Stats report.
- Use Screaming Frog Log File Analyzer to detect patterns in Googlebot’s behavior.
- Identify High-Crawl and Low-Crawl Pages
- Prioritize pages that Google crawls frequently—these are often the most valuable.
- If important pages aren’t crawled enough, improve their internal linking and ensure they are in your sitemap.
- Detect and Fix Crawl Errors
- Find pages returning 404 or 500 errors and fix them with proper redirects.
- Identify excessive crawling of unnecessary pages (e.g., filter pages, admin pages) and block them using robots.txt or noindex tags.
- Optimize Crawl Budget
- Search engines allocate a limited crawl budget to each site.
- Reduce crawl waste by blocking non-essential pages from being crawled.
- Ensure that Googlebot spends its time on high-value content.
By analyzing log files, you can improve crawl efficiency, ensuring that search engines prioritize the right content for indexing and ranking.
-
JavaScript SEO and Rendering Optimization
JavaScript is increasingly used for dynamic and interactive content, but search engines struggle to crawl and render JavaScript-heavy websites. Ensuring that Googlebot can properly render your site is critical for SEO success.
How JavaScript Affects SEO
Unlike traditional HTML, JavaScript-powered pages require rendering before they become fully visible to search engines. Google’s crawling and indexing process for JavaScript-based websites follows three steps:
-
- Crawling – Googlebot discovers the page but may not immediately see all content.
- Rendering – Google processes JavaScript to generate the full page.
- Indexing – Once rendered, Google can analyze and rank the content.
If JavaScript is not executed correctly, Google may fail to see important content, resulting in lower rankings.
Common JavaScript SEO Issues
- Delayed content rendering – Content loads dynamically after Googlebot’s initial crawl, leading to incomplete indexing.
- Blocked JavaScript files – robots.txt or server settings may prevent search engines from rendering JavaScript.
- Excessive client-side rendering (CSR) – Search engines struggle to execute JavaScript-heavy content.
How to Optimize JavaScript for SEO
-
-
Stronger SEO Starts With a Smarter Audit!
Get a data-driven Technical SEO Audit and take the first step toward better rankings.
Contact UsTools to Conduct a Technical SEO Audit
A technical SEO audit is essential for ensuring that your website is optimized for search engine crawling, indexing, and performance.
Without the right tools, identifying and fixing technical SEO issues can be time-consuming and inefficient.
Fortunately, a variety of SEO auditing tools exist to help analyze and improve your site’s crawlability, site speed, indexability, security, and overall technical health.
Here’s a comprehensive list of the best tools for conducting a technical SEO audit, categorized by their primary functions.
Featured Article: How Does SEO Work? (Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking Explained)
Website Crawling and Indexing Analysis Tools
Crawling and indexing are core components of a technical SEO audit. These tools help identify issues such as broken links, duplicate content, redirect errors, and indexability problems.
-
Screaming Frog SEO Spider
One of the most powerful SEO auditing tools, Screaming Frog SEO Spider allows you to crawl a website like a search engine and identify common technical issues.
Key Features
- Detects broken links, 404 errors, and redirect chains.
- Finds duplicate title tags, meta descriptions, and H1 tags.
- Analyzes robots.txt files, canonical tags, and XML sitemaps.
- Provides insights on internal linking structure.
- Generates log file analysis to see how Googlebot interacts with your site.
Best For:
SEO professionals looking for an in-depth technical analysis of a website. -
Google Search Console
Google Search Console (GSC) is a must-have tool for monitoring how Google crawls, indexes, and ranks your website.
Key Features:
- Identifies indexing issues through the Coverage Report.
- Displays crawl errors and blocked resources.
- Tracks Core Web Vitals (LCP, FID, CLS) for page speed and performance insights.
- Provides mobile usability reports to fix mobile responsiveness issues.
- Shows which pages Google has indexed and which are excluded.
Best For:
Website owners, SEO professionals, and developers tracking Google’s crawling and indexing behavior. -
Sitebulb
Sitebulb is an advanced SEO crawler that combines website crawling and data visualization for technical SEO audits.
Key Features:
- Creates graphical reports of website structure for better understanding.
- Detects orphan pages, internal linking issues, and duplicate content.
- Offers automated recommendations to fix technical SEO issues.
- Conducts mobile-friendly and page speed analysis.
Best For:
SEO agencies and consultants who prefer visual reports and structured data analysis.Website Performance and Core Web Vitals Tools
Page speed and user experience are critical ranking factors. These tools help optimize loading times, interactivity, and visual stability.
-
Google PageSpeed Insights
Google PageSpeed Insights (PSI) analyzes page speed and suggests optimizations to improve performance.
Key Features:
- Measures Core Web Vitals: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
- Provides separate performance scores for mobile and desktop versions.
- Gives actionable recommendations to improve speed, such as image compression, lazy loading, and script optimization.
Best For:
Developers and site owners optimizing page speed and Core Web Vitals. -
GTmetrix
GTmetrix provides detailed page speed insights beyond what Google PageSpeed Insights offers.
Key Features:
- Measures fully loaded time, total page size, and number of requests.
- Provides a Waterfall Chart to diagnose slow-loading resources.
- Identifies JavaScript, CSS, and server performance issues.
- Offers global server location testing to analyze speed differences across regions.
Best For:
Businesses and developers optimizing website performance across different devices and locations. -
Lighthouse (Google DevTools)
Lighthouse is an open-source Chrome DevTools feature that evaluates website performance, accessibility, SEO, and best practices.
Key Features:
- Runs simulated audits on any page for performance analysis.
- Checks for progressive web app (PWA) optimization.
- Provides field data and lab data for debugging page speed issues.
Best For:
Developers and SEO specialists optimizing user experience and page performance.Mobile-Friendliness and Security Tools
Mobile optimization and security are essential for SEO rankings. These tools ensure that your site is mobile-friendly and HTTPS-secured.
-
Google Mobile Usability Report (in Search Console)
This tool helps identify mobile experience issues directly within Google Search Console.
Key Features:
- Detects text too small to read, clickable elements too close together, and viewport issues.
- Shows which pages fail Google’s mobile-friendliness tests.
- Provides mobile usability insights per page.
Best For:
Ensuring that websites meet Google’s mobile-first indexing requirements. -
SSL Labs – SSL Test
SSL Labs’ SSL Test checks the security and validity of a website’s SSL certificate.
Key Features:
- Verifies whether HTTPS is implemented correctly.
- Detects mixed content issues (insecure HTTP elements on an HTTPS page).
- Analyzes the SSL certificate strength and encryption levels.
Best For:
Ensuring website security and HTTPS compliance.Structured Data and Schema Markup Tools
Structured data improves search engine understanding and enhances SERP appearances with rich results.
-
Google Rich Results Test
Google’s Rich Results Test verifies whether structured data is correctly implemented.
Key Features:
- Checks FAQ, product, review, and breadcrumb schema markup.
- Identifies missing or incorrect structured data elements.
Best For:
Webmasters adding schema markup for enhanced SERP listings. -
Schema.org Markup Validator
The Schema.org validator helps validate JSON-LD, Microdata, and RDFa structured data.
Key Features:
- Identifies errors in structured data implementation.
- Supports multiple schema markup formats.
Best For:
SEO professionals ensuring correct structured data markup for Google.Log File Analysis and Advanced SEO Tools
Log file analysis helps track how search engines crawl your site.
-
Screaming Frog Log File Analyzer
A companion tool to Screaming Frog SEO Spider, this tool provides deep insights into Googlebot’s crawling behavior.
Key Features:
- Tracks how often Googlebot crawls specific URLs.
- Identifies crawl errors, slow-loading pages, and server response times.
Best For:
SEO specialists optimizing crawl budget and indexing efficiency.All-in-One Technical SEO Suites
-
Ahrefs Site Audit
Ahrefs is a complete SEO suite with a powerful site audit tool.
Key Features:
- Finds crawl errors, duplicate content, and Core Web Vitals issues.
- Detects JavaScript rendering problems.
- Tracks technical health scores over time.
Best For:
SEO professionals needing a full-scale website audit tool. -
Semrush Site Audit
Semrush Site Audit provides an automated technical SEO report.
Key Features:
- Detects indexability, speed, and security issues.
- Provides a prioritized list of fixes.
Best For:
Businesses looking for an all-in-one SEO audit solution.
Featured Article: The Ultimate Guide to URL Structures: SEO Best Practices & Future Trends
Conclusion
Technical SEO is the foundation of search engine optimization. Without a well-optimized technical structure, even the best content and backlink strategies may fail to produce meaningful results.
Ensuring that your website is crawlable, indexable, fast, secure, and mobile-friendly is crucial for ranking well in search engines and providing an optimal user experience.
If you haven’t conducted a technical SEO audit recently, now is the time.
Ensure your website is optimized for speed, security, mobile-friendliness, and proper indexing. Whether you’re a business owner, an SEO professional, or a developer, mastering technical SEO is key to long-term digital success.
Investing in technical SEO today will not only improve search rankings and traffic but also create a seamless user experience that drives engagement and conversions.
Unlock Your Website’s Full Potential!
Get a detailed Technical SEO Audit to fix hidden issues and boost your rankings.
Contact UsFAQs
1. What is a Technical SEO Audit and Why is it Important?
2. How Often Should You Perform a Technical SEO Audit?
- Small to medium websites: Every 3 to 6 months
- Large or enterprise websites: Every 1 to 3 months
- E-commerce websites: Every 1 to 2 months due to frequent product updates
- After major website changes: Immediately after redesigns, migrations, or algorithm updates
Regular audits help prevent ranking drops, crawl inefficiencies, and indexing issues, ensuring search engine visibility.
3. What Are the Most Common Technical SEO Issues?
- Slow Page Speed – Poor Core Web Vitals performance (LCP, FID, CLS).
- Broken Links & Redirect Issues – 404 errors, redirect chains, and looped redirects.
- Crawlability & Indexability Problems – Blocked pages in robots.txt, noindex tags, or orphan pages.
- Duplicate Content & Canonicalization Errors – Incorrect or missing canonical tags.
- Mobile Usability Issues – Unresponsive design, viewport problems, and poor touch elements.
- Structured Data Errors – Missing or improperly implemented schema markup.
Fixing these issues improves SEO performance, user experience, and search engine rankings.
4. What Tools Are Best for Conducting a Technical SEO Audit?
- Google Search Console – Monitors indexing, coverage issues, and mobile usability.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider – Crawls websites to detect broken links, redirects, and duplicate content.
- Google PageSpeed Insights & Lighthouse – Evaluates site speed and Core Web Vitals.
- Ahrefs Site Audit & SEMrush Site Audit – Provides a complete technical SEO health report.
- Sitebulb – Offers in-depth visual reports for site architecture and internal linking.
- GTmetrix – Assesses page speed performance and recommendations.
Using a combination of these tools ensures optimal website performance and better search rankings.

