- Schema markup, also known as structured data, is metadata added to a webpage’s HTML to help search engines understand its content.
- Using schema markup can lead to richer search results (rich snippets) and a 20-30% higher click-through rate.
- Schema acts as a universal language for search engines, helping them recognize specific details like product prices and reviews.
- For implementation, you can use WordPress plugins like Yoast SEO or Schema Pro, or create it manually with JSON-LD.
- Advanced strategies include combining multiple schema types and optimizing for voice search using specific schema types like FAQ and How-To.
Imagine this: You search for a product on Google, and among the ten blue links, one result stands out—it has a star rating, price, availability, and even an image.
That result is more likely to get your click, right?
That’s the power of Schema Markup.
Schema markup is one of the most underutilized yet highly effective SEO techniques.
It helps search engines understand your content better and, more importantly, enhances how your website appears in search results.
Websites that implement structured data properly have a 20-30% higher click-through rate (CTR) on average compared to those that don’t, according to Google.
Despite its potential, many websites either overlook or misuse schema markup, missing out on rich snippets, featured results, and even voice search rankings.
The good news? Implementing schema is easier than you think—and it can be a direct line to boosting your SEO visibility.
In this guide, we’ll break down:
- What schema markup is and how it works.
- Why it’s a critical factor for SEO.
- The different types of schema markup and when to use them.
- A step-by-step guide to implementing it correctly.
- Advanced strategies to maximize its benefits.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear roadmap for using schema markup to outperform competitors and dominate search results. Let’s get started.
Can You Find Your Website on Google?
If not, your customers can’t either. Let’s fix that with expert SEO strategies!
Contact UsWhat Is Schema Markup?
Schema markup, also known as structured data, is a form of metadata added to a webpage’s HTML to help search engines understand its content in a more structured way.
It’s like giving Google, Bing, and other search engines a roadmap to interpret your site beyond just reading text.
Developed by Schema.org, a collaborative project by Google, Microsoft, Yahoo, and Yandex, schema markup acts as a universal language that tells search engines exactly what different elements on your page mean.
Instead of just seeing text about a product, for example, search engines can recognize price, reviews, availability, and more—leading to richer, more informative search results.
How Does Schema Markup Work?
Let’s say you run a restaurant and want your Google search results to display your business hours, location, and customer reviews.
Without schema markup, search engines might struggle to extract and present this data properly. But with structured data, you can explicitly define these details, ensuring they appear in search results in an eye-catching way.
Here’s a basic example of JSON-LD schema markup for a restaurant:
<script type="application/ld+json">{ "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "Restaurant", "name": "The Italian Bistro", "address": { "@type": "PostalAddress", "streetAddress": "123 Main Street", "addressLocality": "New York", "addressRegion": "NY", "postalCode": "10001", "addressCountry": "US" }, "telephone": "+1-212-555-1234", "openingHours": "Mo-Su 11:00-22:00", "aggregateRating": { "@type": "AggregateRating", "ratingValue": "4.5", "reviewCount": "120" }}</script>
With this schema in place, Google can display business hours, address, and star ratings right in search results, making the listing more appealing and informative.
Why Is Schema Markup Important?
- Enhances search visibility – Websites with structured data often secure rich results, which are visually enhanced snippets that attract more clicks.
- Boosts click-through rates (CTR) – Studies show that rich results can increase CTR by up to 30%.
- Improves search engine understanding – Structured data helps Google and other search engines to categorize content accurately.
- Essential for voice search – Google Assistant and Siri rely on structured data to fetch direct answers for voice queries.
Schema markup isn’t just a technical SEO tactic—it’s a competitive advantage. Websites that leverage it effectively can stand out in search results, drive more organic traffic, and provide users with a better experience.
Featured Article: The Importance of Title Tags and How to Optimize Them
Why Schema Markup Is Crucial for SEO
Schema Markup isn’t just about making your search results look better—it’s a direct SEO asset that can impact your rankings, visibility, and user engagement.
Search engines constantly refine their algorithms to provide users with the most relevant and informative results, and structured data plays a key role in this process.
-
Schema Markup Improves Search Visibility and Click-Through Rates (CTR)
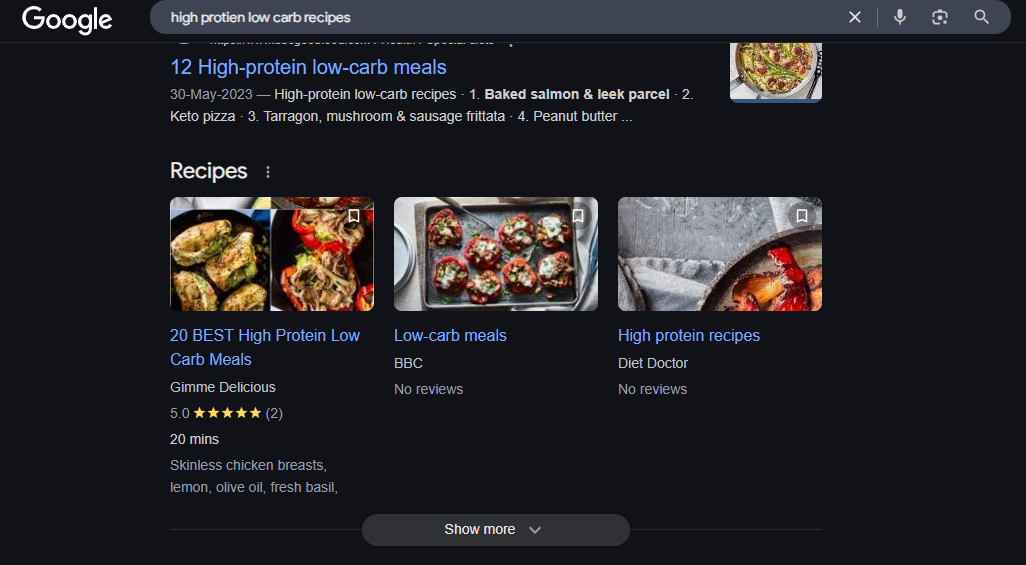
According to a study by Search Engine Land, pages that utilize structured data see an average 20-30% increase in organic click-through rates (CTR). Why? Because rich results stand out from standard blue links.
For example, compare these two search results for a recipe:
- Without schema markup: A plain text link with a meta description.
- With schema markup: A result displaying an image, cooking time, calories, and star ratings.
Users are naturally more inclined to click on visually rich, informative results, giving you a higher chance of attracting organic traffic.
-
Helps Search Engines Understand Your Content Better
Search engines rely on crawling and indexing to interpret web pages, but context matters. Schema Markup adds a layer of meaning, clarifying what each element of a page represents.
For example:
- If your page mentions “The Matrix,” schema can clarify whether it refers to the movie or a mathematical concept.
- A product page with schema markup can explicitly define attributes like price, availability, brand, and reviews, allowing Google to structure this data accordingly.
By improving search engines’ understanding of your content, schema markup increases the likelihood of your content appearing in relevant searches, reducing ambiguity and enhancing SEO precision.
-
Essential for Featured Snippets and Voice Search Optimization
Schema Markup plays a crucial role in position zero results, such as Google’s featured snippets and voice search responses.
- A 2023 Backlinko study found that 40.7% of voice search results come from pages using schema markup.
- Google’s structured data often feeds direct answers, which are used by voice assistants like Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant.
If you’re looking to optimize for voice search, FAQ schema, How-To schema, and Local Business schema are essential for providing concise, structured answers that search engines prefer.
-
Can Indirectly Influence Rankings
While Google has stated that structured data is not a direct ranking factor, it impacts engagement metrics that influence rankings, such as:
- Higher CTR: More clicks tell search engines that your result is relevant.
- Lower bounce rates: Structured data can provide users with exactly what they’re looking for, reducing the need to return to search results.
- Better dwell time: Pages that provide structured, rich content encourage users to stay longer.
In competitive industries, even a small increase in engagement metrics can be the difference between ranking #3 and #1.
-
Strengthens E-A-T (Expertise, Authority, Trustworthiness)
Google’s algorithm favors authoritative and trustworthy sources, and structured data helps reinforce E-A-T by:
- Clarifying authorship using Author schema for blog posts.
- Validating business legitimacy with Organization schema (e.g., business name, logo, address).
- Displaying real customer feedback using Review schema.
For businesses in industries like health, finance, and legal services, properly structured schema markup can reinforce credibility, signaling to Google that your content is reliable and authoritative.
With search engine algorithms becoming more AI-driven, structured data is more important than ever.
It enhances user experience, increases your visibility in SERPs, and aligns with the way search engines process information today.
Featured Article: The Ultimate Guide to URL Structures: SEO Best Practices & Future Trends
Types of Schema Markup and Their Use Cases
Schema markup is incredibly versatile, with over 800 different schema types listed on Schema.org.
However, not all are equally important for SEO. Below are the most impactful schema types, along with when and where to use them.
-
Product Schema (For eCommerce and Retail Websites)
Product Schema If you run an online store, Product schema is essential for showcasing key product details directly in search results. It enables Google to display:
- Price (including discounts)
- Availability (In stock, Out of stock, Limited stock)
- Star ratings (Aggregate user reviews)
- Brand and description
Example JSON-LD for Product Schema:
<script type="application/ld+json">{ "@context": "https://schema.org/", "@type": "Product", "name": "Wireless Noise Cancelling Headphones", "image": "https://example.com/headphones.jpg", "description": "High-quality wireless headphones with active noise cancellation.", "brand": { "@type": "Brand", "name": "SoundX" }, "aggregateRating": { "@type": "AggregateRating", "ratingValue": "4.7", "reviewCount": "1345" }, "offers": { "@type": "Offer", "price": "199.99", "priceCurrency": "USD", "availability": "https://schema.org/InStock" }}</script>Who should use it?
- eCommerce stores (Amazon, Shopify, WooCommerce)
- Retail brands selling products directly
- Affiliate marketers promoting products
-
Review Schema (For Blogs, Products and Local Businesses)
Review Schema Review schema is one of the most powerful structured data types because it adds star ratings to search results, significantly boosting CTR.
Best used for:
- Product reviews
- Business reviews
- Service reviews
Who should use it?
- Review websites (tech reviews, travel blogs, SaaS comparisons)
- Local businesses (restaurants, salons, dentists)
- eCommerce websites with user-generated reviews
-
Article Schema (For Blogs and News Websites)
News Schema If you publish blog content or news articles, implementing Article schema helps search engines understand your content better and increases the chances of appearing in Google Discover.
Who should use it?
- News websites (New York Times, BBC, Forbes)
- Blogs (SEO blogs, lifestyle blogs, marketing blogs)
- Publishers focused on trending topics
Example JSON-LD for Article Schema:
<script type="application/ld+json">{ "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "Article", "headline": "The Ultimate Guide to Schema Markup", "author": { "@type": "Person", "name": "Shakeel Ahmed" }, "datePublished": "2024-03-07", "publisher": { "@type": "Organization", "name": "Nexa Growth", "logo": { "@type": "ImageObject", "url": "https://nexagrowth.co.uk/logo.png" } }}</script> -
Organization Schema (For Businesses and Brands)
Organization Schema If you run a company, Organization schema helps Google verify your brand’s identity and displays important business details such as:
- Company name & logo
- Official website & social media links
- Customer service contact details
Who should use it?
- Businesses of any size (startups to enterprises)
- Personal brands & agencies
- Local businesses
Why it matters?
Google often pulls Organization schema data for Knowledge Panels, helping establish credibility and authority. -
Local Business Schema (For Local SEO and Google Business Profile)
Local Business Schema If you operate a physical business location, the Local Business schema is essential. It improves Google Maps visibility and helps potential customers find your:
- Business name, address, and phone number (NAP details)
- Operating hours
- Reviews and ratings
Who should use it?
- Restaurants, cafes, bars
- Medical practitioners (dentists, doctors, chiropractors)
- Law firms, agencies, and service-based businesses
-
FAQ and How-To Schema (For SEO and Featured Snippets)
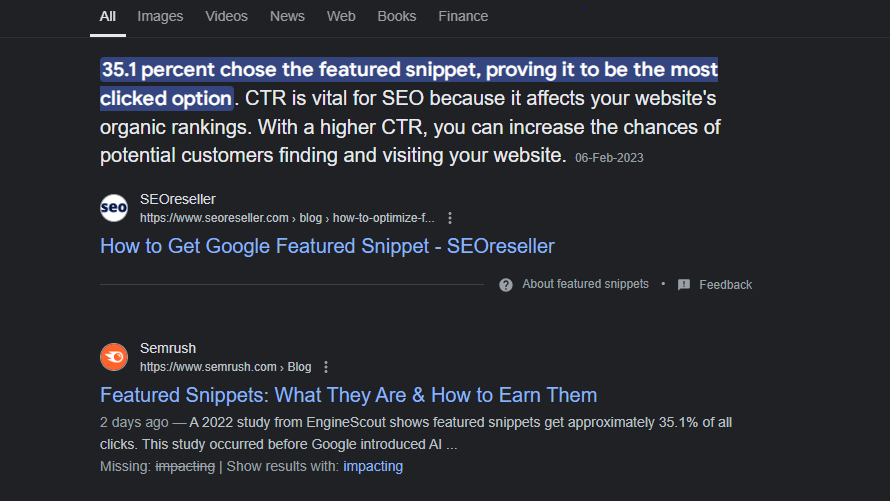
Featured Snippet Schema FAQ and How-To schema help websites appear in Google’s featured snippet section, providing users with direct answers to their queries.
Best used for:
- Answering common customer questions
- Step-by-step guides
- Informational blog posts
Why it matters?
Google prioritizes structured FAQ and How-To results for zero-click searches, helping drive brand visibility without paid ads.Which Schema Type Should You Use?
Schema Type Best For Key Benefits Product Schema eCommerce, affiliate sites Rich product snippets, improved CTR Review Schema Product & service-based sites, local businesses Star ratings in SERPs Article Schema Blogs, news websites Helps with Google Discover Organization Schema Businesses, agencies, brands Enhances Knowledge Panel presence Local Business Schema Restaurants, clinics, service providers Boosts Google My Business rankings FAQ Schema Blogs, eCommerce, service pages Increases chances of featured snippets Now that we’ve covered the most important types of schema markup, let’s explore how to implement it step by step on your website for maximum SEO benefits.
Your Competitors Are Stealing Your Clicks.
Take them back with a powerful SEO strategy that puts YOU in the spotlight. Ready to fight back?
Contact UsHow to Implement Schema Markup on Your Website (Step by Step)
Adding schema markup to your website might sound technical, but it’s easier than most people think.
Whether you’re using a WordPress site, Shopify store, or custom HTML, the process remains largely the same.
Below, we’ll walk through the step-by-step process to ensure your schema markup is correctly implemented and validated.
Step 1: Choose the Right Schema Type
Before you begin, determine which schema type best suits your content. Ask yourself:
- Is this a product page? → Use Product Schema
- Is this an informational blog post? → Use Article Schema
- Are you adding customer reviews? → Use Review Schema
- Do you want to optimize for local SEO? → Use Local Business Schema
To see a full list of available schema types, visit Schema.org.
Step 2: Use Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper
Google offers a free tool that makes adding structured data quick and easy—Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper.
- Go to the tool and select the data type you want to mark up (e.g., Article, Local Business, Product).
- Enter the URL of the page you want to add schema to.
- Highlight and tag elements (e.g., product name, price, review rating).
- Click “Create HTML” to generate the schema markup.
Step 3: Generate JSON-LD Code
Once Google’s tool creates your structured data, it provides two formats:
JSON-LD (Recommended) – Google’s preferred format, added as a script in the <head> section of your page.
Microdata – Requires adding schema tags within your existing HTML.
For beginners, JSON-LD is the easiest method since it doesn’t interfere with your existing page content.
Step 4: Manually Embed Schema Markup in Your HTML
If you’re manually adding schema markup, place the JSON-LD script within the <head> section of your webpage.
Example: Adding Schema Markup to a Product Page
<script type="application/ld+json">{ "@context": "https://schema.org/", "@type": "Product", "name": "Smartphone X Pro", "image": "https://example.com/smartphone.jpg", "description": "The latest Smartphone X Pro with 5G connectivity and 128GB storage.", "brand": { "@type": "Brand", "name": "TechBrand" }, "aggregateRating": { "@type": "AggregateRating", "ratingValue": "4.8", "reviewCount": "1023" }, "offers": { "@type": "Offer", "price": "799.99", "priceCurrency": "USD", "availability": "https://schema.org/InStock" }}</script>
Once added, save and publish the page.
Step 5: Validate Using Google’s Rich Results Test
Before going live, test your structured data using Google’s Rich Results Test.
- Enter your URL or paste the JSON-LD code.
- Click Test URL/Code and wait for Google to analyze it.
- If any errors appear, revise your schema and retest.
Tip: If your schema isn’t working, check for:
- Missing or incorrect data fields
- Improper nesting of JSON-LD properties
- Incorrect schema types
Step 6: Monitor Performance in Google Search Console
After implementing schema, track its performance using Google Search Console.
- Navigate to Enhancements → Rich Results.
- Check for valid schema markup and any detected errors.
- Keep an eye on click-through rates (CTR) to see if schema markup is improving engagement.
Tip: If your structured data isn’t appearing in search results immediately, don’t panic. Google may take a few days to weeks to index and display rich results.
Step 7: Automate Schema Markup with Plugins (For WordPress Users)
If you’re using WordPress, you can automate schema implementation with SEO plugins like:
- Rank Math – Automatically generates schema for posts, products, and reviews.
- Yoast SEO – Supports basic structured data for articles and breadcrumbs.
- Schema Pro – Ideal for advanced schema automation.
Simply install one of these plugins, select the schema type, and let the plugin handle the markup for you.
Schema markup is one of the most effective SEO techniques that many websites still ignore. By implementing structured data:
- Your search results will stand out with rich snippets.
- Google will better understand your content.
- You’ll increase CTR and improve engagement.
Featured Article: What Is On-Page SEO? A Beginner’s Guide for 2026
Advanced Schema Markup Strategies for Maximum SEO Impact
Now that you understand how to implement schema markup, let’s take it a step further.
Many businesses stop at the basics, but advanced schema strategies can significantly boost your visibility, improve click-through rates, and even future-proof your site for evolving search trends.
Below are some expert-level tactics to get the most out of structured data.
-
Combine Multiple Schema Types for Better Visibility
Most websites implement only one schema type per page—but combining multiple relevant schema types creates richer search results.
Example: Local Business + FAQ + Review Schema for a Restaurant
<script type="application/ld+json">{ "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "Restaurant", "name": "The Gourmet Kitchen", "address": { "@type": "PostalAddress", "streetAddress": "123 Main Street", "addressLocality": "New York", "addressRegion": "NY", "postalCode": "10001", "addressCountry": "US" }, "telephone": "+1-212-555-7890", "openingHours": "Mo-Su 11:00-22:00", "aggregateRating": { "@type": "AggregateRating", "ratingValue": "4.8", "reviewCount": "345" }, "servesCuisine": "Italian", "acceptsReservations": "True", "menu": "https://example.com/menu", "faq": { "@type": "FAQPage", "mainEntity": [{ "@type": "Question", "name": "Do you offer vegan options?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "Yes, we have a variety of vegan dishes on our menu." } }, { "@type": "Question", "name": "Do you take online reservations?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "Yes, you can book a table online through our website." } }] }}</script>Why This Works:
- The Local Business schema improves local search rankings.
- The Review schema adds star ratings to search results.
- The FAQ schema increases chances of appearing in featured snippets.
Pro Tip: Google loves structured content, so using multiple schema types makes your search results more attractive and informative.
-
Optimize for Voice Search and AI Assistants
With nearly 50% of searches happening via voice assistants like Google Assistant and Alexa, schema markup can help your content become the preferred answer in voice search results.
Best Schema Types for Voice Search
- FAQ Schema → Short, direct answers to common queries.
- How-To Schema → Step-by-step guides with actionable information.
- Speakable Schema → Highlights sections of your content that are optimized for voice search.
How to Implement Speakable Schema (For News and Blogs):
<script type="application/ld+json">{ "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "SpeakableSpecification", "name": "Schema Markup Guide", "url": "https://example.com/schema-markup-guide", "cssSelector": ["#intro", "#key-takeaways"]}</script>Why This Works:
- Google can read your content aloud via smart assistants.
- Increases the chances of ranking in zero-click searches.
-
Use Event Schema to Promote Webinars & Conferences
If you host events, Event schema can display event dates, locations, and ticket prices directly in search results.
Example: Schema Markup for a Webinar
<script type="application/ld+json">{ "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "Event", "name": "SEO Masterclass 2024", "startDate": "2024-06-10T19:00", "endDate": "2024-06-10T21:00", "eventAttendanceMode": "https://schema.org/OnlineEventAttendanceMode", "eventStatus": "https://schema.org/EventScheduled", "location": { "@type": "VirtualLocation", "url": "https://example.com/seo-webinar" }, "organizer": { "@type": "Organization", "name": "Nexa Growth", "url": "https://nexagrowth.co.uk" }, "offers": { "@type": "Offer", "price": "49.99", "priceCurrency": "USD", "availability": "https://schema.org/InStock" }}</script>Why This Works:
- Your event details appear in Google’s Event Listings.
- Users can see event details directly in search results, boosting attendance.
-
Monitor and Fix Schema Errors in Google Search Console
Even if you add schema markup correctly, errors can still occur. That’s why regular validation is crucial.
How to Monitor Schema in Google Search Console
- Log into Google Search Console.
- Navigate to Enhancements > Rich Results.
- Check for any “Invalid” or “Warnings” under structured data.
- Click on the error, fix the issue, and request revalidation.
Common Schema Errors and Fixes:
Error How to Fix It Missing required fields Check Schema.org to ensure all required fields are included. Invalid JSON-LD formatting Validate with Google’s Rich Results Test. Unsupported schema types Ensure schema type is listed on Schema.org and supported by Google. Pro Tip: Set up automated alerts in Google Search Console to notify you of structured data issues.
-
Keep Up With Google’s Schema Updates
Google frequently updates its structured data guidelines, so staying informed is critical to maintaining search visibility.
Best Resources for Schema Updates:
- Google’s Structured Data Developer Guide
- Schema.org Official Site
- Google Search Central Blog
Why This Matters:
- Some schema types become obsolete, affecting rankings.
- Google adds new structured data features that competitors might not be using yet.
Google’s Looking for You. Are You Showing Up?
Search engines crave optimized content—let’s make sure they find and rank you first!
Contact UsSchema Markup Best Practices and Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even though schema markup is a powerful tool for SEO, incorrect implementation can lead to errors, wasted efforts, or even penalties from Google.
To ensure you’re maximizing the benefits, follow these best practices while avoiding common mistakes that could negatively impact your search performance.
-
Always Use Google’s Preferred JSON-LD Format
There are three ways to implement schema markup:
- JSON-LD (Recommended by Google)
- Microdata (Embedded within HTML)
- RDFa (Less commonly used)
Google has explicitly stated that JSON-LD is the preferred method because it’s easier to implement, edit, and validate.
Instead of modifying HTML tags directly, JSON-LD sits inside a <script> tag, keeping it separate from your content.
Best Practice:
- Always use JSON-LD unless your CMS/platform restricts it.
- Place JSON-LD inside the <head> tag for optimal crawling.
-
Validate Schema Markup Before Going Live
Many websites unknowingly publish broken schema markup, which means search engines ignore it entirely. Avoid this by validating your structured data before deployment.
Best Tools for Schema Validation:
- Google’s Rich Results Test
- Schema Markup Validator
- Google Search Console (Enhancements → Rich Results)
Best Practice:
- Validate before publishing and after any website updates.
- Regularly monitor schema errors in Google Search Console.
-
Use Only Relevant and Supported Schema Types
Not all schema types are supported by search engines, and using irrelevant schema markup can lead to errors or manual actions from Google.
Do:
- Use schema types that match your content (e.g., Product schema for products, FAQ schema for FAQs).
- Follow Google’s list of supported schema types here.
Avoid:
- Applying Product schema to a blog post.
- Using JobPosting schema for a generic service page.
Best Practice:
- Check Schema.org and Google’s Developer Guidelines before adding new markup.
-
Keep Schema Markup Data Accurate and Updated
Many websites add structured data once and forget about it, leading to outdated or inaccurate information, which can result in manual penalties from Google.
Do:
- Update schema markup whenever content changes (e.g., pricing, availability, reviews).
- Use dynamic schema generation if your CMS supports it (e.g., eCommerce platforms like Shopify and WooCommerce).
Avoid:
- Displaying wrong product pricing or availability in structured data.
- Keeping old event schema for events that have already passed.
Best Practice:
- Set reminders to check and update structured data quarterly.
-
Use FAQ Schema and How-To Schema for Featured Snippets
FAQ and How-To schema are among the most effective for featured snippets and voice search optimization.
Do:
- Add FAQ schema to blog posts and service pages to increase SERP visibility.
- Use How-To schema for guides and tutorials to improve zero-click search results.
Avoid:
- Adding excessive FAQs just to manipulate rankings (Google may flag this).
- Using FAQ schema for low-quality, duplicate, or misleading content.
Best Practice:
- Write concise, direct answers to maximize the chances of being featured in search results.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Schema Markup
- Using Incorrect or Unsupported Schema Types
Google only supports certain schema types for rich results. Using unsupported or misused schema types won’t improve rankings and may cause validation errors. - Not Nesting Schema Properly
When using multiple schema types on a single page, they must be properly nested. Incorrect nesting can confuse search engines.
Example of Correct Nesting:(Review Schema within Product Schema){ "@context": "https://schema.org/", "@type": "Product", "name": "Wireless Headphones", "aggregateRating": { "@type": "AggregateRating", "ratingValue": "4.5", "reviewCount": "87" }} - Using Fake Reviews or Manipulated Ratings
Google has cracked down on websites using fake review schema. If your website includes structured data for reviews that don’t exist or are manipulated, you could face a manual penalty. - Forgetting to Test and Monitor Schema Markup Regularly
Schema Markup is not a one-time task. Many businesses set it up once and forget about it, leading to outdated information or schema errors over time. - Assuming Schema Markup Directly Boosts Rankings
While schema markup enhances visibility and CTR, it is not a direct ranking factor. It improves engagement, which can lead to better rankings, but it won’t automatically push your site to page one.
Conclusion
Schema markup is one of the most effective yet underutilized SEO tactics that can transform how your website appears in search results.
By adding structured data, you’re not just making it easier for search engines to understand your content—you’re also making your pages more engaging, informative, and clickable.
Despite not being a direct ranking factor, schema markup supports critical SEO elements like user experience, search intent fulfillment, and search visibility—all of which contribute to higher rankings over time.
If you haven’t implemented schema markup yet, now is the time to start. Whether you’re running an eCommerce store, a local business, or a content-focused website, structured data can provide a competitive edge in search results.
Your Website Deserves the VIP Treatment.
Give it the SEO glow-up it needs to attract, engage, and convert visitors like never before!
Contact Us
