- A 404 error is an HTTP status code that indicates a page does not exist.
- 70% of users who encounter a 404 page will not return to the website.
- A hard 404 returns a correct 404 status code, while a soft 404 returns a 200 OK status, which can waste crawl budget.
- You can use tools like Google Search Console to identify 404 errors.
- You should fix 404 errors by using 301 redirects for moved or deleted pages.
Imagine this: You’re searching for a specific piece of information, maybe a product or an article, and you click on a link—only to be met with the dreaded “404 Page Not Found” error.
Frustrating, right? You’re not alone.
According to research, 70% of users who encounter a 404 page will not return to your website.
For website owners, a 404 error can become a silent traffic killer.
A single 404 error might seem insignificant, but when left unchecked, it can become a major problem, affecting user experience, search engine rankings, and even revenue.
Google has emphasized the importance of maintaining a crawlable, error-free site, as too many broken pages can lead to lost search rankings and wasted crawl budget.
But here’s the good news: fixing 404 errors isn’t as complicated as it sounds.
This guide will cover everything you need to know to fix 404 errors. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap to keeping your website error-free and ensuring visitors (and search engines) never hit a dead end again.
Let’s get started.
Your Website Has Potential—Let’s Unlock It!
With the proper SEO, your site can attract more visitors and turn them into loyal customers.
Contact UsWhat Is a 404 Error?
A 404 error, or “Page Not Found” error, is an HTTP status code that tells users and search engines that the page they are trying to access does not exist.
This can happen for several reasons—maybe the page was deleted, the URL was mistyped, or the link pointing to it is broken.
Think of it as trying to visit a store that has moved locations, but there’s no sign telling you where to go next.
You’re frustrated, unsure of what to do, and more likely to leave. Users experience this when they hit a 404 page on your site.
How Do 404 Errors Work?
When a visitor requests a page on your website, the server checks to see if the URL exists. The server delivers the page with a 200 OK response if it does.
If it doesn’t, the server returns a 404 Not Found response, signaling that the page can’t be located.
Why Do 404 Errors Matter?
A few occasional 404 errors won’t tank your site’s performance, but persistent issues can create significant problems:
- Bad User Experience – Nearly 88% of online users say they won’t return to a website after a bad experience.
- SEO Ranking Drops – Google reduces rankings for websites with excessive broken links, affecting traffic and search visibility.
- Lost Revenue Opportunities – If key landing pages or product pages return 404 errors, you could lose potential sales and leads without realizing it.
Now that we understand what a 404 error is, let’s look at the different types and why they matter.
Featured Article: SEO Copywriting: What It Is & How to Do It in 2026
Types of 404 Errors: Hard 404 vs. Soft 404
Not all 404 errors are created equal. While they may look the same to users, search engines treat them differently based on how your server responds. Understanding the difference can help you fix them more effectively and prevent unnecessary SEO damage.
Hard 404 Errors
A challenging 404 error occurs when a webpage is completely missing, and the server correctly returns a 404 status code. This tells both users and search engines that the page no longer exists.
Common causes of problematic 404 errors include:
- A page was deleted without setting up a redirect
- A user mistyped the URL
- An external website is linking to a non-existent page
Problematic 404 errors are not necessarily bad for SEO if they happen occasionally. However, if they occur frequently on important pages or high-traffic links, they can negatively impact search rankings and user experience.
Soft 404 Errors
A soft 404 error is a bit trickier. This happens when a webpage appears missing, but instead of returning a proper 404 status code, the server redirects users to an unrelated page or serves a blank or thin-content page with a 200 OK status.
Why does this matter?
Because Google sees this as misleading.
Instead of properly recognizing that a page is gone, search engines may keep it in their index, leading to wasted crawl budget and potential ranking issues.
Soft 404 errors often occur when:
- A website redirects missing pages to the homepage instead of a relevant page
- A thin-content page is served instead of a proper 404 page
- An automatic redirect sends users to a generic category page instead of a specific alternative
Google Search Console can flag soft 404 errors, making them easier to spot and fix. The best solution is to set up proper 301 redirects for removed pages or allow an accurate 404 response when necessary.
Now that we understand the types of 404 errors, let’s explore the common reasons they occur in the first place.
Featured Article: Common On-Page SEO Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Common Causes of 404 Errors
404 errors don’t just appear out of nowhere. They are usually the result of changes to your website, technical issues, or simple human errors. Identifying the root cause is the first step in fixing them effectively.
-
Deleted or Moved Pages Without Redirects
One of the most common causes of 404 errors is when a webpage is deleted or its URL changes without setting up a 301 redirect. This can happen during:
- Website migrations
- Content restructuring
- Product discontinuations
- Blog updates where URLs are modified
If you don’t tell search engines and users where the new page is, they will continue trying to access the old URL, resulting in a 404 error.
-
Broken Internal and External Links
A single broken link can lead users to a dead end, frustrating their browsing experience. Broken links usually happen when:
- A linked page has been removed
- The website structure has changed
- The link was entered incorrectly
External links (from other websites) can also cause 404 errors if they point to pages that no longer exist on your site. This impacts user experience and can hurt your backlink profile if valuable referring domains link to broken pages.
-
URL Typos and Case Sensitivity Issues
Sometimes, a simple typo is the reason behind a 404 error. URLs are case-sensitive, so /Product-Page and /product-page might be treated as different URLs on some servers. Common mistakes include:
- Misspelled words in the URL
- Extra spaces or hyphens
- Incorrect capitalization on case-sensitive servers
-
Incorrect Domain Name or DNS Issues
If a domain is expired, incorrectly configured, or not pointing to the correct hosting server, users may encounter 404 errors. This is particularly common after:
- Switching web hosting providers
- Updating domain DNS settings
- Registering a new domain but failing to set up proper redirects
-
CMS and Plugin Issues
For WordPress and other content management systems (CMS), some plugin conflicts or settings can cause 404 errors. Common scenarios include:
- Improper permalink settings
- Corrupt .htaccess files
- Conflicting SEO plugins affecting redirects
-
Incorrect Website Migration or Rebranding
If you’ve recently migrated your website to a new domain or changed your URL structure without properly setting up 301 redirects, users and search engines will continue trying to access old pages that no longer exist.
This can cause massive ranking drops and lead to thousands of 404 errors in Google Search Console.
-
Expired or Changed Backlinks
If other websites have linked to your content, but you’ve since changed or removed the linked page, those external visitors will land on a 404 page.
This is particularly harmful because backlinks contribute to SEO rankings, and a high-quality referring link leading to a 404 page is a missed opportunity.
Let’s Put Your Website in the Spotlight.
Show up where it matters most and stay ahead of the competition with expert SEO
Contact UsHow to Identify 404 Errors on Your Website
Fixing 404 errors starts with knowing where they exist. You can’t fix what you don’t track. Fortunately, several tools make it easy to find broken links, missing pages, and other issues that cause 404 errors.
Here’s how to systematically identify them.
-
Using Google Search Console (GSC)
Google Search Console is one of the best tools for identifying 404 errors because it shows how Google itself sees your website.
How to Check for 404 Errors in Google Search Console
- Log in to Google Search Console and select your website.
- Go to Coverage under the Indexing section.
- Look for pages marked as “Not Found (404)” or “Soft 404” errors.
- Click on each URL to see where the error is happening.
- Download the report and start working on fixes.
Google typically updates this report every few days, so make it a habit to check it at least once a month to catch new issues before they affect rankings.
-
Using Screaming Frog SEO Spider
Screaming Frog is a website crawling tool that helps detect broken links and missing pages in real time.
How to Find 404 Errors Using Screaming Frog
- Download and install Screaming Frog SEO Spider.
- Enter your website URL and start a full crawl.
- Once the crawl is complete, go to the Response Codes tab.
- Filter by “Client Error (4xx)” to see all pages returning a 404 error.
- Click on each URL to see which internal pages are linking to it.
This tool is excellent for auditing your internal links, ensuring you don’t have pages leading visitors to dead ends.
-
Using Ahrefs or Semrush for Broken Backlinks
If external websites are linking to pages that no longer exist, you might be losing valuable traffic and SEO benefits.
How to Check for 404 Errors in Ahrefs or SEMrush
- Open Ahrefs Site Explorer or Semrush Backlink Audit.
- Enter your domain and navigate to the Broken Backlinks section.
- Look for links pointing to 404 pages on your site.
- Export the list and consider 301 redirects to relevant pages.
Fixing broken backlinks helps retain link equity, crucial for maintaining rankings.
-
Checking Server Logs for 404 Requests
For a more technical approach, analyzing your server logs can reveal how often users encounter 404 errors and from where.
How to Check Server Logs for 404 Errors
- Log in to your hosting control panel or use an FTP client to access your server.
- Find and open the access.log file.
- Search for lines containing HTTP/1.1″ 404 to see where errors occur.
This method helps detect 404 errors caused by bots, outdated bookmarks, or old URLs still being accessed.
-
Using Browser Extensions for Quick Checks
If you want a quick way to check for 404 errors on a single page, browser extensions like Check My Links (Chrome) or Broken Link Checker (Firefox) can help. Install the extension and scan your webpage to find any broken links.
Featured Article: Featured Snippets: How to Optimize for Position Zero in 2026
Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing 404 Errors
Now that you’ve identified where 404 errors exist on your website, it’s time to fix them. The solution may vary depending on the cause of the error.
Below is a structured, step-by-step approach to resolving 404 errors effectively.
Fixes for Website Visitors
If you’re encountering a 404 error as a user, here are a few quick troubleshooting steps:
- Refresh the Page – Sometimes, a temporary server glitch can cause a 404 error. Press Ctrl + R (Windows) or Cmd + R (Mac) to reload the page.
- Check the URL – A small typo can lead to a 404 error. Double-check for missing letters, extra slashes, or incorrect capitalization.
- Clear Browser Cache and Cookies – If a cached version of a broken page is being stored, clearing your browser cache might resolve the issue.
- Try Accessing the Page from Another Device or Browser. If the page works elsewhere, the issue could be browser-specific.
But if you own the website, you’ll need a more technical approach.
Fixes for Website Owners
-
Implement 301 Redirects for Deleted or Moved Pages
If a page has been removed or its URL has changed, a 301 redirect ensures that users and search engines are sent to the correct page instead of hitting a 404 error.
How to Set Up a 301 Redirect (WordPress & .htaccess)
- For WordPress: Use plugins like Redirection or Yoast SEO Premium to set up redirects.
- For Apache Servers: Edit your .htaccess file and add:
Redirect 301
/old-page https://yourwebsite.com/new-page- For Nginx Servers: Add this to your configuration file:
rewrite ^/old-page$ https://yourwebsite.com/new-page permanent;- For Shopify & Wix: Use the built-in URL redirect tools.
Redirecting old URLs helps preserve SEO rankings and ensures users reach relevant content.
-
Fix Internal Links Pointing to 404 Pages
Broken internal links create a frustrating experience for visitors and waste crawl budget.
How to Fix Internal Links
- Use Screaming Frog or Google Search Console to identify internal links pointing to 404 pages.
- Update those links to point to the correct existing pages.
- If a suitable replacement page doesn’t exist, set up a 301 redirect to a relevant page instead.
-
Restore Important Pages That Were Deleted
If a page was removed by mistake but still receives traffic or backlinks, consider restoring it rather than redirecting it.
How to Restore Deleted Pages
- Check if you have a backup of the deleted page using Google Cache or Wayback Machine.
- Recreate the content on the same URL if it was valuable for users or SEO.
- If the page isn’t recoverable, redirect the URL to the closest relevant page instead.
-
Create a Custom 404 Page to Improve User Experience
Even if you can’t fix every 404 error, you can minimize frustration by designing a helpful 404 page.
What to Include in a Custom 404 Page
- A friendly, non-technical error message (“Oops! This page doesn’t exist.”)
- A search bar to help users find what they’re looking for
- Links to popular pages or a homepage button
- A contact form so users can report broken links
Examples of Great 404 Pages
- Airbnb – Uses humor and provides redirection.
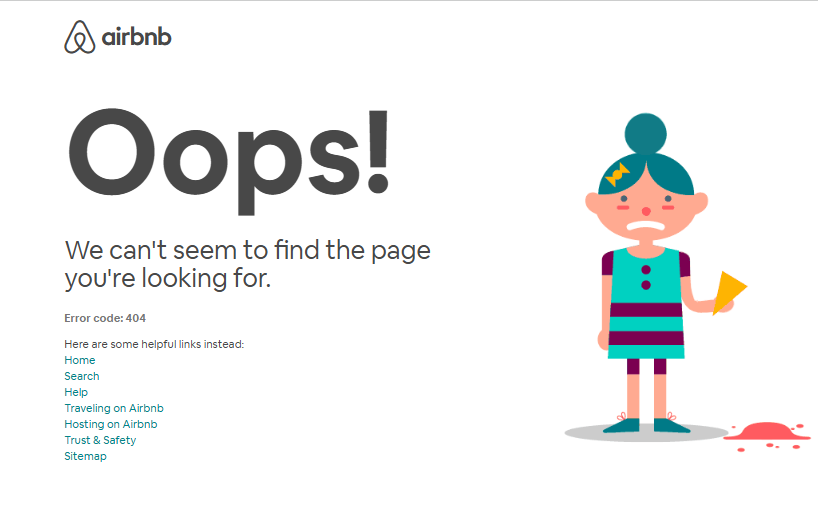
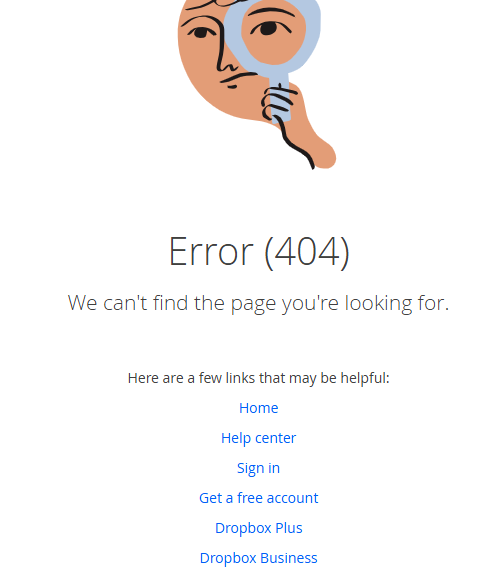
Airbnb’s 404 Error Page - Dropbox – Displays an illustrated search action with a link to support.
Dropbox’s 404 Error Page - GitHub incorporates a fun, interactive design, with a pop-up to sign in and a search bar for redirection.
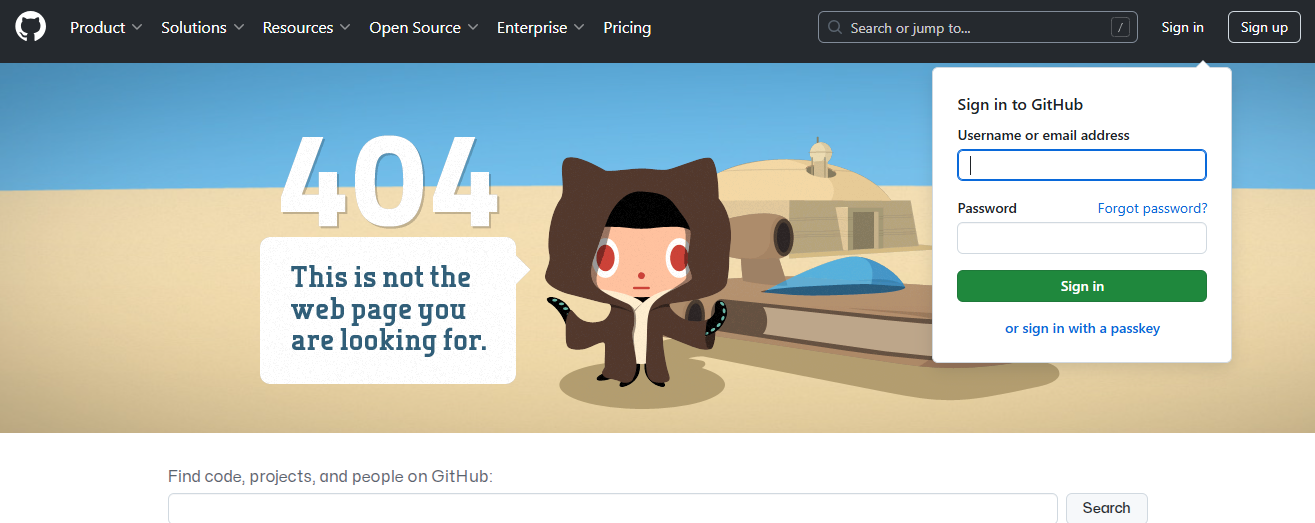
GitHub’s 404 Error Page
Creating a helpful 404 page can reduce bounce rates and keep users engaged instead of leaving your site.
-
Update Your XML Sitemap and Submit to Google
If your site has undergone significant changes (e.g., content restructuring or migration), update your sitemap to prevent Google from indexing broken URLs.
How to Submit an Updated Sitemap
- Generate a new sitemap.xml file using tools like Yoast SEO (WordPress) or XML-Sitemaps.com.
- Upload the updated sitemap to your website’s root directory.
- Please submit it to Google Search Console under the Sitemaps section.
This helps Google index only valid pages and removes outdated URLs from search results.
When to Let a 404 Error Stay
Not all 404s need to be fixed. If a page is permanently deleted and has no traffic, backlinks, or relevance, leaving it as a 404 is perfectly fine. Google understands that some pages naturally disappear over time.
Featured Article: Image SEO: 20+ Tips for Image SEO Optimization in 2026
SEO Impact of 404 Errors and Why You Should Fix Them
404 errors don’t just frustrate users—they can also impact your website’s SEO, rankings, and overall performance.
While occasional 404 errors won’t destroy your search rankings, excessive or poorly handled 404s can lead to lost traffic, reduced crawl efficiency, and weaker domain authority.
-
User Experience (UX) and Bounce Rate
When users land on a broken page, they will likely leave the site immediately. Studies show that:
- 88% of users will not return to a website after a bad experience.
- A single 404 error can increase the bounce rate by up to 30%, signaling to Google that users aren’t finding what they need.
A well-maintained website with working links and relevant redirects keeps users engaged, reducing bounce rates and improving session duration—two key behavioral signals that search engines consider when ranking sites.
-
Wasted Crawl Budget and Indexing Issues
Google allocates specific resources to crawl each website, called the crawl budget. If Googlebot encounters too many 404 errors, it may:
- Waste time crawling broken pages instead of indexing valuable content.
- Delay the discovery of new or updated pages, slowing down SEO improvements.
In Google’s words: “Having many 404s does not directly affect a site’s ranking, but they can negatively impact crawl efficiency.”
If your important pages aren’t getting crawled because Google is busy checking broken URLs, it can hurt your site’s visibility.
-
Loss of Link Equity (SEO Value of Backlinks)
Backlinks are one of the most substantial ranking factors in Google’s algorithm. If authoritative sites link to a page no longer exists, that valuable link equity is lost—unless you implement proper 301 redirects.
For example:
- If Forbes, HubSpot, or another high-authority website linked to one of your pages, but it now returns a 404, Google ignores that link’s SEO value.
- By redirecting the link to a relevant, active page, you retain the link juice and pass it to another valuable part of your site.
How to Fix Lost Backlink Value Due to 404 Errors
- Use Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Google Search Console to identify backlinks pointing to 404 pages.
- Reach out to the linking websites and request that they update the link (if possible).
- Set up 301 redirects to a relevant page, ensuring you retain the SEO value.
-
Mobile vs. Desktop SEO Impact
Google’s mobile-first indexing means your website’s mobile performance matters more than ever.
If 404 errors primarily appear on mobile versions of your site, they can impact rankings more severely than desktop-only issues.
404 errors on mobile can be caused by:
- Faulty AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) configurations.
- Improper mobile URL redirects.
- Mobile site structure differs from the desktop version.
Running a mobile usability test in Google Search Console can help spot mobile-specific 404s that need fixing.
-
E-commerce and Revenue Loss
For e-commerce sites, 404 errors can directly affect sales and conversion rates. If product pages, checkout links, or category pages return 404 errors, customers lose trust and abandon their purchase.
A study by Baymard Institute found that:
- 69.8% of online shoppers abandon their cart before completing a purchase.
- A bad user experience, including broken links, is one of the top reasons for abandonment.
Every 404 error on a transactional page is a lost revenue opportunity for businesses relying on online sales. Fixing them quickly ensures customers don’t drop off before making a purchase.
Featured Article: Internal Linking for SEO: The Complete Guide for 2026
Best Practices to Prevent 404 Errors
Fixing 404 errors is essential, but preventing them from occurring in the first place is even better.
A proactive approach helps maintain a smooth user experience, protects your SEO rankings, and ensures search engines index your site efficiently.
Here are some of the best strategies to keep your website free from unnecessary 404 errors.
-
Conduct Regular Site Audits
One of the most effective ways to prevent 404 errors is by running frequent website audits to detect broken links, outdated pages, and missing content.
How Often Should You Audit for 404 Errors?
- For large, frequently updated websites: Once a month
- For small or medium-sized websites: Every three months
- After significant site changes: Immediately post-migration or redesign
Recommended Tools for Auditing
- Google Search Console – Tracks 404 errors in the “Indexing” report.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider – Crawls your website for broken internal links.
- Ahrefs or SEMrush – Identifies lost backlinks and broken external links.
-
Maintain a Consistent URL Structure
A structured, predictable URL format reduces the chances of broken links when updating your site.
Best Practices for URL Management
- Avoid changing URLs unless necessary.
- If you must update a URL, implement a 301 redirect immediately.
- Keep URLs short, descriptive, and keyword-friendly to improve readability and indexing.
- Use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) or special URL characters.
-
Set Up Proper Redirects for Removed Pages
If a page is permanently deleted or its URL changes, setting up 301 redirects ensures visitors and search engines are sent to the correct location.
When to Use a 301 vs. 302 Redirect
- 301 Redirect (Permanent) – Best for permanently removed or moved pages. Passes full SEO value.
- 302 Redirect (Temporary) – Use only if the page is expected to return (e.g., seasonal promotions).
Redirects should always point users to the most relevant active page, not just the homepage, to avoid soft 404 issues.
-
Collect User Feedback on 404 Pages
Users encountering 404 errors might know about broken links before you do. Adding a reporting feature to your 404 page allows visitors to alert you about missing content.
How to Encourage User Feedback
- Add a simple contact form: “Found a broken link? Let us know.”
- Include a search bar so users can find related content.
- Offer links to popular pages or the homepage to reduce frustration.
This approach helps you identify and fix errors faster while maintaining engagement.
-
Keep Your XML Sitemap Updated
An outdated XML sitemap can cause Google to crawl and index pages that no longer exist, leading to 404 errors in search results.
How to Keep Your Sitemap Clean
- Use Yoast SEO (WordPress) or Google XML Sitemaps to generate an updated sitemap automatically.
- Remove URLs that return 404 errors or are no longer relevant.
- Submit the revised sitemap to Google Search Console to ensure search engines have the latest version.
Regularly updating your sitemap ensures Google and other search engines focus on indexing your important pages rather than wasting resources on broken links.
Conclusion
404 errors are inevitable in website management, but they don’t have to be a roadblock to your success.
They can frustrate users, hurt your search rankings, and waste valuable SEO efforts when left unchecked.
However, with the right strategies—such as identifying broken links, implementing 301 redirects, conducting regular site audits, and keeping your XML sitemap updated—you can minimize their impact and maintain a seamless browsing experience.
The key takeaway?
Fixing 404 errors isn’t just about repairing broken pages—it’s about improving user experience, optimizing your site’s crawlability, and protecting your SEO rankings.
By staying proactive and following best practices, you can ensure that visitors and search engines always find the right pages without hitting dead ends.
If you haven’t audited your site for 404 errors yet, now is the time. Start by checking Google Search Console or using a crawling tool like Screaming Frog to identify and resolve broken links.
A well-maintained website isn’t just good for SEO—it’s essential for keeping visitors happy and engaged.
Be Seen, Be Found, Be Chosen.
Make it easy for your customers to find you with Nexa Growth’s strong, smart SEO strategy.
Contact Us
