- On-page SEO involves optimizing a web page’s internal elements to improve its search rankings.
- Key factors for on-page SEO are relevance, authority, and user experience.
- Google’s algorithm updates, like the Helpful Content Update and Core Web Vitals, have a significant impact on on-page SEO.
- Advanced strategies include using schema markup to unlock rich snippets and improve click-through rates.
- Improving readability and user experience through simple language and multimedia content is crucial for engagement.
Did you know that 75% of users never scroll past the first page of Google search results?
That means if your website isn’t ranking at the top, you’re losing out on potential traffic, leads, and sales.
In an era where 93% of online experiences begin with a search engine, mastering on-page SEO is no longer optional—it’s a necessity.
But what exactly is on-page SEO, and why does it matter so much?
In simple terms, on-page SEO refers to the strategies and optimizations you make directly on your web pages to improve their search rankings.
It involves everything from keyword placement and content quality to URL structure and internal linking—all crucial factors that help Google understand and rank your content.
However, Google’s algorithm is getting smarter. With over 200 ranking factors, search engines now prioritize relevance, user experience, and content quality more than ever before.
A decade ago, stuffing keywords into your content might have worked. Today, it’ll get you penalized.
So, how do you optimize your pages the right way in 2026?
This comprehensive guide will walk you through:
- The fundamentals of on-page SEO
- Proven techniques to boost rankings and engagement
- Advanced strategies like Schema Markup, NLP, and Featured Snippets
- How to audit and improve your content for long-term success
By the end of this guide, you’ll have an SEO blueprint to ensure your website ranks higher, attracts more traffic, and converts visitors into customers.
Ready to learn more? Let’s get started!
Optimize Your Website for Maximum Impact
Nexa Growth’s On-Page SEO services fine-tune your content, keywords, and structure to boost rankings and drive more traffic
Contact UsThe Basics of On-Page SEO
To understand what on-page SEO really is, we need to start at the basics.
What Is On-Page SEO?
On-Page SEO refers to all the optimizations you make directly on your web pages to improve their visibility in search engine results.
Unlike off-page SEO, which focuses on external signals like backlinks, on-page SEO is 100% in your control—making it one of the most effective ways to improve rankings.
Here’s what on-page SEO helps with:
- Higher Rankings – Search engines better understand your content, leading to better visibility.
- More Organic Traffic – Better rankings = more clicks from users.
- Improved User Experience – A well-optimized page loads faster, is easier to read and provides valuable content.
- Better Conversion Rates – Users who find what they’re looking for are more likely to take action.
Featured Article: What Is SEO and Why Is It Important for Businesses in 2026?
On-Page SEO vs. Off-Page SEO: What’s the Difference?
Many people confuse On-Page SEO with Off-Page SEO, but they serve different purposes.
| Feature | On-Page SEO | Off-Page SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Content and page structure | Backlinks and external signals |
| Examples | Keywords, meta tags, headings, URL structure, internal links | Link building, social media signals, brand mentions |
| Control | Full control over optimizations | Indirect control (depends on third parties) |
| Main Goal | Make content search-friendly and user-friendly | Build trust and authority |
To rank well, you need both on-page and off-page SEO. But on-page SEO is the foundation—without it, off-page efforts won’t be as effective.
How Search Engines Evaluate On-Page SEO
Google’s algorithm has evolved significantly over the years. Today, it focuses on three key factors when ranking web pages:
- Relevance – Does your content match the user’s search intent?
- Authority – Is your page a trusted source on the topic?
- User Experience (UX) – Is your website fast, mobile-friendly, and engaging?
Let’s break down how each factor influences your rankings:
| Ranking Factor | Why It Matters | Key Optimization Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Relevance | Google matches content to search intent | Use targeted keywords naturally, answer user queries |
| Authority | Trusted, authoritative sites rank higher | Use internal and external links, build topic clusters |
| User Experience (UX) | Poor UX = high bounce rates & low rankings | Improve site speed, readability, and mobile optimization |
In short, Google rewards pages that provide clear, well-structured, and valuable content—and punishes those that are slow, spammy, or difficult to navigate.
The Role of Google’s Algorithm Updates in On-Page SEO
Google releases thousands of algorithm updates every year, but some have a huge impact on how pages rank.
Here are a few game-changing updates that affect on-page SEO:
| Google Update | Impact on On-Page SEO | What You Need to Do |
|---|---|---|
| Helpful Content Update (2022) | Prioritizes people-first content over AI-generated or spammy content | Focus on valuable, well-researched articles |
| Core Web Vitals Update (2021) | Page speed and UX became direct ranking factors | Optimize site speed, mobile-friendliness, and interactivity |
| BERT Update (2019) | Google understands natural language better | Write conversational, intent-focused content |
By keeping up with these changes and applying on-page SEO best practices, you can stay ahead of the competition and future-proof your rankings.
Why On-Page SEO Matters
If you’re wondering whether On-Page SEO is worth your time, consider this: 53.3% of all website traffic comes from organic search.
That means if your site isn’t properly optimized, you’re missing out on a massive opportunity to attract visitors, leads, and sales.
The Relationship Between On-Page SEO and Rankings
Google processes over 8.5 billion searches per day, but not all results make it to the first page.
In fact, the top 3 organic search results receive 54.4% of all clicks, while results on page two barely get any traffic.
So, what determines whether your page lands in the top spots or disappears into search engine oblivion?
- Relevance: Google ranks pages that best match the user’s search query.
- Content Quality: Unique, well-researched content performs better than thin, duplicate content.
- On-Page SEO Signals: Titles, headings, internal links, and metadata help Google understand and rank your content.
- User Engagement: A well-structured page with a good UX keeps visitors on your site longer, reducing bounce rates.
Here’s a quick look at how On-Page SEO factors impact rankings:
| On-Page SEO Factor | Impact on Rankings |
|---|---|
| Target Keywords | Help Google determine relevance |
| Title & Meta Tags | Influence click-through rates (CTR) |
| Internal Linking | Improves crawlability and ranking potential |
| Page Speed | Affects bounce rates and user experience |
| Schema Markup | Enhances rich snippets & visibility |
Without on-page SEO, even the best content won’t rank well because search engines won’t fully understand it.
How On-Page SEO Impacts Organic Traffic
Let’s look at a real-world example of how optimizing on-page SEO can improve organic traffic.
A case study by Ahrefs found that:
- Updating and optimizing old content increased organic traffic by 146% in 6 months.
- Improving internal linking helped a website boost page rankings by 40 positions in Google search.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how on-page SEO improvements can impact your traffic:
| SEO Improvement | Estimated Traffic Boost |
|---|---|
| Optimizing Title Tags and Meta Descriptions | +10-30% CTR increase |
| Enhancing Content Quality and Length | +50-100% engagement boost |
| Speeding Up Page Load Time | -25-50% bounce rate reduction |
| Adding Schema Markup | +15-35% higher visibility in SERPs |
The bottom line? Optimized pages attract more clicks, keep visitors engaged longer, and convert better.
Common On-Page SEO Mistakes That Hurt Rankings
Even if you’re implementing On-Page SEO, mistakes can hold you back. Here are some of the biggest pitfalls and how to avoid them:
| Mistake | Why It’s Bad | How to Fix It |
|---|---|---|
| Keyword Stuffing | Google penalizes pages with unnatural keyword use | Use keywords naturally within the content |
| Duplicate Content | Reduces page authority and confuses search engines | Create original content and use canonical tags |
| Ignoring Internal Links | Misses opportunities to boost other pages | Link to relevant pages to improve SEO |
| Slow Page Speed | This leads to high bounce rates and low rankings | Optimize images, scripts, and server performance |
| Poor Mobile Optimization | Google prioritizes mobile-friendly pages | Use responsive design and check with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test |
By avoiding these mistakes and focusing on proven on-page SEO techniques, you can significantly improve rankings and organic traffic.
Fundamental On-Page SEO Elements
To rank higher in search engines, you need to get the fundamentals of On-Page SEO right.
Google’s algorithms analyze hundreds of factors, but the core elements that impact rankings the most include:
- Content Quality – Is the content helpful, original, and engaging?
- Keyword Optimization – Are keywords used strategically without stuffing?
- Title and Meta Tags – Do they accurately describe the page and encourage clicks?
- URL Structure – Is it clean, short, and keyword-friendly?
- Internal and External Linking – Are links helping users and search engines navigate content?
Let’s break these down in detail.
-
Writing Unique and Helpful Content
Content is at the core of on-page SEO. Google’s Helpful Content Update prioritizes content that genuinely helps users rather than just being optimized for search engines.
What Makes Content “SEO-Friendly”?
Factor Why It Matters Best Practices Originality Google penalizes duplicate or copied content Ensure all content is unique and adds new insights Depth Thin content struggles to rank Cover topics comprehensively (aim for 1000+ words where needed) Engagement Google tracks user behavior (time on page, bounce rate) Use a conversational tone, visuals, and examples Search Intent If content doesn’t match what users want, it won’t rank Align with informational, commercial, or navigational intent Google prioritizes content that answers user queries thoroughly, so instead of just writing for SEO, create content that delivers value first.
-
Placing Target Keywords Strategically
Keyword optimization remains one of the most important ranking factors, but keyword stuffing can get your page penalized. The key is strategic placement.
Where to Place Your Keywords for Maximum Impact
Placement Importance Title Tag One of the strongest ranking factors—place the primary keyword naturally. First 100 Words Helps Google understand the topic early on. Headings (H1, H2, H3) Improves content structure and search relevance. URL Short, descriptive URLs with keywords rank better. Meta Description Influences click-through rates (though not a direct ranking factor). Alt Text for Images Helps with image SEO and accessibility. Throughout Content Use naturally—avoid overstuffing. Example of good keyword placement:
❌ Bad Keyword Placement: “On-Page SEO is On-Page SEO because On-Page SEO helps On-Page SEO rankings.”
✔ Good Keyword Placement: “On-Page SEO is essential because it helps search engines understand and rank your content effectively.” -
Writing Keyword-Rich Title Tags
Your title tag is the first thing users and search engines see. A well-optimized title can significantly boost rankings and click-through rates.
Best Practices for Title Tags
- Keep it under 60 characters (longer titles get cut off in search results).
- Place the target keyword close to the beginning.
- Make it compelling—engage users with numbers, questions, or power words.
- Avoid clickbait—ensure the title accurately reflects the content.
Example of a high-performing title tag:
“What Is On-Page SEO? A Beginner’s Guide (2026)”
-
Crafting Click-Worthy Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions don’t directly impact rankings, but they influence click-through rates (CTR).
How to Write Effective Meta Descriptions
- Keep it under 160 characters.
- Include the target keyword naturally.
- Make it compelling—explain why users should click.
- Use an active voice and a call to action.
Example:
“Learn everything about On-Page SEO in this 2026 guide. Discover strategies to rank higher and drive more organic traffic today!” -
Using Headings and Subheadings for Structure
Headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.) help break up content for readability and improve SEO by signaling topic relevance to search engines.
Best Practices for Headings
- Use only one H1 per page (this should be the main title).
- Use H2s for main sections and H3s for subpoints.
- Incorporate keywords naturally in headings.
- Make them descriptive and engaging.
-
Optimizing URLs for Better Crawlability
A clean, keyword-rich URL structure improves rankings and makes pages easier for both users and search engines to understand.
Examples of Good vs. Ineffective URLs
❌ Ineffective URL:
example.com/onpageseo-article-112233✅ Good URL:
example.com/on-page-seo-guideBest Practices for URLs
- Keep them short and descriptive.
- Use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_).
- Avoid unnecessary numbers or random strings.
- Include a primary keyword naturally.
-
Strategic Internal and External Linking
Internal links help search engines navigate your site, while external links boost credibility.
Internal Linking Best Practices
- Link to relevant pages naturally within the content.
- Use keyword-rich anchor text (but avoid over-optimization).
- Ensure important pages receive multiple internal links.
External Linking Best Practices
- Link to authoritative sources (e.g., industry studies, government sites).
- Use natural anchor text that flows with the content.
- Open external links in a new tab to keep users on your site.
By optimizing these fundamental elements, you’ll create a strong on-page SEO foundation that helps your site rank higher and attract more traffic.
Featured Article: How Does SEO Work? (Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking Explained)
Advanced Content Optimization Strategies
Now that you understand the fundamental elements of On-Page SEO, it’s time to take your optimization efforts to the next level.
Google’s algorithm prioritizes content that is informative and keyword-optimized, well-structured, engaging, and aligned with search intent.
This section covers advanced strategies to improve your content quality, enhance readability, and increase user engagement.
-
Understanding and Satisfying Search Intent
One of the biggest mistakes in SEO is targeting keywords without considering user intent.
Google doesn’t just match keywords—it prioritizes pages that best satisfy what the user is looking for.
Types of Search Intent and How to Optimize for Them
Search Intent Purpose Example Queries Best Optimization Strategies Informational Users want knowledge or answers “What is On-Page SEO?” Write detailed, authoritative content with clear explanations and visuals Navigational Users seek a specific website or brand “Google Search Console login” Ensure the brand name is optimized, use internal linking Commercial Users are researching before making a purchase “Best SEO tools for beginners” Provide comparisons, reviews, and pros/cons Transactional Users are ready to take action “Buy SEO course online” Optimize CTAs, product pages, and structured data If your page doesn’t match the dominant intent behind a keyword, Google won’t rank it highly, even if it’s well-optimized.
How to Identify Search Intent for Any Keyword
- Google your target keyword and analyze the top-ranking pages—are they guides, product pages, or listicles?
- Check the “People Also Ask” section to see related queries.
- Use tools like Semrush or Ahrefs to analyze competitor content and intent signals.
-
Using the Inverted Pyramid Model for SEO Content
Most users don’t read entire articles—they scan for quick answers. That’s why the Inverted Pyramid Model is an effective way to structure content.
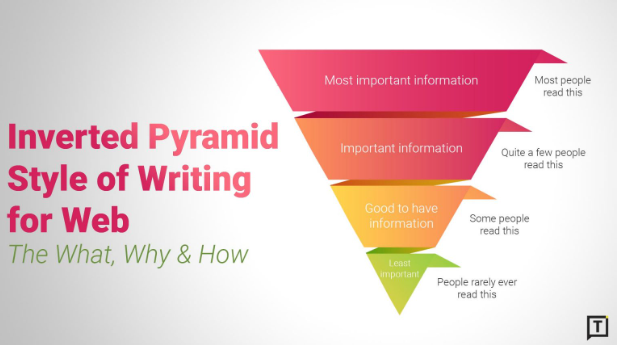
A Visual of an Inverted Pyramid Model by Typewriter Media How it works:
- Start with the most important information (answer the main question right away).
- Expand on supporting details with examples and explanations.
- Provide additional insights and advanced strategies at the end.
This structure ensures engagement from both readers and search engines by placing valuable content upfront.
-
The Importance of Keyword Frequency and Variations
Google’s algorithm no longer just looks for exact-match keywords—it understands semantic relevance and variations.
Instead of repeating the same keyword excessively, use LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords and synonyms.
Best Practices for Keyword Optimization
- Use primary keywords in the title, H1, first 100 words, and last paragraph.
- Sprinkle related terms and synonyms naturally throughout the content.
- Optimize for voice search queries (long-tail conversational phrases).
Example:Instead of overusing “On-Page SEO”, incorporate variations like:
- “SEO for website optimization”
- “On-site SEO techniques”
- “Improving search rankings through On-Page factors”
This improves readability and prevents keyword stuffing while still signaling topic relevance to Google.
-
Writing for Humans and Search Engines
Google’s AI models, including RankBrain and BERT, evaluate how well content serves human readers, not just how well it’s optimized for keywords.
How to Write Engaging, SEO-Optimized Content
Writing Factor Why It Matters Best Practices Readability Google favors easy-to-read content Use short paragraphs (2-3 sentences max) Conversational Tone Improves engagement Avoid jargon and write how people talk Bullet Points and Lists Helps with featured snippets Use lists for steps, comparisons, and summaries Multimedia (Images, Videos, Infographics) Keeps users engaged Add relevant visuals to break up text
Pro Tip: Use Hemingway Editor or Grammarly to improve readability and remove complex sentences. -
Formatting for Featured Snippets
Featured snippets (also known as position zero) are Google’s way of displaying quick answers directly in search results.
Winning a featured snippet can significantly boost click-through rates.
Types of Featured Snippets and How to Optimize for Them
Snippet Type Description How to Optimize Paragraph Snippet Short text answers (40-60 words) Answer questions concisely in the first 100 words List Snippet Numbered or bulleted lists Use clear subheadings and bullets for steps Table Snippet Comparison or structured data Format data into tables Video Snippet Google highlights a video section Add timestamps to key moments in YouTube videos Example of a Featured Snippet-Optimized Answer:
Question: What is On-Page SEO?
Optimized Answer (40-60 words):
“On-Page SEO refers to optimizing individual web pages to improve search rankings. It includes content quality, keyword placement, meta tags, internal linking, and user experience factors like page speed and mobile-friendliness. These optimizations help search engines understand the page’s content and enhance visibility in search results.”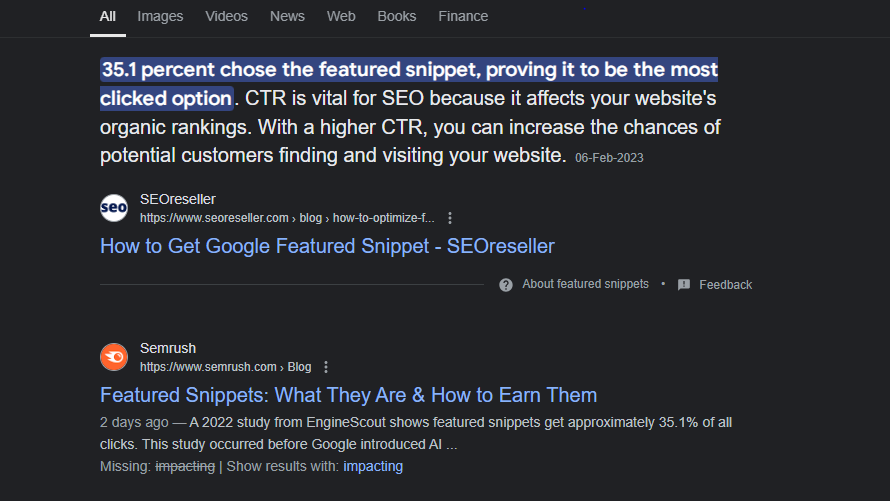
An Example of a Featured Snippet Key Takeaways for Advanced Content Optimization
- Match search intent—analyze the top results before creating content.
- Structure content using the Inverted Pyramid Model for better engagement.
- Use LSI keywords instead of repeating the same term excessively.
- Write conversationally and keep paragraphs short.
- Format content for featured snippets using lists, tables, and concise answers.
By applying these advanced content optimization techniques, you’ll not only improve search rankings but also create content that keeps users engaged and converts visitors into customers.
On-Page SEO: How to Optimize for User Engagement and Retention
Ranking high on Google is only half the battle—keeping users on your site and engaging with your content is just as important.
Google tracks user behavior metrics like bounce rate, dwell time, and click-through rate (CTR) to determine whether your page is valuable. If users leave too quickly, your rankings may drop.
This section covers key strategies to improve user engagement, reduce bounce rates, and increase content retention.
-
Improving Readability and UX
A website that is difficult to read or navigate will drive users away, no matter how good the content is.
Readability and user experience (UX) play a direct role in rankings because they impact how long visitors stay on your page.
Best Practices for Readability and UX
Factor Why It Matters Best Practices Short Paragraphs Large text blocks overwhelm readers Keep paragraphs 2-3 sentences max Simple Language Complex words make content harder to understand Write at a Grade 6-8 reading level Bullet Points and Lists Improves skim ability Use for key points, steps, or summaries Subheadings (H2, H3) Helps with navigation and structure Use descriptive, keyword-rich subheadings Whitespace and Layout Crowded pages increase bounce rates Add enough spacing for easy reading Example of Poor Readability vs. Optimized Readability
❌ Hard to Read:
“On-Page SEO is an important aspect of digital marketing because it helps websites rank higher on search engines. This involves optimizing various elements such as keywords, content quality, and internal linking to improve search visibility. Ensuring that your site is mobile-friendly and loads quickly is also crucial for SEO rankings. Without proper On-Page SEO, websites struggle to attract organic traffic, leading to low engagement and conversions.”✅ Optimized for Readability:
What Is On-Page SEO?
On-Page SEO is the process of optimizing web pages to rank higher in search engines. It includes:- Keyword placement in titles, headings, and content
- High-quality, user-friendly content
- Fast page speed and mobile optimization
- Strategic internal linking
-
The Role of Multimedia in Engagement
A text-heavy page can be overwhelming. Adding images, videos, infographics, and charts improves engagement, readability, and dwell time.
How Multimedia Impacts SEO
Multimedia Type SEO Benefit Implementation Tip Images Improves visual appeal and supports content Use alt text with keywords for SEO Videos Increases dwell time and engagement Embed short, relevant videos Infographics Helps simplify complex topics Use clear visuals & minimal text Charts & Tables Improves information retention Format data into easy-to-read tables How to Optimize Images for SEO
- Use descriptive filenames (e.g.,
on-page-seo-checklist.pnginstead ofimage123.jpg). - Compress images to improve load speed (use tools like TinyPNG).
- Include alt text with relevant keywords.
Example of an Optimized Image Alt Tag
❌ Bad Alt Tag:
image1.jpg
✅ Good Alt Tag:"On-Page SEO checklist for ranking higher in Google" - Use descriptive filenames (e.g.,
-
Formatting for Better User Retention
A well-structured page guides users smoothly through the content.
Best Practices for Formatting Content
- Use bold and italics to highlight key points.
- Break up long sections with subheadings and images.
- Add jump links (anchor links) for easy navigation.
Example of Good vs. Bad Formatting:
❌ Bad Formatting:
“Optimizing title tags, meta descriptions, and images is crucial for SEO. These elements help search engines understand your page and influence click-through rates. Additionally, adding internal links, improving page speed, and structuring content with headings improve rankings.”✅ Good Formatting:
<H2> Key Elements of a Great Coffee Shop
<H3> 1. Atmosphere & Ambiance
- Cozy seating and warm lighting create a welcoming vibe
- Background music and decor enhance the overall experience
<H3> 2. Quality Coffee & Menu Variety
- Freshly roasted beans and expertly crafted drinks
- Options for all tastes, including non-coffee beverages and pastries
<H3> 3. Friendly and Efficient Service
- Knowledgeable baristas who make great recommendations
- Quick service without compromising quality
-
Reduce Bounce Rate and Increase Dwell Time
Bounce rate measures how many users leave your site after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate signals poor user engagement, which can lower rankings.
Ways to Reduce Bounce Rate
Strategy How It Helps Improve Page Speed Faster pages reduce frustration and abandonment Add Internal Links Keeps users navigating your site longer Optimize Above-the-Fold Content Make sure users immediately see valuable info Use Engaging Headlines Hook users in the first few seconds Enhance Mobile-Friendliness Mobile users leave quickly if the site isn’t responsive Example of Optimizing Above-the-Fold Content:
❌ Ineffective:
- A long block of text with no clear message
- No CTA or internal links
✅ Good:
- A clear headline and value proposition
- Quick summary or bullet points to hook readers
- Call-to-action (CTA) button to guide the user
Key Takeaways for User Engagement and Retention
- Break content into readable sections (short paragraphs, bullet points, headings).
- Use multimedia (images, videos, charts) to improve engagement.
- Optimize formatting to make content scannable and digestible.
- Reduce bounce rates by enhancing page speed, mobile responsiveness, and internal linking.
- Improve above-the-fold content so users find value immediately.
By improving readability, adding visuals, and structuring content effectively, your site will keep visitors engaged longer, sending positive ranking signals to Google.
Struggling to Rank? Let’s Fix That!
Nexa Growth’s On-Page SEO services make sure your site is fully optimized for search engines and users. Better rankings start here—let’s get to work!
Contact UsInternal and External Linking Strategies
Linking is one of the most powerful yet underrated aspects of on-page SEO.
Internal and external links guide search engines and users through your website, distribute authority, and improve overall page rankings.
A well-structured linking strategy helps:
- Improve search engine crawlability by connecting related pages.
- Increase user engagement by directing visitors to relevant content.
- Boost rankings by passing link equity (PageRank) to important pages.
In this section, we’ll cover the best internal and external linking strategies to maximize your SEO performance.
Strategic Internal Linking for SEO and UX
Internal links connect pages within your website, helping both users and search engines navigate your content.
A strong internal linking strategy improves rankings and keeps users engaged longer.
Best Practices for Internal Linking
| Strategy | Why It’s Important | How to Implement |
|---|---|---|
| Link to High-Value Pages | Distributes authority to key pages | Prioritize links to money pages (service pages, pillar content) |
| Use Descriptive Anchor Text | Helps search engines understand link context | Avoid generic text like “click here”—use keyword-rich anchor text |
| Add Contextual Links Naturally | Enhances user experience and relevance | Link where it makes sense, not just for SEO |
| Don’t Overload Pages with Links | Too many links dilute SEO value | Aim for 3-5 internal links per 1000 words |
| Use a Logical Site Structure | Helps crawlers understand relationships between pages | Organize pages into topic clusters |
Example of Good Internal Linking
✅ “For more details, check out our SEO Audit Checklist to ensure your site is fully optimized.”
How to Build a Strong Internal Linking Structure
A well-planned internal linking structure improves site authority and rankings.
-
Use the Topic Cluster Model
Instead of linking randomly, group related content around pillar pages.
Example: Internal Linking for On-Page SEO
- Pillar Page: On-Page SEO Guide
- Cluster Content:
- How to Optimize Title Tags
- Internal Linking Best Practices
- Image Optimization for SEO
- On-Page SEO vs. Off-Page SEO
- Cluster Content:
Each supporting article links back to the pillar page, strengthening its authority.
- Pillar Page: On-Page SEO Guide
-
Prioritize Deep Linking
Many sites only link to their home pages, but deep linking (linking to specific internal pages) improves SEO.
- Ineffective Linking Example: All blog posts only link to the homepage.
- Good Linking Example: Blog posts link to other relevant blogs, services, and resources.
-
Fix Broken Internal Links
Broken links hurt user experience and SEO. Use tools like:
- Google Search Console (Crawl Errors Report)
- Ahrefs Site Audit
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider
The Right Way to Use External Links
External links (links to other websites) add credibility and help search engines understand your content.
When to Use External Links
- To cite authoritative sources (studies, research, government websites).
- To add value for readers (e.g., linking to Google’s official SEO guidelines).
- To support claims with data (e.g., statistics from trusted sources).
Best Practices for External Linking
| Strategy | Why It’s Important | How to Implement |
|---|---|---|
| Link to High-Authority Sites | Builds credibility and trust | Use sources like Google, Moz, Ahrefs, HubSpot |
| Use Relevant Links | Keeps content useful and focused | Avoid unrelated links that don’t support the topic |
| Set External Links to Open in a New Tab | Keeps users on your site | Use target="_blank" in your HTML |
| Use NoFollow for Low-Trust Links | Prevents passing link equity to untrusted sites | Add rel="nofollow" for sponsored or affiliate links |
Example of Good External Linking:
✅ “According to Google’s SEO Guide, internal linking plays a key role in crawlability.”
Internal vs. External Links: Key Differences
| Factor | Internal Links | External Links |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Helps navigate within your site | Adds credibility and connects to external resources |
| SEO Impact | Distributes link equity (PageRank) internally | Passes link equity to external sites |
| Anchor Text | Uses keyword-rich anchor text | Uses natural, relevant text |
| Control | Full control over links | No control over external sites’ content |
Both internal and external links are crucial for SEO success. A balanced mix ensures your website is both well-structured and authoritative.
Common Linking Mistakes to Avoid
Even with a strong strategy, linking mistakes can hurt SEO instead of helping it.
Top Mistakes and How to Fix Them
| Mistake | Why It’s Bad | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Broken Links | Hurts user experience and SEO | Regularly check and fix using Google Search Console |
| Overuse of Internal Links | Too many links dilute SEO value | Stick to 3-5 internal links per article |
| Linking to Low-Quality External Sites | Can harm credibility | Only link to trusted sources |
| Not Updating Old Links | Outdated links reduce relevance | Regularly update links to current resources |
| Forgetting to Use Anchor Text Wisely | Generic text like “click here” wastes SEO value | Use keyword-rich, descriptive anchor text |
By avoiding these mistakes and implementing strategic linking, you can boost rankings, improve user engagement, and strengthen your site’s SEO authority.
Key Takeaways for Internal and External Linking
- Use internal links to guide users and pass SEO value to important pages.
- Follow a topic cluster model to organize content effectively.
- Ensure external links point to authoritative, relevant sources.
- Fix broken links regularly to maintain site credibility.
- Optimize anchor text for clarity and SEO impact.
By implementing these proven linking strategies, you’ll enhance both search engine rankings and user experience, leading to higher engagement and conversions.
Technical On-Page SEO Enhancements
While content and keywords are essential, technical on-page SEO ensures that search engines can properly crawl, index, and rank your pages.
A well-optimized website isn’t just about great content—it must also be fast, mobile-friendly, and technically sound to perform well in search results.
This section covers the most important technical optimizations that impact On-Page SEO.
Improving Page Speed for Higher Rankings
Page speed is a direct ranking factor in Google’s algorithm. Studies show that:
- 53% of users leave a page if it takes more than 3 seconds to load.
- Faster pages increase engagement and conversions by reducing bounce rates.
How to Check Your Page Speed
Use tools like:
Best Practices to Improve Page Speed
| Optimization | Benefit | How to Implement |
|---|---|---|
| Compress Images | Reduces load time | Use TinyPNG or WebP format |
| Enable Browser Caching | Stores files for faster loading | Set cache expiration headers |
| Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) | Speeds up global load times | Use Cloudflare or AWS CloudFront |
| Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML | Reduces file size | Use Autoptimize (WordPress) or manual minification |
| Reduce Redirects | Prevents unnecessary load delays | Fix 301 redirects and broken links |
| Enable GZIP Compression | Reduces page size | Enable via .htaccess file |
By implementing these optimizations, you can significantly improve page speed, which helps rankings and enhances user experience.
Mobile-Friendliness and Responsive Design
With over 60% of searches coming from mobile devices, Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning your site’s mobile version is more important than desktop for ranking.
How to Test Mobile-Friendliness
- Google Mobile-Friendly Test (search.google.com/test/mobile-friendly)
- Check in Google Search Console (Mobile Usability Report)
- Manually test on different devices and screen sizes.
Best Practices for Mobile Optimization
| Factor | Why It Matters | How to Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Responsive Design | Ensures content adapts to all screen sizes | Use CSS media queries or mobile-friendly themes |
| Fast Load Times | Mobile users leave slow sites quickly | Optimize images, use lazy loading |
| Thumb-Friendly Navigation | Makes tapping easier | Use larger buttons and proper spacing |
| Avoid Pop-ups and Intrusive Ads | Google penalizes mobile-unfriendly pop-ups | Use exit-intent pop-ups only |
| Readable Text and Spacing | Small text hurts usability | Set font size to at least 16px |
A mobile-optimized site improves user experience, engagement, and rankings.
Core Web Vitals: How They Affect On-Page SEO
Google’s Core Web Vitals focus on page experience and performance metrics. These vitals are part of Google’s ranking factors.
Core Web Vitals Metrics
| Metric | What It Measures | Ideal Score |
|---|---|---|
| Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) | How fast the largest element loads | Under 2.5s |
| First Input Delay (FID) | How fast users can interact with the page | Under 100ms |
| Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) | Prevents unexpected layout shifts | Under 0.1 |
How to Improve Core Web Vitals
- Optimize LCP by compressing images and using lazy loading.
- Reduce FID by minimizing JavaScript execution time.
- Prevent CLS by defining image dimensions and avoiding layout shifts.
Check performance using Google PageSpeed Insights and Search Console’s Core Web Vitals Report.
Proper Use of Canonical Tags
Canonical tags (rel=”canonical”) prevent duplicate content issues and ensure search engines index the correct page.
When to Use Canonical Tags
- If you have similar pages with slight variations (e.g., product pages).
- If you publish guest posts that appear on multiple websites.
- To consolidate multiple versions of the same page (
http/httpsorwww/non-www).
Example of a Canonical Tag in HTML
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/on-page-seo-guide" />
Using canonical tags consolidates SEO value and avoids ranking dilution.
Key Takeaways for Technical On-Page SEO
- Page speed is critical—optimize images, enable caching, and reduce redirects.
- Mobile-friendliness is a ranking factor—ensure a responsive, fast-loading site.
- Core Web Vitals impact SEO—monitor LCP, FID, and CLS.
- Canonical tags prevent duplicate content issues and consolidate SEO value.
By focusing on technical SEO enhancements, you ensure your pages are fully optimized for search engines and users, leading to higher rankings and better user experience.
Schema Markup and Structured Data
Schema markup, also known as structured data, is a powerful yet often overlooked on-page SEO element.
It helps search engines better understand your content and display enhanced results in SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages).
By implementing schema markup, you can unlock rich snippets, which make your listing more prominent and attractive in search results.
What Is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is a type of microdata that provides additional context about a webpage’s content. It allows search engines to display rich results, such as:
- Star ratings and reviews
- FAQ dropdowns
- Product prices and availability
- Event details
- Author and publishing date
Websites that use schema markup often see higher CTRs (click-through rates) because their results stand out more than plain-text listings.
How Schema Markup Helps SEO
While schema markup isn’t a direct ranking factor, it improves user experience and engagement, which indirectly boosts rankings.
| Benefit | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Increases Visibility | Makes search results more attractive and informative |
| Boosts CTR | Rich snippets encourage more clicks compared to plain results |
| Improves Content Understanding | Helps Google categorize and display your content correctly |
| Enhances Local SEO | Displays business information like address, phone number, and reviews |
Websites that implement schema markup properly often rank higher and gain more organic traffic.
Types of Schema Markup and When to Use Them
Google supports multiple types of schema markup, but here are the most common and their use cases:
| Schema Type | Purpose | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Article Schema | Helps Google understand news and blog content | Blog posts, news articles |
| FAQ Schema | Displays expandable Q&A in search results | FAQ pages, product pages |
| Review Schema | Shows star ratings in search results | Product pages, service reviews |
| Organization Schema | Displays business details like name, logo, and social links | Homepages, About Us pages |
| Breadcrumb Schema | Shows navigation path in search results | Websites with multiple categories |
| Event Schema | Displays event details, date, and location | Webinars, conferences, workshops |
How to Implement Schema Markup
There are three main ways to add schema markup to a webpage:
-
Using JSON-LD (Recommended by Google)
JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is the easiest and most SEO-friendly way to add structured data.
Example of FAQ Schema Markup (JSON-LD format)
<script type="application/ld+json"> { "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "FAQPage", "mainEntity": [ { "@type": "Question", "name": "What is On-Page SEO?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "On-Page SEO refers to optimizations made directly on a webpage to improve search engine rankings." } }, { "@type": "Question", "name": "Why is On-Page SEO important?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "On-Page SEO helps search engines understand content and improves visibility in search results." } } ] } </script>Where to Add It: Paste this in the
<head>section or just before the</body>tag of your webpage. -
Using Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper
If you’re not comfortable with coding, Google offers a Schema Markup Helper:
- Go to Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper.
- Select the type of schema you want to generate.
- Highlight elements on your page and assign structured data labels.
- Copy the generated code and add it to your website.
-
Using WordPress Plugins
For WordPress users, plugins like:
- Rank Math
- Yoast SEO
- Schema Pro
Allow you to automatically generate and implement schema markup without coding.
Testing and Validating Schema Markup
Before publishing, always test your schema markup to ensure there are no errors.
Best Tools for Schema Validation:
- Google Rich Results Test (search.google.com/test/rich-results)
- Schema Markup Validator (validator.schema.org)
- Google Search Console (Enhancements Report)
If you see errors, double-check the JSON-LD syntax and ensure all required fields are included.
Real-World Example: Impact of Schema Markup on SEO
A study by Search Engine Journal found that websites using schema markup experienced:
- A 30% increase in CTR due to rich snippets.
- A 12% boost in organic traffic within three months.
- More featured snippet placements, improving visibility.
This shows that structured data is one of the easiest ways to gain a competitive edge in search results.
Key Takeaways for Schema Markup
- Schema markup helps Google understand and display content better.
- Using rich snippets increases CTR and visibility.
- The best implementation method is JSON-LD, as recommended by Google.
- Always test and validate your structured data before publishing.
- Websites with schema markup see better rankings and more organic traffic.
By implementing structured data correctly, your website will stand out in search results, attract more clicks, and improve user engagement—all critical for On-Page SEO success.
Image and Video Optimization
Optimizing images and videos is another crucial yet often overlooked aspect of on-page SEO.
Search engines rely on alt text, file names, and structured data to understand multimedia content.
Optimized visuals enhance user engagement, improve rankings, and drive more traffic from Google Images and video search results.
In this section, we’ll cover best practices for optimizing images and videos to improve both search visibility and page performance.
How Image Optimization Impacts SEO
Images contribute to user experience and SEO in several ways:
- Faster Page Load Speeds – Large, unoptimized images slow down your website, leading to higher bounce rates.
- Improved Accessibility – Alt text helps visually impaired users and allows Google to interpret images.
- More Search Visibility – Properly optimized images can rank in Google Images, driving extra traffic.
- Better UX and Engagement – Pages with high-quality visuals perform better and keep users engaged longer.
Best Practices for Image Optimization
| Factor | Why It Matters | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| File Format | Determines image quality and size | Use WebP or JPEG for a balance between quality and compression |
| File Size Compression | Large images slow down page speed | Use tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or ShortPixel |
| Descriptive File Names | Helps Google understand the image context | Name files descriptively (e.g., on-page-seo-guide.png instead of IMG001.jpg) |
| Alt Text Optimization | Improves accessibility and SEO | Use keyword-rich alt text describing the image |
| Lazy Loading | Prevents unnecessary loading | Enable lazy loading so images load only when visible |
| Structured Data for Images | Helps images appear in rich results | Use ImageObject schema markup |
Example of an Optimized Image Alt Text
❌ Ineffective Alt Text: "image1.jpg"
❌ IneffectiveAlt Text: "SEO infographic"
✅ Good Alt Text: "A complete guide to On-Page SEO with best practices for ranking higher on Google."
Video Optimization for SEO
With video consumption growing rapidly, Google prioritizes video content in search rankings, especially for how-to guides and tutorials.
Where Video Optimization Matters
- YouTube SEO – YouTube is the second-largest search engine and optimized videos rank in Google Video Search.
- Google SERPs – Google often displays video results at the top of search pages.
- Website Engagement – Videos increase dwell time, which can boost rankings.
Best Practices for Video Optimization
| Factor | Why It’s Important | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Video Title and Description | Helps Google rank the video | Use keywords naturally in the title and description |
| Transcripts and Captions | Increases accessibility and SEO | Add captions and transcripts for better indexing |
| Video Thumbnail | Influences CTR | Use custom, high-quality thumbnails |
| Schema Markup | Helps videos appear in search results | Implement VideoObject schema |
| Fast Load Speed | Improves UX & rankings | Host on YouTube, Vimeo, or a CDN instead of self-hosting |
Example of Video Schema Markup (JSON-LD Format)
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "VideoObject",
"name": "On-Page SEO: Complete Beginner's Guide",
"description": "Learn how to optimize your web pages for higher rankings in Google search.",
"thumbnailUrl": "https://example.com/thumbnail.jpg",
"uploadDate": "2026-02-14",
"duration": "PT5M33S",
"embedUrl": "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=example",
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Nexa Growth",
"logo": {
"@type": "ImageObject",
"url": "https://example.com/logo.png"
}
}
}
</script>
Adding structured data increases the likelihood of appearing in Google’s video carousel results.
Key Takeaways for Image and Video Optimization
- Use compressed images (WebP, JPEG) for faster load times.
- Optimize alt text with relevant keywords and descriptions.
- Use lazy loading to improve page speed and performance.
- Host videos on trusted platforms (YouTube, Vimeo) instead of self-hosting.
- Implement schema markup to increase visibility in Google Images and Video Search.
By optimizing images and videos, your website will rank better, load faster, and engage users more effectively, leading to higher conversions and lower bounce rates.
Advanced On-Page SEO Techniques
As Google’s algorithm continues to evolve, basic on-page SEO is no longer enough.
To outperform competitors and rank in the top search results, you need to implement advanced techniques that align with Google’s AI-driven ranking factors.
This section covers cutting-edge SEO strategies, including voice search optimization, featured snippets, natural language processing (NLP), and passage indexing.
-
Optimizing for Voice Search
Voice search is on the rise, with over 50% of searches expected to be voice-based by 2026.
Optimizing for voice search helps you capture a growing audience using virtual assistants like Google Assistant, Siri, and Alexa.
Key Characteristics of Voice Search Queries
- Conversational and Long-Tail – Users ask full questions instead of typing short keywords.
- Question-Based – Queries start with “who,” “what,” “where,” “why,” and “how.”
- Local Intent – Many voice searches are for local businesses and services (“near me” searches).
Voice Search Optimization Strategies
Strategy Why It Works How to Implement Use Conversational Language Google favors natural phrasing for voice results Write in a clear, human-like tone Target Long-Tail Keywords Voice searches are often question-based Optimize for FAQ-style queries Optimize for Local SEO Most voice searches have local intent Claim and optimize Google My Business (GMB) Improve Page Speed Voice searches favor fast-loading pages Use CDNs, lazy loading, and compressed images Use Structured Data Helps Google extract relevant answers Implement FAQ and Speakable schema Example of an Optimized FAQ for Voice Search
❌ Ineffective:
“On-Page SEO is important because it helps pages rank better in search engines.”✅ Good (Voice Search-Friendly):
Question: Why is On-Page SEO important?
Optimized Answer: On-page SEO is essential because it helps search engines understand your content, leading to higher rankings and more traffic. It includes optimizing titles, meta descriptions, keywords, and page speed.This concise, direct answer improves your chances of ranking in Google’s voice search results.
-
Targeting Featured Snippets (Position Zero)
Featured snippets, also known as “position zero” results, appear above the first organic result and drive a higher CTR (click-through rate) than standard listings.
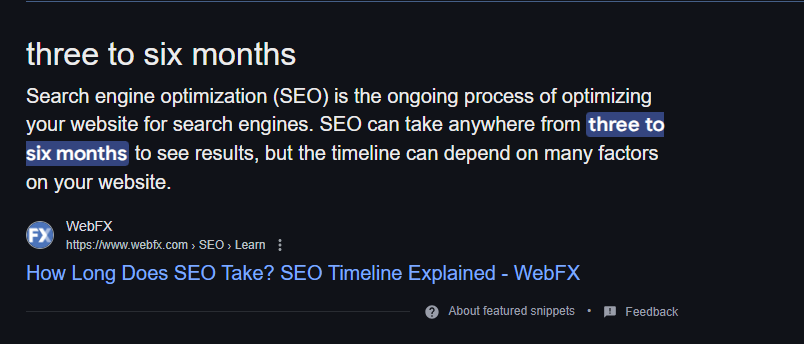
An Example of Position Zero Types of Featured Snippets and How to Optimize for Them
Snippet Type Example How to Optimize Paragraph Snippet Direct answer (40-60 words) Provide concise answers in the first 100 words List Snippet Bulleted or numbered list Use ordered (OL) or unordered (UL) lists Table Snippet Comparison data tables Format data into clear tables Video Snippet YouTube or embedded videos Optimize video titles, descriptions, and transcripts Example of a Featured Snippet-Optimized Answer
Question: What are the best On-Page SEO techniques?
✅ Optimized Answer (40-60 words):
“The best On-Page SEO techniques include optimizing title tags, meta descriptions, and content structure. Use internal linking, improve page speed, and implement schema markup to enhance visibility. Focus on mobile-friendliness and Core Web Vitals to improve rankings.”- Keep answers between 40-60 words.
- Use bold subheadings (Google prefers well-structured content).
- Answer questions clearly and concisely.
-
Using NLP (Natural Language Processing) for SEO
Google’s BERT & MUM algorithms use NLP (Natural Language Processing) to better understand search intent and rank content that aligns with user queries.
How NLP Affects SEO
- Google can now understand context, not just keywords.
- Synonyms and related terms matter more than keyword stuffing.
- User intent is more important than exact-match keywords.
How to Optimize for NLP-Based Search Rankings
Strategy Why It Works How to Implement Use Natural, Conversational Language Google rewards human-like writing Avoid robotic, keyword-stuffed content Optimize for Search Intent Matches how users ask questions Write detailed, intent-based answers Use Contextual Keywords Helps Google understand topic relevance Include LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords Answer “People Also Ask” Questions Google ranks pages that match user questions Research PAAs in search results and address them
Example: Instead of writing:“Best On-Page SEO techniques to improve SEO rankings and Google rankings.”
Write naturally:
“Some of the best on-page SEO techniques include improving meta tags, enhancing page speed, and structuring content effectively. These strategies help search engines understand and rank your content higher.”This humanized approach aligns with Google’s NLP models and improves ranking chances.
-
Optimizing for Passage Indexing
Passage Indexing is a Google algorithm update that ranks specific sections (passages) of content, rather than just full pages. This means:
- Even long-form content with deep topics can rank for multiple queries.
- Well-structured subheadings and clear sections increase ranking potential.
- Pages don’t have to be fully optimized—Google extracts relevant parts automatically.
How to Optimize for Passage Indexing
- Break content into well-defined sections (using H2, H3, H4).
- Use clear, keyword-rich subheadings to help Google understand content structure.
- Answer multiple questions within a single article (e.g., FAQs, how-to guides).
- Write longer, in-depth articles with multiple ranking opportunities.
Example of Passage Optimization:
✅ Good Subheading Structure:
- H2: What is On-Page SEO?
- H3: Why is On-Page SEO Important?
- H3: Best On-Page SEO Techniques
- H3: Common On-Page SEO Mistakes to Avoid
This structure makes it easier for Google to rank specific sections independently.
Key Takeaways for Advanced On-Page SEO
- Voice search optimization is crucial for future SEO—use conversational language and long-tail keywords.
- Featured snippets (position zero) drive the most clicks—structure answers clearly.
- Google’s NLP & BERT algorithms prioritize natural, human-like writing.
- Passage indexing allows individual sections to rank, making the content structure more important than ever.
By implementing these advanced techniques, you’ll ensure that your website ranks not just for standard queries, but also for emerging SEO trends like voice search and AI-driven rankings.
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO) and SEO
Ranking high in search results is important, but what happens after a user lands on your page?
If visitors leave without taking action—whether it’s making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or filling out a contact form—your SEO efforts aren’t delivering maximum value.
This is where Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO) meets SEO.
A well-optimized page not only attracts visitors but guides them toward meaningful actions, increasing leads, sales, and revenue.
The Relationship Between CRO and SEO
While SEO focuses on driving traffic, CRO ensures that traffic converts into customers or leads.
Both work together to create a seamless user experience that keeps visitors engaged and encourages action.
| SEO Focus | CRO Focus |
|---|---|
| Increasing organic traffic | Turning visitors into customers |
| Improving page rankings | Enhancing user experience (UX) |
| Reducing bounce rates | Encouraging user interaction (clicks, sign-ups, purchases) |
| Optimizing content for search intent | Crafting persuasive CTAs and layouts |
A page can rank #1 on Google, but if it doesn’t convert, it’s not achieving its full potential.
A/B Testing for Better UX and Engagement
A/B testing (split testing) allows you to compare two variations of a webpage to determine which performs better in terms of engagement, conversions, and bounce rates.
What Can You A/B Test?
| Element | Why It Matters | Testing Ideas |
|---|---|---|
| Headlines | The first thing users see; affects engagement | Test different power words and structures |
| Call-to-Action (CTA) | Drives conversions | Test button color, size, wording |
| Images and Visuals | Impacts trust and engagement | Compare stock vs. real images |
| Page Layout | Affects readability & focus | Test single-column vs. multi-column |
| Form Length | Impacts lead generation | Compare short vs. long forms |
Example of an A/B Test for CTAs
| Variation | CTA Text | Conversion Rate |
|---|---|---|
| A (Control) | “Sign Up Now” | 2.5% |
| B (Test Version) | “Get Your Free Trial” | 5.1% |
In this case, Version B doubled conversions because it offered a clear benefit.
Tools for A/B Testing:
- Google Optimize (Free testing tool by Google)
- Optimizely (Advanced CRO and testing platform)
- VWO (Visual Website Optimizer)
Optimizing CTA Placement for Maximum Conversions
Your Call-to-Action (CTA) placement can make or break your conversion rate.
Best CTA Placement Strategies
| CTA Placement | Effectiveness | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Above the Fold | Grabs attention immediately | “Start Your Free Trial” at the top |
| Mid-Content | Engages readers before they leave | CTA button after explaining benefits |
| Exit-Intent Popup | Captures leaving visitors | Discount offer popup when a user moves the cursor to exit |
| Sticky CTA | Keeps CTA visible at all times | Floating “Get a Quote” button |
A badly placed CTA can cost you conversions, so always test different placements.
How Page Speed Affects Conversions
A slow-loading page doesn’t just hurt SEO—it kills conversions.
- A 1-second delay in page load time can result in a 7% reduction in conversions.
- Pages that load in 2 seconds or less convert higher than slower pages.
Page Speed vs. Conversion Rate
| Load Time | Bounce Rate | Conversion Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 1s | 10% | 3.5% |
| 3s | 32% | 2.3% |
| 5s | 90% | 0.8% |
Actionable Steps to Improve Page Speed for CRO:
- Compress images and enable lazy loading.
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN).
- Optimize for mobile performance.
Building Trust with Social Proof and Reviews
Users are more likely to convert when they see trust signals such as reviews, testimonials, and ratings.
How to Use Social Proof for Higher Conversions
| Social Proof Type | Impact | Example Placement |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Reviews | Builds credibility | Below CTA or product pages |
| Case Studies | Shows real-world success | “How We Helped X Increase Traffic by 200%” |
| Trust Badges (SSL, Awards, Certifications) | Increases trust in security | Checkout pages, signup forms |
| User Count (“Join 50,000+ Subscribers”) | Creates FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) | Above the fold |
Reducing Form Abandonment for Higher Lead Generation
Long, complex forms scare users away. Optimizing lead forms can dramatically increase sign-ups and conversions.
Best Practices for Optimizing Forms
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Too Many Fields | Keep it short—3-5 fields max |
| Unclear CTA | Use action-driven phrases like “Get My Free Quote” |
| No Autofill | Enable Google Autofill for a smoother experience |
| Lack of Progress Indicators | Use a step-by-step form if longer |
Example of an Optimized Form vs. a Poorly Designed Form
❌ Ineffective Form:
- Full name
- Phone
- Company Name
- Industry
- Address
- Job Title
- Website
- Submit Button
✅ Optimized Form (Higher Conversions):
- First Name
- Email Address
- What Service Do You Need? (Dropdown)
- Submit Button: “Get My Free Consultation”
The optimized form keeps it short, simple, and frictionless, leading to higher conversions.
Key Takeaways for CRO SEO Integration
- A/B testing helps refine UX and increase conversions.
- CTA placement matters—test above-the-fold, mid-content, and sticky CTAs.
- Faster pages convert better—optimize speed for both SEO and CRO.
- Social proof builds trust—use reviews, testimonials, and case studies.
- Short, optimized forms reduce friction and increase sign-ups.
By aligning SEO with CRO, you attract visitors and turn them into customers, maximizing the ROI of your SEO efforts.
Monitoring, Auditing, and Updating Content
SEO is not a one-time task—it requires ongoing monitoring, auditing, and optimization.
Google frequently updates its algorithm, user behavior evolves, and competitors improve their content. Without regular maintenance, your rankings can drop, leading to decreased traffic and conversions.
This section will guide you through how to audit, track, and update your on-page SEO to stay ahead of the competition.
How to Perform an On-Page SEO Audit
A thorough SEO audit helps identify issues that could be hurting your rankings and ensures that your pages remain optimized.
Key Areas to Audit for On-Page SEO
| SEO Factor | What to Check | How to Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Title and Meta Tags | Are they optimized and unique? | Ensure primary keywords are included naturally |
| Content Quality | Is content outdated or thin? | Refresh with new data, insights, and examples |
| Internal Linking | Are key pages interlinked properly? | Add contextual links to boost the SEO structure |
| Keyword Optimization | Are keywords placed naturally? | Use LSI keywords and avoid keyword stuffing |
| Technical SEO | Are there broken links or crawl errors? | Use Google Search Console to detect & fix issues |
| Mobile-Friendliness | Does the page perform well on mobile? | Optimize for Core Web Vitals & responsive design |
| Page Speed | Is the page loading within 2-3 seconds? | Compress images, minify CSS/JS, use CDN |
| Schema Markup | Is structured data implemented? | Validate using Google’s Rich Results Test |
Performing an SEO audit quarterly ensures your content remains competitive and ranks higher over time.
Best Tools to Track On-Page SEO Performance
To measure SEO success, you need to track key performance indicators (KPIs) using data-driven tools.
Top SEO Tools for Monitoring Performance
| Tool | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Tracks organic traffic, ranking keywords, indexing issues |
| Google Analytics | Measures user behavior, bounce rates, session duration |
| Ahrefs / SEMrush | Finds keyword opportunities, backlink analysis, content gaps |
| Screaming Frog SEO Spider | Detects broken links, duplicate content, missing tags |
| PageSpeed Insights | Checks Core Web Vitals & speed optimization |
| Surfer SEO | Analyzes content optimization gaps |
Using these tools regularly allows you to make data-backed SEO improvements.
How to Update and Refresh Old Content
Updating old content can dramatically boost rankings. A study by Ahrefs found that updating outdated blog posts led to a 146% increase in organic traffic within 6 months.
What to Update in Existing Content?
| Update Type | Why It Helps | Actionable Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Refresh Data and Stats | Keeps content relevant and credible | Replace old statistics with recent industry trends |
| Improve Readability | Enhances user engagement | Shorten paragraphs, use bullet points and visuals |
| Optimize for New Keywords | Expands ranking opportunities | Use Google Search Console to find new keyword opportunities |
| Add Internal Links | Strengthens website structure | Link to newer, high-authority pages |
| Update Meta Tags | Improves CTR | Write a compelling, keyword-rich meta description |
| Enhance Multimedia | Increases engagement | Add infographics, videos, and images |
| Check for Broken Links | Improves user experience | Use Ahrefs or Screaming Frog to fix 404 errors |
When and How to Update Old Content for SEO Gains
Not all content needs frequent updates. Some pages require small tweaks, while others may need a full rewrite.
How Often Should You Update Content?
| Content Type | Update Frequency |
|---|---|
| Evergreen Guides (SEO, Marketing, Tech, etc.) | Every 6-12 months |
| Industry Trends and Data-Driven Articles | Every 3-6 months |
| News and Time-Sensitive Topics | Update as needed |
| Product/Service Pages | Every 6-12 months or when changes occur |
Steps to Update Content for SEO Growth
- Analyze performance – Use Google Search Console to check ranking drops.
- Find content gaps – Identify missing subtopics or FAQs based on competitor research.
- Enhance readability – Improve structure using subheadings, bullet points, and visuals.
- Optimize keyword strategy – Find new ranking opportunities using Ahrefs or SEMrush.
- Add fresh internal links – Link to newer, relevant content for better authority distribution.
- Submit for re-indexing – After updates, request indexing in Google Search Console for faster ranking improvements.
Key Takeaways for Monitoring and Updating On-Page SEO
- SEO audits help identify ranking drops and optimization opportunities.
- Tracking tools like Google Search Console and Ahrefs provide data-driven insights.
- Updating old content boosts rankings—refresh stats, keywords, and internal links.
- Regular performance tracking ensures long-term SEO success.
By regularly auditing, tracking, and updating your On-Page SEO, you can stay ahead of algorithm changes, improve rankings, and drive continuous organic growth.
Common On-Page SEO Myths and Misconceptions
With SEO constantly evolving, many outdated strategies and misconceptions still circulate.
Following incorrect on-page SEO advice can hurt your rankings, waste time, and lead to penalties from Google.
In this section, we’ll debunk common On-Page SEO myths and explain what truly works in 2026.
Myth #1: Keyword Density Matters More Than Quality
✅ Fact: Google no longer ranks pages based on a fixed keyword density. Instead, it prioritizes content quality, relevance, and search intent.
Why This Myth Exists
- In the early 2000s, keyword stuffing worked because Google’s algorithm was less sophisticated.
- SEOs used to target exact-match keywords multiple times to manipulate rankings.
Reality in 2026
- Google’s BERT and NLP updates focus on semantic search and intent-based ranking.
- Using natural language and keyword variations (LSI keywords) improves rankings more than repeating the same phrase.
What to Do Instead:
✅ Focus on writing naturally—place keywords in titles, headings, and first 100 words but don’t force them.
✅ Use LSI keywords & synonyms to cover the topic comprehensively.
✅ Optimize for search intent, not just keywords.
Myth #2: Longer Content Always Ranks Higher
✅ Fact: While longer content often ranks well, word count alone doesn’t guarantee rankings.
Why This Myth Exists
- Studies show that pages ranking in the top 3 results often have 1,500+ words.
- Many assume writing longer articles guarantees higher rankings.
Reality in 2026
- Google ranks content that satisfies search intent, not just longer articles.
- Thin content (under 500 words) struggles, but word count should match user intent.
- Some queries require short answers, while others need in-depth guides.
What to Do Instead
✅ Analyze competitor rankings to determine the ideal content length for your topic.
✅ Prioritize content depth—cover all relevant subtopics.
✅ Focus on readability & structure rather than just increasing word count.
Myth #3: Meta Descriptions Directly Affect Rankings
✅ Fact: Meta descriptions don’t impact rankings directly, but they affect click-through rates (CTR), which can influence SEO.
Why This Myth Exists
- Many assume that meta descriptions containing keywords boost rankings.
- Google bolds matching keywords in search results, making them more visible.
Reality in 2026
- Google rewrites meta descriptions for 70% of search results based on user queries.
- Well-written meta descriptions increase CTR, leading to more traffic.
What to Do Instead:
✅ Write compelling meta descriptions (under 160 characters) to attract clicks.
✅ Include target keywords naturally to increase visibility in search results.
✅ Focus on user engagement & clickability, not just keyword stuffing.
Myth #4: Internal Links Don’t Matter as Much as Backlinks
✅ Fact: Internal linking is a powerful SEO strategy that helps distribute PageRank and authority across your website.
Why This Myth Exists
- Backlinks (external links) are well-known ranking factors.
- Internal links are underutilized, but they improve crawlability and rankings.
Reality in 2026
- Google uses internal links to understand website structure and hierarchy.
- Internal links help spread the authority to weaker pages, boosting their rankings.
What to Do Instead:
✅ Use contextual internal linking to connect relevant pages.
✅ Prioritize deep linking (linking to inner pages, not just the homepage).
✅ Avoid overloading with links—focus on quality, not quantity.
Myth #5: Google Prefers New Content Over Old Content
✅ Fact: Older, high-quality content often ranks better than newly published pages—if it’s regularly updated.
Why This Myth Exists
- Google sometimes displays “fresh” results for trending queries.
- Many believe that publishing new content constantly is necessary for rankings.
Reality in 2026
- Google favors established, authoritative content that remains relevant.
- Updating old content can significantly boost rankings without writing new posts.
What to Do Instead:
✅ Regularly refresh existing content (update stats, add new sections).
✅ Monitor Google Search Console for ranking drops & update pages accordingly.
✅ Focus on content quality rather than just publishing frequency.
Myth #6: You Need to Submit Every Page to Google for Indexing
✅ Fact: Google automatically crawls & indexes most websites without manual submission.
Why This Myth Exists
- New website owners often believe manual submission is necessary for rankings.
- Google provides a URL inspection tool to request indexing, leading to confusion.
Reality in 2026
- Googlebot regularly crawls websites with proper internal linking & sitemaps.
- Manual indexing requests should only be used for urgent updates (e.g., fixing de-indexed pages).
What to Do Instead:
✅ Use Google Search Console to monitor indexing issues.
✅ Ensure your website has a proper XML sitemap submitted in the Search Console.
✅ Improve crawlability with internal links and structured navigation.
Myth #7: Image SEO Doesn’t Matter for Rankings
✅ Fact: Optimized images improve search rankings, user experience, and page speed.
Why This Myth Exists
- Many SEOs focus only on text-based SEO and ignore image optimization.
- Some assume Google can’t “see” images, making them irrelevant for rankings.
Reality in 2026
- Google’s image recognition AI analyzes image relevance, alt text, and metadata.
- Google Image Search drives 10%+ of all web traffic.
What to Do Instead:
✅ Use descriptive file names (e.g., on-page-seo-guide.png).
✅ Optimize alt text for accessibility and search visibility.
✅ Compress images & use WebP format to improve load times.
Key Takeaways: SEO Myths vs. Reality
| SEO Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| Keyword density is a major ranking factor | Google prioritizes context, relevance, and user intent |
| Longer content always ranks better | Content depth and relevance matter more than word count |
| Meta descriptions directly impact rankings | They don’t affect rankings but boost CTR |
| Internal links aren’t as important as backlinks | Internal linking improves SEO structure and rankings |
| New content ranks better than old content | Updated old content can outrank new pages |
| You must manually submit pages for indexing | Google automatically crawls well-structured websites |
| Image SEO doesn’t impact rankings | Optimized images improve page speed & Google Image Search rankings |
Step-by-Step SEO Checklist for On-Page Optimization
Use this on-page SEO checklist to ensure every page on your site is fully optimized:
- Title Tag Optimization – Includes primary keyword and is under 60 characters.
- Meta Description – Concise, compelling, and includes keywords naturally.
- URL Structure – Clean, short, and contains target keyword.
- Header Tags (H1-H3) – Organized logically with keywords in headings.
- Keyword Optimization – Keywords placed naturally without stuffing.
- Content Quality – Well-structured, informative, covers all key subtopics.
- Internal Links – Links to relevant pages to improve site navigation.
- External Links – Includes authoritative outbound links to trusted sources.
- Image SEO – Descriptive filenames, compressed images, and alt text.
- Page Speed – Loads in under 3 seconds (use Google PageSpeed Insights to test).
- Mobile Optimization – Fully responsive and passes Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
- Schema Markup – FAQ, Review, or Video schema added where applicable.
- User Engagement Optimization – Easy-to-read layout, short paragraphs, and engaging visuals.
- Call-to-Actions (CTAs) – Clear, well-placed CTAs to drive conversions.
- Regular Content Updates – Content reviewed and updated every 6-12 months.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Mastering on-page SEO is not just about applying best practices—it’s about understanding how search engines and users interact with your content.
Google’s algorithms are evolving, but the core principles of great SEO remain the same: provide valuable content, optimize for user experience, and ensure search engines can easily understand and index your pages.
In this guide, we’ve covered everything you need to optimize your web pages for higher rankings and better user engagement.
Now, let’s summarize the key takeaways and outline actionable next steps to ensure your SEO efforts lead to measurable success.
Key Takeaways From This Guide
| SEO Factor | Key Optimization Strategies |
|---|---|
| Content Optimization | Focus on search intent, readability, and user engagement |
| Keyword Placement | Use target keywords naturally in titles, headings, and meta descriptions |
| Internal Linking | Link to high-value pages to improve crawlability and authority |
| Page Speed and Core Web Vitals | Optimize load times, mobile usability, and site performance |
| Schema Markup and Structured Data | Implement FAQ, Review, and Video schema for rich results |
| Multimedia Optimization | Use compressed images, alt text, and video SEO |
| Advanced Techniques | Optimize for voice search, featured snippets, and NLP-based search |
| Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO) | Place CTAs strategically, optimize forms, and use social proof |
| Regular Content Updates | Keep content fresh by updating stats, improving readability, and adding new sections |
SEO is a long-term strategy—consistent optimization, monitoring, and updates are essential for maintaining and improving rankings.
Final Thoughts: The Road to SEO Success
SEO success doesn’t happen overnight. It requires continuous effort, testing, and adaptation to changing search engine algorithms.
By following the strategies in this guide, you’ll:
- Improve your rankings and organic traffic.
- Optimize your site for user experience and engagement.
- Stay ahead of competitors with advanced SEO techniques.
- Convert more visitors into customers with effective CRO strategies.
The next step? Take action. Start by auditing your existing pages, implementing the SEO checklist, and refining your content strategy.
Your website’s success starts with on-page SEO. Now it’s time to execute.
Boost Your Rankings with Nexa Growth!
Get a complete on-page SEO optimization that drives traffic and improves visibility.
Contact UsFAQs
1. What is the difference between On-Page SEO and Off-Page SEO?
2. How long does it take to see results from On-Page SEO?
3. Can you over-optimize On-Page SEO?
4. What are the most important On-Page SEO factors for 2026?
- Search Intent Optimization – Ensuring content fully answers the user’s query.
- Core Web Vitals and Page Speed – Fast-loading, mobile-friendly sites rank better.
- Internal Linking Strategy – Linking relevant pages to improve SEO structure.
- Schema Markup Implementation – Enhancing visibility with rich snippets in SERPs.

